Write A Polynomial In Standard Form
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
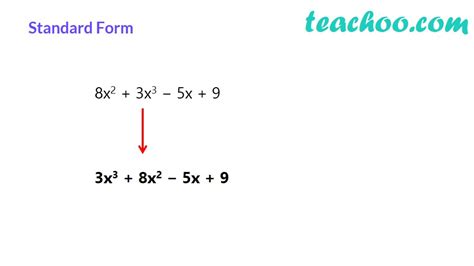
Table of Contents
Writing a Polynomial in Standard Form: A Comprehensive Guide
Polynomials are fundamental building blocks in algebra, forming the basis for many advanced mathematical concepts. Understanding how to write a polynomial in standard form is crucial for simplifying expressions, solving equations, and performing various algebraic manipulations. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of polynomial standard form, exploring its definition, significance, and practical applications. We'll cover examples, techniques, and tips to help you master this essential algebraic skill.
Understanding Polynomials
Before diving into standard form, let's clarify what a polynomial is. A polynomial is an expression consisting of variables (often represented by x, y, etc.) and coefficients, combined using addition, subtraction, and multiplication, but never division by a variable. The exponents of the variables must be non-negative integers.
Examples of Polynomials:
- 3x² + 2x - 5
- 4y³ - 7y + 1
- 2x⁴ + 5x² - x + 9
- 5 (a constant is also considered a polynomial)
Non-Examples of Polynomials:
- 1/x + 2 (division by a variable)
- x⁻² + 3x (negative exponent)
- √x + 4 (fractional exponent)
Defining Standard Form of a Polynomial
The standard form of a polynomial arranges its terms in descending order of their exponents. This means the term with the highest exponent comes first, followed by the term with the next highest exponent, and so on, until the constant term (the term without a variable) is last.
Key characteristics of a polynomial in standard form:
- Descending order of exponents: The exponents of the variable decrease from left to right.
- Combined like terms: Similar terms (terms with the same variable and exponent) are combined to simplify the expression.
- Coefficients in front of variables: The numerical coefficients are written before the variable terms.
Writing Polynomials in Standard Form: Step-by-Step Guide
Let's break down the process of writing a polynomial in standard form with a detailed, step-by-step approach:
Step 1: Identify the Terms
First, identify all the individual terms within the polynomial. Remember, a term is a single number, variable, or the product of numbers and variables. For instance, in the polynomial 2x³ - 5x + 4x² + 7, the terms are 2x³, -5x, 4x², and 7.
Step 2: Determine the Degree of Each Term
The degree of a term is the sum of the exponents of its variables. For example:
- The degree of 2x³ is 3.
- The degree of -5x is 1 (remember x is equivalent to x¹).
- The degree of 4x² is 2.
- The degree of 7 (constant term) is 0.
Step 3: Arrange the Terms in Descending Order of Degree
Arrange the terms in descending order based on their degrees. The term with the highest degree comes first, followed by the term with the next highest degree, and so on, until the constant term (degree 0) is at the end.
Step 4: Combine Like Terms (if applicable)
If the polynomial has like terms (terms with the same variable and exponent), combine them by adding or subtracting their coefficients.
Step 5: Write the Polynomial
Finally, write the polynomial with the terms arranged in descending order of degree, with the coefficients in front of the variables, and the constant term at the end.
Examples of Converting to Standard Form
Let's work through some examples to solidify your understanding:
Example 1:
Write the polynomial 5x + 3x² - 7 + 2x³ in standard form.
- Identify terms: 5x, 3x², -7, 2x³
- Determine degrees: 1, 2, 0, 3
- Arrange in descending order: 2x³, 3x², 5x, -7
- Combine like terms: No like terms to combine.
- Standard form: 2x³ + 3x² + 5x - 7
Example 2:
Write the polynomial 4x² - 6x⁴ + 2x² + 8x - 3 in standard form.
- Identify terms: 4x², -6x⁴, 2x², 8x, -3
- Determine degrees: 2, 4, 2, 1, 0
- Arrange in descending order: -6x⁴, 4x², 2x², 8x, -3
- Combine like terms: 4x² + 2x² = 6x²
- Standard form: -6x⁴ + 6x² + 8x - 3
Example 3 (with multiple variables):
Write the polynomial 3xy² + 2x²y - 5 + xy in standard form. Note that when dealing with multiple variables, we often prioritize the order based on alphabetical order of the variables.
- Identify terms: 3xy², 2x²y, -5, xy
- Determine degrees: 3, 3, 0, 2 (degree is the sum of exponents)
- Arrange in descending order (alphabetical then descending degree): 2x²y, 3xy², xy, -5
- Combine like terms: No like terms to combine.
- Standard form: 2x²y + 3xy² + xy - 5
Significance of Standard Form
Writing a polynomial in standard form offers several significant advantages:
- Easy Comparison: It makes it easier to compare polynomials based on their degree and leading coefficient (the coefficient of the term with the highest degree).
- Simplified Operations: Performing operations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication becomes simpler and more organized.
- Finding Roots: Finding the roots (solutions) of polynomial equations is often easier when the polynomial is in standard form.
- Identifying Key Features: The standard form helps in identifying important characteristics of the polynomial function, such as its end behavior and turning points (in graphical representation).
- Polynomial Division: Polynomial long division is significantly easier and more systematic when both the dividend and divisor are in standard form.
Advanced Topics and Considerations
- Polynomials in Multiple Variables: The principles of standard form extend to polynomials with more than one variable. The order is typically determined by prioritizing the highest degree, then using alphabetical order to break ties.
- Complex Coefficients: Polynomials can have complex numbers as coefficients. The process of writing them in standard form remains the same; simply maintain the order of the exponents.
- Factoring Polynomials: Writing a polynomial in standard form is a crucial first step before attempting to factor it. Factoring often simplifies the expression and reveals valuable information about its roots.
Conclusion
Mastering the skill of writing polynomials in standard form is essential for success in algebra and related mathematical fields. By following the step-by-step guide and practicing the provided examples, you'll be well-equipped to handle various polynomial expressions with confidence. Remember, the standard form enhances clarity, simplifies operations, and unveils valuable information about the polynomial's behavior. Consistent practice will solidify your understanding and allow you to tackle more advanced polynomial concepts effectively. This thorough understanding of polynomials and their standard form will lay a solid groundwork for future mathematical endeavors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
1 2x 1 2x X 1
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 7 20 As A Percent
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Element Is Shiny And Conducts Heat And Electricity
Mar 28, 2025
-
3x 2y 6 In Slope Intercept Form
Mar 28, 2025
-
How To Find The Mass Of A Planet
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write A Polynomial In Standard Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
