Find The Area Inside The Oval Limaçon
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
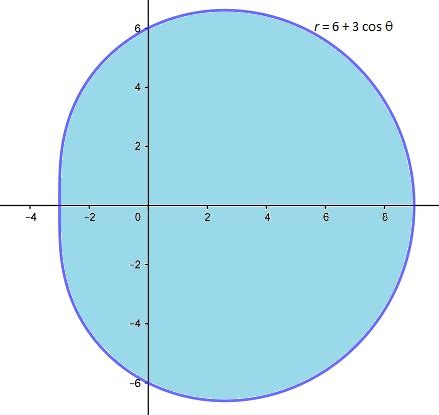
Table of Contents
Finding the Area Inside an Oval Limaçon: A Comprehensive Guide
The limaçon, a fascinating curve with a rich history in mathematics and art, presents a compelling challenge for those interested in calculus and geometry. This article will delve into the intricacies of calculating the area enclosed within a specific type of limaçon: the oval limaçon. We'll explore different approaches, from understanding the curve's polar equation to employing integration techniques. By the end, you'll possess a robust understanding of how to tackle this problem and appreciate the elegance of the solution.
Understanding the Oval Limaçon
Before embarking on the area calculation, let's solidify our understanding of the oval limaçon itself. Defined by its polar equation, the oval limaçon differs from other types of limaçons due to its unique characteristics.
The Polar Equation: r = a + b cos θ
The general polar equation of a limaçon is given by: r = a + b cos θ (or r = a + b sin θ, depending on the orientation). The values of 'a' and 'b' determine the shape of the limaçon. For an oval limaçon, the condition a > b > 0 must hold true. This inequality guarantees that the curve remains convex and doesn't exhibit any inner loop, unlike other types of limaçons (like the cardioid or the limaçon with an inner loop).
Let's visualize this:
a: This parameter controls the overall size of the limaçon. A largeraresults in a larger limaçon.b: This parameter determines the degree of dimpling or indentation in the limaçon. A largerb(while still maintaininga > b) results in a more pronounced dimple. Ifa = b, the limaçon becomes a cardioid. Ifa < b, an inner loop appears.
Visualizing the Oval Limaçon
Imagine a circle rolling around another circle. The path traced by a point on the circumference of the rolling circle describes a limaçon. For an oval limaçon, this rolling circle is smaller than the stationary circle, preventing the formation of the inner loop. This image helps intuitively grasp the shape we're dealing with.
Calculating the Area Using Polar Coordinates
The most efficient way to calculate the area inside an oval limaçon is through integration in polar coordinates. The area element in polar coordinates is given by dA = ½ r² dθ.
Setting up the Integral
To find the total area, we integrate this area element over the entire range of θ that defines one complete loop of the limaçon. Since the cosine function has a period of 2π, integrating from 0 to 2π encompasses the entire area. Therefore, our integral becomes:
Area = ½ ∫₀²π (a + b cos θ)² dθ
Solving the Integral
This integral requires expanding the square and utilizing trigonometric identities for simplification. Let's break it down step-by-step:
-
Expanding the square: (a + b cos θ)² = a² + 2ab cos θ + b² cos² θ
-
Trigonometric Identity: Recall that cos² θ = (1 + cos 2θ)/2. Substituting this into the integral:
Area = ½ ∫₀²π [a² + 2ab cos θ + b²(1 + cos 2θ)/2] dθ
-
Separating the integral: We can separate this into individual integrals, each easier to solve:
Area = ½ [∫₀²π a² dθ + ∫₀²π 2ab cos θ dθ + ∫₀²π (b²/2) dθ + ∫₀²π (b²/2) cos 2θ dθ]
-
Evaluating the integrals:
- ∫₀²π a² dθ = 2πa²
- ∫₀²π 2ab cos θ dθ = 0 (The integral of cosine over a full period is zero.)
- ∫₀²π (b²/2) dθ = πb²
- ∫₀²π (b²/2) cos 2θ dθ = 0 (The integral of cosine over a full period is zero.)
-
Combining the results:
Area = ½ (2πa² + πb²) = π(a² + b²/2)
Therefore, the area enclosed within an oval limaçon is given by the elegant formula: π(a² + b²/2).
Alternative Approaches and Considerations
While polar coordinates offer the most direct and efficient method, it's worthwhile to briefly mention alternative approaches and some important considerations.
Cartesian Coordinates
While possible, using Cartesian coordinates to calculate the area would involve significantly more complex integration, requiring solving for y in terms of x from the equation and then performing a considerably more challenging double integral. It's strongly advised to stick to polar coordinates for this problem.
Numerical Methods
For particularly complex limaçons or variations on the basic equation, numerical methods of integration (like Simpson's rule or the trapezoidal rule) can provide an approximate solution. These methods are useful when analytical solutions are difficult to obtain.
Understanding the Limitations
The formula π(a² + b²/2) holds specifically for the oval limaçon, where a > b > 0. If these conditions are not met (e.g., the limaçon has an inner loop), the integration limits and the resulting area formula will differ substantially. It's crucial to always check the conditions before applying this formula.
Applications and Further Exploration
The limaçon, and its area calculation, isn't just a mathematical curiosity. It finds applications in various fields:
- Engineering: The shapes of certain gears and cams can be modeled using limaçons, making the area calculation important for design optimization.
- Physics: Certain wave patterns and interference phenomena exhibit limaçon-like shapes, making the area relevant to their analysis.
- Art and Design: The aesthetically pleasing shape of the limaçon has led to its use in various artistic and design contexts, from creating patterns to inspiring architectural forms.
Conclusion
Calculating the area inside an oval limaçon, while seemingly a complex problem at first, is elegantly solved using polar coordinates and integration. Understanding the polar equation of the limaçon and applying the appropriate integration techniques leads to a straightforward and satisfying solution: π(a² + b²/2). This formula provides a concise and powerful tool for analyzing the properties of this beautiful mathematical curve, opening doors to further exploration in mathematics and its applications across various scientific and artistic domains. By mastering this technique, you gain a valuable skillset applicable to a broader range of area calculations in polar coordinates. Remember always to carefully consider the conditions of the problem and choose the most appropriate method for accurate and efficient solutions.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Plasma Membrane Of A Muscle Cell Is Called The
Mar 28, 2025
-
180 Inches Is How Many Yards
Mar 28, 2025
-
1 2x 1 2x X 1
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is 7 20 As A Percent
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Element Is Shiny And Conducts Heat And Electricity
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Find The Area Inside The Oval Limaçon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
