A Square Is ____ A Rectangle.
listenit
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
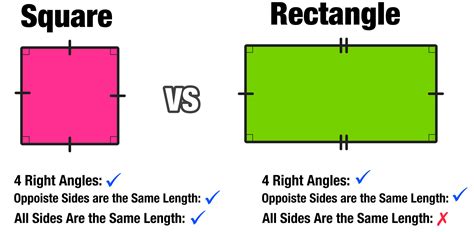
Table of Contents
A Square is ALWAYS a Rectangle: Understanding Geometric Relationships
The statement "a square is a rectangle" often sparks debate among geometry enthusiasts. While seemingly simple, this statement encapsulates a fundamental concept in geometry: the relationship between different shapes and their defining properties. Understanding this relationship requires a deep dive into the characteristics of squares and rectangles, clarifying why a square is unequivocally classified as a rectangle. This article will comprehensively explore this topic, demystifying the connection and strengthening your understanding of geometric classifications.
Defining Squares and Rectangles: A Foundation for Understanding
Before we delve into the relationship between squares and rectangles, let's clearly define each shape based on their defining properties.
The Square: A Shape of Precision
A square is a two-dimensional geometric figure characterized by the following properties:
- Four equal sides: All four sides of a square are congruent, meaning they possess the same length.
- Four right angles: Each of the four interior angles of a square measures exactly 90 degrees. This means all angles are right angles.
- Equal diagonals: The diagonals of a square (lines connecting opposite corners) are equal in length and bisect each other at a right angle.
- Parallel sides: Opposite sides of a square are parallel to each other. This is a crucial property shared with rectangles.
These four defining properties make a square a very specific and symmetrical shape. The precision and symmetry are key to its relationship with other quadrilaterals.
The Rectangle: A Broader Definition
A rectangle, unlike a square, has a slightly broader definition:
- Four right angles: Similar to a square, a rectangle must have four interior angles, each measuring 90 degrees.
- Opposite sides equal and parallel: Rectangles have two pairs of opposite sides that are equal in length and parallel to each other.
Notice the key difference: while a rectangle requires only that opposite sides are equal, a square necessitates that all sides are equal. This subtle yet crucial difference establishes the hierarchical relationship between these two shapes.
Why a Square is ALWAYS a Rectangle: Exploring the Inclusive Nature of Geometric Definitions
The statement "a square is a rectangle" holds true because a square perfectly satisfies all the criteria required to be classified as a rectangle. Let's break this down:
- Right Angles: A square, by definition, has four right angles (90-degree angles). This is a fundamental requirement for any shape to be classified as a rectangle.
- Opposite Sides Equal and Parallel: A square not only has opposite sides that are equal in length but also parallel. This satisfies the second requirement for being a rectangle.
Therefore, since a square possesses all the characteristics of a rectangle, it logically follows that a square is a subset of rectangles. It's a special case of a rectangle – a rectangle with the added constraint that all sides are equal.
Think of it like this: all squares are rectangles, but not all rectangles are squares. This is a fundamental concept in set theory, where squares form a subset within the larger set of rectangles.
Understanding Set Theory and Geometric Classification
The relationship between squares and rectangles perfectly illustrates the principles of set theory. Imagine two sets:
- Set A: The set of all rectangles.
- Set B: The set of all squares.
In this context, Set B is entirely contained within Set A. Every element (every square) in Set B is also an element in Set A (a rectangle). However, Set A contains elements (rectangles) that are not in Set B (non-square rectangles). This demonstrates the inclusive nature of the geometric classification.
Visualizing the Relationship: Diagrams and Illustrations
Visual representations can significantly enhance understanding. Imagine a Venn diagram:
- The larger circle represents the set of all rectangles.
- A smaller circle, completely inside the larger circle, represents the set of all squares.
This visually demonstrates that the set of squares is a subset of the set of rectangles. No square exists outside the realm of rectangles.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
Understanding the relationship between squares and rectangles has significant applications in various fields:
- Construction and Engineering: In architecture and civil engineering, both squares and rectangles are fundamental building blocks. Understanding their properties is crucial for constructing stable and efficient structures. A square window frame is still a rectangular frame.
- Computer Graphics and Programming: In computer graphics and programming, precise geometric definitions are essential. The ability to accurately classify shapes impacts operations like collision detection and area calculations.
- Mathematics and Geometry: This fundamental concept underpins more advanced geometric concepts and theorems. Understanding the hierarchy of shapes facilitates the development of further mathematical reasoning and problem-solving skills.
Addressing Common Misconceptions and Clarifying Confusion
The inclusive nature of the relationship often leads to confusion. It's vital to dispel some common misconceptions:
- A rectangle is a square (FALSE): While all squares are rectangles, not all rectangles are squares.
- Squares and rectangles are entirely separate shapes (FALSE): Squares are a specific type of rectangle.
- This relationship is arbitrary (FALSE): The relationship is based on well-defined geometric properties.
Conclusion: Embracing the Precision of Geometric Definitions
The statement "a square is a rectangle" is not a matter of opinion but a logical consequence of the precise definitions of these two shapes. Understanding this relationship enhances our understanding of geometric classifications and demonstrates the elegance and logic embedded within mathematical principles. By grasping the inclusive nature of geometric definitions, we strengthen our foundational knowledge of geometry and its numerous applications. The clarity and precision of these definitions underscore the power of mathematical language and its ability to describe and categorize the world around us. This foundational knowledge serves as a cornerstone for further exploration into more complex geometric concepts and their practical implications. The understanding developed here extends beyond the simple relationship of squares and rectangles, and lays the groundwork for a deeper understanding of geometric shapes and their relationships. The ability to classify and analyze shapes is a crucial skill with applications across various disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Convert Wavelength To Meters
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons In Argon
Mar 17, 2025
-
1 1 X 2 Power Series
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Percent Of 75 Is 40
Mar 17, 2025
-
Translating Graph Up By 4 Units
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Square Is ____ A Rectangle. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
