A Quadrangle With 1 Right Angle
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
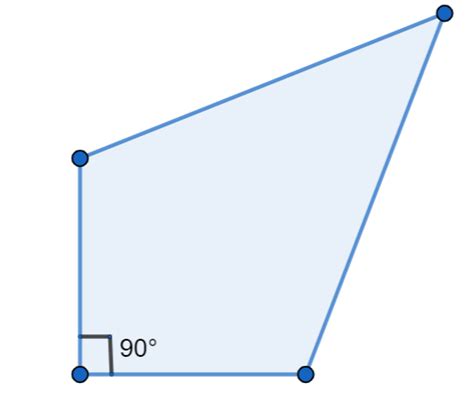
Table of Contents
A Quadrangle with One Right Angle: Exploring its Properties and Variations
A quadrangle, also known as a quadrilateral, is a polygon with four sides and four angles. When one of these angles measures 90 degrees (a right angle), the properties of the quadrangle become significantly more defined and interesting. This article delves deep into the characteristics of a quadrangle possessing a single right angle, exploring its various forms, unique features, and mathematical implications. We will unpack different types of quadrilaterals falling under this category, examining their individual properties, and highlighting the key distinctions between them.
Types of Quadrilaterals with One Right Angle
While a square or rectangle boasts four right angles, the presence of just one right angle opens the door to a wider range of possibilities within the family of quadrilaterals. This category isn't as neatly defined as those with more right angles, leading to a fascinating array of shapes and mathematical explorations. Let's explore some key types:
1. Right-Angled Trapezoid (Right Trapezoid)
A right trapezoid is a trapezoid with at least one right angle. A trapezoid, remember, is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides (bases). In a right trapezoid, one of the non-parallel sides is perpendicular to the parallel bases. This creates a distinct geometrical shape.
Properties of a Right Trapezoid:
- One pair of parallel sides: This defining characteristic of a trapezoid remains.
- Two right angles: While the definition states at least one, right trapezoids always have two adjacent right angles. This results from the perpendicularity of one of the non-parallel sides to the parallel bases.
- Two other angles: The remaining two angles are supplementary (adding up to 180 degrees). These angles are not necessarily equal unless the trapezoid is also an isosceles trapezoid (discussed later).
- Area calculation: The area of a right trapezoid is calculated similarly to that of any trapezoid: Area = (1/2) * (sum of parallel sides) * height, where the height is the length of the perpendicular side.
2. Irregular Quadrilaterals with One Right Angle
This category encompasses the most diverse group. It's a broad class of quadrilaterals that possess one right angle but don't meet the specific requirements of other quadrilateral types (like trapezoids or kites). These quadrilaterals exhibit varied side lengths and angles, aside from the single 90-degree angle. They lack the predictable regularity of shapes like rectangles or squares.
Properties of Irregular Quadrilaterals with One Right Angle:
- One 90-degree angle: This is the only guaranteed property.
- Three other angles: These angles can have any value, provided their sum, along with the right angle, adds up to 360 degrees.
- Varying side lengths: Sides can be of any length, leading to a wide array of possible shapes.
- Area calculation: The area calculation requires a more complex approach than that of regular quadrilaterals, often breaking it down into smaller triangles or employing coordinate geometry.
3. Special Cases within Irregular Quadrilaterals
While largely irregular, some quadrilaterals with one right angle can exhibit additional specific properties, blurring the lines between classifications. Imagine an irregular quadrilateral where one right angle is formed by two sides of unequal lengths, and the other sides are such that it might be nearly impossible to determine an easily applicable area calculation method. This illustrates how the complexity arises within this subset of one-right-angled quadrilaterals.
Exploring Further Properties and Relationships
Let's delve deeper into some of the mathematical relationships inherent within these quadrilaterals:
Pythagorean Theorem and its Implications
The Pythagorean theorem finds relevance when dealing with right-angled quadrilaterals, specifically right trapezoids. The presence of the right angle allows us to use the theorem to determine relationships between the lengths of the sides. In a right trapezoid, if we focus on the right-angled triangle formed by the right angle and its adjacent sides, the theorem directly applies. This enables the calculation of unknown side lengths given information about others.
Area Calculations: A Comparative Analysis
Calculating the area of a quadrilateral with one right angle depends heavily on its specific type. While a right trapezoid has a straightforward formula, irregular quadrilaterals may require more advanced techniques such as breaking them down into triangles, using coordinate geometry, or applying more sophisticated formulas involving trigonometric functions. The choice of method depends on the given information (side lengths, angles, coordinates, etc.).
Relationships with Other Geometric Shapes
The concept of "one right angle" creates an intriguing intersection with other geometric shapes. For instance, a right trapezoid can be viewed as a combination of a rectangle and a triangle, making it easier to analyze some of its properties. This highlights the interconnectedness of geometric concepts and the importance of recognizing patterns and relationships across different shapes.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The mathematical principles related to quadrilaterals with one right angle extend beyond theoretical exploration and find numerous applications in various fields:
Architecture and Construction
Right trapezoids and other quadrilaterals with a right angle appear frequently in building designs. Roof structures, window frames, and land plots often feature these shapes. Understanding their properties is essential for accurate measurements, material estimations, and structural integrity in construction projects.
Engineering and Design
Engineering projects frequently involve quadrilaterals with one right angle, from the design of mechanical components to the layout of infrastructure. Precise calculations of areas, angles, and distances are critical for functionality, efficiency, and safety.
Computer Graphics and Game Development
In computer graphics and game development, these shapes are fundamental building blocks for creating complex 2D and 3D environments. Understanding their properties and manipulating them computationally is essential for creating realistic and visually appealing graphics.
Conclusion: Beyond the Basics
While the simple description "a quadrangle with one right angle" might initially seem straightforward, the diverse range of shapes encompassed within this category reveals a rich mathematical landscape. Understanding the variations, properties, and relationships inherent in these figures goes beyond basic geometry, revealing the interconnectedness and practical application of mathematical principles in various domains. From calculating areas to understanding structural integrity, the implications of a single right angle within a quadrilateral have significant reach and impact. Further exploration of this topic can lead to deeper insights into advanced geometric concepts and their real-world significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Ph Of Buffer Solution
Mar 27, 2025
-
5 Less Than The Product Of 3 And A Number
Mar 27, 2025
-
Where Is Most Of Earths Freshwater Stored
Mar 27, 2025
-
How Many Protons Does Strontium Have
Mar 27, 2025
-
Is The Earth Older Than The Sun
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about A Quadrangle With 1 Right Angle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
