9 Protons 10 Neutrons 9 Electrons
listenit
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
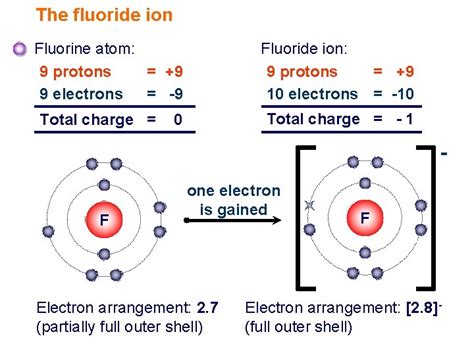
Table of Contents
9 Protons, 10 Neutrons, 9 Electrons: Unveiling the Mystery of Fluorine-19
The seemingly simple statement, "9 protons, 10 neutrons, 9 electrons," actually encapsulates a wealth of information about a specific atom: Fluorine-19, the most common and stable isotope of the element fluorine. This article delves into the details of this atomic configuration, exploring its implications for the properties of fluorine, its applications, and its importance in various scientific fields.
Understanding the Atomic Structure: A Foundation for Understanding Fluorine-19
To fully grasp the significance of 9 protons, 10 neutrons, and 9 electrons, we need to understand the fundamental building blocks of an atom.
-
Protons: Positively charged particles residing in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons (atomic number) defines the element. In this case, 9 protons unequivocally identify the atom as fluorine (F).
-
Neutrons: Neutral particles (no charge) also located in the nucleus. The number of neutrons, along with the number of protons, determines the atom's mass number. Fluorine-19 has a mass number of 19 (9 protons + 10 neutrons). Isotopes are atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons.
-
Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Thus, fluorine-19 has 9 electrons, balancing the positive charge of the 9 protons.
The specific arrangement of these subatomic particles dictates the atom's behavior and its interactions with other atoms and molecules.
The Significance of the Isotope Fluorine-19
Fluorine exists in nature primarily as Fluorine-19 (¹⁹F). While other isotopes exist, they are radioactive and unstable, decaying quickly into other elements. The stability of Fluorine-19 is crucial to its abundance and its role in various natural processes and applications. Its stability arises from the strong nuclear force holding the protons and neutrons together within its nucleus. The particular combination of 9 protons and 10 neutrons leads to a favorable balance of nuclear forces, resulting in a very long half-life – essentially, it's stable.
The prevalence of Fluorine-19 makes it the cornerstone of fluorine's chemical properties and reactivity. Its single unpaired electron in its outermost shell makes it highly reactive, readily forming strong bonds with other atoms. This high reactivity is fundamental to its numerous applications.
Fluorine-19 in Chemistry and its Chemical Properties
The 9 protons, 10 neutrons, and 9 electrons of Fluorine-19 dictate its chemical behavior. Its high electronegativity – its tendency to attract electrons in a chemical bond – is a direct consequence of its atomic structure. This strong pull on electrons leads to the formation of highly polar bonds when fluorine interacts with other atoms.
Highly Reactive Nature
This high reactivity makes fluorine a powerful oxidizing agent. It readily accepts electrons from other atoms, often resulting in vigorous reactions. This property is exploited in various industrial processes and applications, although it also demands careful handling due to the potential for hazardous reactions.
Formation of Strong Bonds
The strong bonds formed by fluorine contribute to the exceptional strength and stability of many fluorine-containing compounds. This is evident in the widespread use of fluorinated polymers, such as Teflon (polytetrafluoroethylene), known for their heat resistance, chemical inertness, and non-stick properties.
Unique Bonding Characteristics
Fluorine's small atomic radius and high electronegativity also lead to unique bonding characteristics. It forms strong hydrogen bonds, influencing the properties of various fluorine-containing compounds and affecting their behavior in biological systems.
Applications of Fluorine-19 and its Compounds
The unique properties stemming from its atomic structure – 9 protons, 10 neutrons, and 9 electrons – make fluorine-19 and its compounds invaluable in numerous fields:
Medicine
-
Medical Imaging: Fluorine-18 (a radioactive isotope, different from Fluorine-19, but still related), is used in Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans for medical imaging. While not directly fluorine-19, understanding fluorine's nuclear properties is essential for developing and using these crucial diagnostic tools.
-
Pharmaceuticals: Fluorine is incorporated into many pharmaceuticals to alter their properties, such as improving their bioavailability, increasing their metabolic stability, or enhancing their binding to specific receptors in the body.
Industry
-
Refrigerants: Although less common now due to their impact on the ozone layer, fluorinated refrigerants were once widely used. The development of new, environmentally friendly refrigerants continues to build upon the understanding of fluorine's chemical properties.
-
Polymers: Fluorine-containing polymers like Teflon (PTFE) and other fluoropolymers are exceptionally resistant to chemicals, heat, and wear. This makes them indispensable in a vast array of applications, from non-stick cookware to high-performance seals and coatings in demanding industrial environments.
-
Aerospace: The unique properties of fluorine-containing materials make them suitable for use in aerospace applications, where extreme conditions demand high-performance materials.
Other Applications
-
Nuclear Energy: Fluorine's chemistry plays a role in nuclear fuel processing and handling.
-
Electronics: Fluorine is used in the production of some electronic components.
-
Agriculture: Fluorine compounds have some applications in agriculture, though their use needs to be carefully managed due to environmental concerns.
Safety Considerations: Handling Fluorine and its Compounds
The high reactivity of fluorine necessitates careful handling and safety precautions. Direct contact with elemental fluorine can cause severe burns and other health problems. Many fluorine compounds are also toxic and require appropriate safety measures during handling, storage, and disposal. Proper training and adherence to safety protocols are paramount when working with fluorine and its derivatives.
Research and Future Directions
Research into fluorine chemistry and its applications continues to expand. Scientists are exploring new ways to harness its unique properties for various purposes, while also addressing environmental and safety concerns. The ongoing quest to understand fluorine's behavior at a fundamental level, driven by its unique atomic configuration of 9 protons, 10 neutrons, and 9 electrons, will undoubtedly yield further advancements and innovations in diverse scientific fields.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of the Periodic Table
The seemingly simple atomic composition of fluorine-19 – 9 protons, 10 neutrons, and 9 electrons – belies its profound impact on numerous aspects of modern life. From the non-stick coating on our cookware to sophisticated medical imaging techniques, fluorine's unique properties are pivotal. Understanding this atomic configuration and its consequences is crucial for developing new applications, improving existing technologies, and ensuring the safe and responsible use of fluorine and its compounds in various sectors. The research and development surrounding fluorine will undoubtedly continue to generate exciting discoveries and improvements in the future. The relatively simple atom is indeed a powerful player in our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Consumer That Eats Only Plants
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Amount Of Energy Required To Raise The Temperature
Apr 04, 2025
-
38 Out Of 40 Is What Percent
Apr 04, 2025
-
Which Polynomial Represents The Sum Below
Apr 04, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons In Al
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 9 Protons 10 Neutrons 9 Electrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
