2 5/6 As An Improper Fraction
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
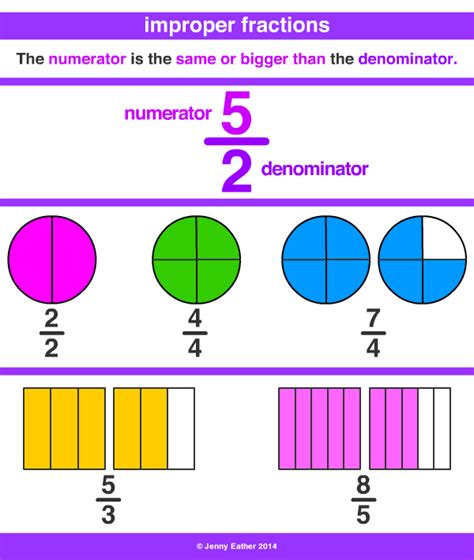
Table of Contents
2 5/6 as an Improper Fraction: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions is a fundamental skill in mathematics, crucial for various applications from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the process of converting the mixed number 2 5/6 into an improper fraction, explaining the underlying principles and providing practical examples to solidify your understanding. We’ll also explore the broader context of mixed numbers and improper fractions, their uses, and why understanding this conversion is essential.
Understanding Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions
Before diving into the conversion, let's clarify the definitions:
-
Mixed Number: A mixed number combines a whole number and a proper fraction. A proper fraction has a numerator (top number) smaller than its denominator (bottom number). For example, 2 5/6 is a mixed number; 2 is the whole number, and 5/6 is the proper fraction.
-
Improper Fraction: An improper fraction has a numerator that is greater than or equal to its denominator. For example, 17/6 is an improper fraction. It represents a value greater than one.
The key difference lies in how they represent quantities. A mixed number visually separates the whole units from the fractional part, while an improper fraction expresses the total quantity as a single fraction. Both represent the same numerical value; they are just different ways of expressing it.
Converting 2 5/6 to an Improper Fraction: The Step-by-Step Process
The conversion of a mixed number to an improper fraction involves a straightforward two-step process:
Step 1: Multiply the whole number by the denominator of the fraction.
In our example, 2 5/6, we multiply the whole number (2) by the denominator of the fraction (6):
2 * 6 = 12
Step 2: Add the numerator of the fraction to the result from Step 1.
Now, we add the numerator of the fraction (5) to the result from Step 1 (12):
12 + 5 = 17
Step 3: Write the result as the numerator over the original denominator.
The result from Step 2 (17) becomes the numerator of the improper fraction, and the original denominator (6) remains unchanged. Therefore, the improper fraction equivalent of 2 5/6 is:
17/6
Visualizing the Conversion
Imagine you have two whole pizzas and 5/6 of another pizza. The mixed number 2 5/6 represents this scenario. To convert this to an improper fraction, we need to represent the entire quantity as slices of pizza.
Each pizza is divided into 6 slices (the denominator). The two whole pizzas give us 2 * 6 = 12 slices. Adding the 5 extra slices from the third pizza gives us a total of 12 + 5 = 17 slices. Since each slice is 1/6 of a pizza, we have 17/6 of a pizza in total. This visually demonstrates how 2 5/6 equals 17/6.
Why is this Conversion Important?
Converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions is vital for several mathematical operations:
-
Addition and Subtraction of Fractions: Adding or subtracting mixed numbers often requires converting them to improper fractions first to simplify the process. This ensures you're working with consistent denominators and prevents errors.
-
Multiplication and Division of Fractions: While possible with mixed numbers, converting them to improper fractions usually streamlines multiplication and division, leading to more efficient calculations.
-
Algebra and Calculus: In higher-level mathematics, improper fractions are often preferred for their ease of manipulation in algebraic expressions and calculus problems.
-
Real-world Applications: Many real-world problems involving fractions, such as measuring ingredients in cooking or calculating distances in construction, benefit from the use of improper fractions for accurate and efficient calculations.
Further Examples: Extending the Concept
Let's apply this conversion process to other mixed numbers:
-
3 1/4:
- Step 1: 3 * 4 = 12
- Step 2: 12 + 1 = 13
- Improper fraction: 13/4
-
1 2/7:
- Step 1: 1 * 7 = 7
- Step 2: 7 + 2 = 9
- Improper fraction: 9/7
-
5 3/8:
- Step 1: 5 * 8 = 40
- Step 2: 40 + 3 = 43
- Improper fraction: 43/8
Converting Improper Fractions Back to Mixed Numbers
The reverse process—converting an improper fraction to a mixed number—is equally important. This involves dividing the numerator by the denominator.
For example, to convert 17/6 back to a mixed number:
-
Divide the numerator (17) by the denominator (6): 17 ÷ 6 = 2 with a remainder of 5.
-
The quotient (2) becomes the whole number part.
-
The remainder (5) becomes the numerator of the fraction.
-
The denominator (6) remains unchanged.
Therefore, 17/6 = 2 5/6.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
The conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions isn't just a theoretical exercise; it has practical implications in numerous real-world situations:
-
Cooking: Recipes often use mixed numbers to represent ingredient quantities. Converting these to improper fractions can simplify calculations when scaling up or down a recipe.
-
Construction and Engineering: Precise measurements are crucial in construction and engineering. Converting mixed numbers to improper fractions helps in accurate calculations involving lengths, areas, and volumes.
-
Finance: Working with fractions of monetary units often requires converting between mixed numbers and improper fractions for accurate calculations of interest, dividends, and shares.
-
Data Analysis: In data analysis, representing data as fractions can be advantageous, and the ability to convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions allows for flexible data manipulation.
Mastering Fraction Conversions: Practice Makes Perfect
The key to mastering the conversion between mixed numbers and improper fractions lies in consistent practice. The more you practice, the more intuitive and effortless the process will become. Work through various examples, gradually increasing the complexity of the numbers involved. This practice will not only solidify your understanding of the concept but also improve your overall mathematical skills. You can find many online resources and workbooks that offer numerous practice problems to help you hone your skills. Remember, consistent practice is the key to mastering any mathematical concept.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Fraction Conversions
Understanding how to convert between mixed numbers and improper fractions is a fundamental skill with far-reaching applications. From simplifying basic arithmetic to solving complex problems in higher-level mathematics and real-world scenarios, this skill is invaluable. By mastering this conversion, you'll enhance your mathematical abilities and open up a world of possibilities for problem-solving and practical application. The step-by-step process detailed here, combined with consistent practice, will equip you with the confidence and proficiency to tackle any fraction conversion challenge. Remember, mathematics is a journey of continuous learning, and mastering fraction conversions is a crucial step in that journey.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What State Of Matter Is Most Common In The Universe
Mar 24, 2025
-
A Quadrilateral Is Always A Rhombus
Mar 24, 2025
-
Wood Burning Chemical Or Physical Change
Mar 24, 2025
-
Integral Of X 4 X 2
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Does Tin Have
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 5/6 As An Improper Fraction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
