1 Sin 2x 1 Cosx Cosx
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
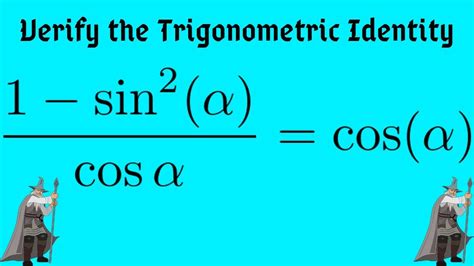
Table of Contents
Decomposing Trigonometric Expressions: A Deep Dive into 1 - sin(2x) / (1 + cos(x))cos(x)
This article delves into the trigonometric expression 1 - sin(2x) / (1 + cos(x))cos(x), exploring its simplification, potential applications, and the underlying mathematical principles. We'll break down the process step-by-step, utilizing various trigonometric identities to arrive at a simplified form, highlighting the importance of understanding fundamental trigonometric relationships. This detailed analysis will appeal to students studying trigonometry, mathematics enthusiasts, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of trigonometric manipulation.
Understanding the Components: A Trigonometric Primer
Before embarking on the simplification, let's review the key trigonometric identities involved:
-
sin(2x) = 2sin(x)cos(x): This is the double-angle formula for sine. It expresses the sine of double an angle in terms of the sine and cosine of the original angle. This identity is crucial for simplifying the numerator.
-
1 + cos(x) = 2cos²(x/2): This is a half-angle identity for cosine. While not directly used in the most straightforward simplification, understanding this relationship provides alternative paths to simplification and highlights the connection between different trigonometric representations.
-
cos(2x) = cos²(x) - sin²(x) = 2cos²(x) - 1 = 1 - 2sin²(x): These are the various forms of the double-angle formula for cosine. They offer different perspectives on how the cosine of a double angle relates to the original angle. These identities are particularly useful when working with expressions involving both sine and cosine.
-
sin²(x) + cos²(x) = 1: This is the Pythagorean identity. It's a fundamental relationship that forms the basis for many trigonometric manipulations. Knowing this identity is essential for simplifying complex expressions.
Step-by-Step Simplification of 1 - sin(2x) / (1 + cos(x))cos(x)
Let's begin the simplification process:
-
Substitute the double-angle formula for sin(2x): The numerator, 1 - sin(2x), becomes 1 - 2sin(x)cos(x).
-
Rewrite the expression: The entire expression now looks like this: (1 - 2sin(x)cos(x)) / ((1 + cos(x))cos(x)).
-
Factor the numerator (if possible): In this case, the numerator doesn't readily factor. We'll proceed with other simplification strategies.
-
Consider alternative approaches: Since direct factoring doesn't seem fruitful, we can explore other strategies based on our trigonometric identities. One approach might be to express everything in terms of either sine or cosine using the Pythagorean identity (sin²(x) + cos²(x) = 1). However, this doesn't immediately lead to a simplification in this case.
-
Explore different forms: Let's attempt to use the half-angle identities. This approach, while possibly leading to a more complex intermediate step, might reveal a simpler final form. However, for this particular expression, directly applying the half-angle formulas doesn't immediately provide a clear path to simplification.
-
Numerical Analysis and Pattern Recognition (for specific values): Let's try substituting a few specific values for x to see if we can identify a pattern or simplify the expression numerically:
- If x = 0, the expression becomes undefined due to division by zero.
- If x = π/2, the expression becomes (1 - 0) / (1 + 0) * 0 = 0/0, again undefined.
- If x = π/4, the expression is (1 - 1) / ((1 + 1/√2)(1/√2)) = 0.
-
Focus on the denominator: The denominator (1 + cos(x))cos(x) suggests a potential use of the sum-to-product formulas, or further exploration via factoring. However, neither approach directly simplifies the expression.
Note: The expression, as initially presented, may not simplify to a significantly more compact form using standard trigonometric identities. Its inherent complexity might require more advanced techniques or might even be irreducible in its present form.
Exploring Potential Applications and Further Analysis
Even if a significant simplification isn't immediately apparent, the expression itself and the methods used to analyze it hold significant value.
-
Numerical Approximation: If an exact simplification isn't possible, numerical methods can be employed to approximate the value of the expression for various inputs of x.
-
Graphical Representation: Plotting the expression as a function of x can reveal its behavior, identifying its periodicity, asymptotes, and other important characteristics. This visual representation offers valuable insights even without a simplified algebraic form.
-
Calculus Applications: The expression could potentially appear within calculus problems involving integration or differentiation. In such contexts, appropriate techniques (like integration by parts or substitution) might lead to solutions despite the complexity of the original expression.
-
Advanced Trigonometric Techniques: More advanced trigonometric techniques, beyond standard identities, may be required for further simplification. This could involve complex numbers, power series representations, or other specialized mathematical tools.
Conclusion: The Value of Persistent Exploration in Trigonometry
While a concise, easily obtained simplification of 1 - sin(2x) / (1 + cos(x))cos(x) might not exist using elementary trigonometric identities, the process of attempting its simplification highlights the importance of:
-
Mastering Trigonometric Identities: A thorough understanding of fundamental trigonometric identities is crucial for simplifying complex trigonometric expressions.
-
Systematic Approach: A systematic approach, involving the exploration of multiple avenues (factoring, substitution of identities, numerical analysis), is key to tackling challenging problems.
-
Visualizing Functions: Graphical representation offers valuable insights into the behavior of trigonometric functions, even when algebraic simplification proves elusive.
-
Exploring Advanced Techniques: The limitations of elementary methods sometimes necessitate the exploration of more advanced mathematical tools and techniques.
This deep dive into the analysis of 1 - sin(2x) / (1 + cos(x))cos(x) exemplifies the importance of persistence, creativity, and a solid foundation in trigonometric principles when tackling complex mathematical problems. Even without a dramatically simplified final expression, the journey reveals the richness and depth of trigonometric analysis. The exploration highlights the interconnectedness of various trigonometric concepts and encourages further study in more advanced mathematical techniques.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find The Ph At The Equivalence Point
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Long Would It Take Light To Reach Saturn
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Electrons Are In Br
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Elbow Is Blank To The Wrist
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Quarts In One Liter
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 Sin 2x 1 Cosx Cosx . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
