How Many Electrons Are In Br
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
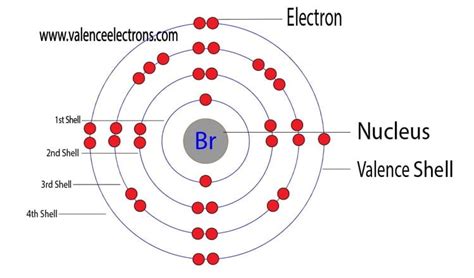
Table of Contents
Delving Deep: How Many Electrons Does Bromine (Br) Possess?
Bromine, a fascinating element with a rich history and diverse applications, holds a significant place in the periodic table. Understanding its electronic structure is key to comprehending its chemical behavior and properties. This in-depth exploration will answer the central question: How many electrons are in Br? We'll move beyond a simple numerical answer to delve into the underlying principles of atomic structure and explore the implications of bromine's electron configuration.
Understanding Atomic Structure: The Foundation
Before we determine the number of electrons in a bromine atom, let's establish a firm understanding of atomic structure. An atom comprises three fundamental subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles residing in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element's atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles also found in the nucleus. They contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons.
The arrangement of electrons in these shells determines an atom's chemical properties and how it interacts with other atoms. This arrangement is described by the electron configuration.
Bromine's Place in the Periodic Table
Bromine (Br) is a nonmetal located in Group 17 (also known as the halogens) and Period 4 of the periodic table. Its atomic number is 35, meaning a neutral bromine atom contains 35 protons. Since the number of electrons in a neutral atom equals the number of protons, a neutral bromine atom possesses 35 electrons.
Electron Configuration: Unveiling the Arrangement
The electron configuration of bromine reveals the specific arrangement of its 35 electrons in various energy levels. This arrangement follows specific rules based on the principles of quantum mechanics:
- Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill the lowest energy levels first.
- Pauli Exclusion Principle: Each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins.
- Hund's Rule: Electrons fill orbitals individually before pairing up.
The electron configuration of bromine is: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁵
Let's break this down:
- 1s²: Two electrons in the first energy level (n=1), which contains one s orbital.
- 2s²: Two electrons in the second energy level (n=2), in the s orbital.
- 2p⁶: Six electrons in the second energy level (n=2), filling the three p orbitals.
- 3s²: Two electrons in the third energy level (n=3), in the s orbital.
- 3p⁶: Six electrons in the third energy level (n=3), filling the three p orbitals.
- 4s²: Two electrons in the fourth energy level (n=4), in the s orbital.
- 3d¹⁰: Ten electrons in the third energy level (n=3), filling the five d orbitals.
- 4p⁵: Five electrons in the fourth energy level (n=4), partially filling the three p orbitals.
This configuration explains bromine's chemical reactivity. The presence of five electrons in the 4p subshell means bromine needs only one more electron to achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in its outermost shell), making it highly reactive and prone to forming ionic or covalent bonds.
Isotopes and Electron Numbers
While the most common isotope of bromine has 35 electrons, it's crucial to understand the concept of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Bromine has two stable isotopes: ⁷⁹Br and ⁸¹Br. Both isotopes have 35 protons and, in their neutral state, 35 electrons. The difference lies in their neutron count – ⁷⁹Br has 44 neutrons, and ⁸¹Br has 46 neutrons. The number of electrons remains consistent regardless of the isotope.
Bromine's Chemical Behavior and Electron Configuration
The electron configuration directly influences bromine's chemical behavior. The five electrons in its outermost shell (valence electrons) are responsible for its high reactivity. Bromine readily accepts one electron to achieve a stable electron configuration similar to the noble gas krypton (Kr). This tendency explains its formation of bromide ions (Br⁻) in ionic compounds and its participation in covalent bonding.
Applications of Bromine and its Electronic Structure
The unique electronic structure of bromine contributes to its diverse applications in various fields:
- Flame Retardants: Brominated flame retardants are added to plastics and textiles to reduce flammability. The bromine atoms interfere with the combustion process, hindering the spread of fire.
- Agriculture: Bromine compounds are used as pesticides and fumigants, although their use is increasingly restricted due to environmental concerns.
- Medicine: Certain bromine compounds have medicinal properties, although their use is also carefully regulated.
- Water Treatment: Bromine compounds are employed in water purification systems as disinfectants, similar to chlorine.
The understanding of bromine's electronic structure is vital in the development and application of these technologies.
Beyond the Basics: Ions and Electron Gain/Loss
A neutral bromine atom has 35 electrons. However, bromine readily forms ions, altering its electron count. The most common ion is the bromide ion (Br⁻), which gains one electron, resulting in a total of 36 electrons.
The electron gain or loss depends on the chemical environment and the nature of the reaction. Understanding this dynamic aspect is crucial for comprehending bromine's role in complex chemical processes.
Conclusion: A Comprehensive Understanding
In conclusion, a neutral bromine atom possesses 35 electrons. This number, derived from its atomic number (35), is fundamental to understanding its chemical behavior and its diverse applications. The detailed electron configuration, 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰4p⁵, reveals the arrangement of these electrons and explains bromine's reactivity and tendency to form the bromide ion (Br⁻) with 36 electrons. The concept of isotopes and the influence of electron gain or loss further enrich our understanding of this fascinating element. The information presented here provides a comprehensive overview, highlighting the connection between bromine's atomic structure, its electron configuration, and its consequential chemical properties and applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lcm Of 5 3 And 4
Mar 15, 2025
-
20 As A Percent Of 50
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is 5 9 In Decimal Form
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Phosphorus
Mar 15, 2025
-
64 Oz Equals How Many Pounds
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Electrons Are In Br . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
