1 6 On A Number Line
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
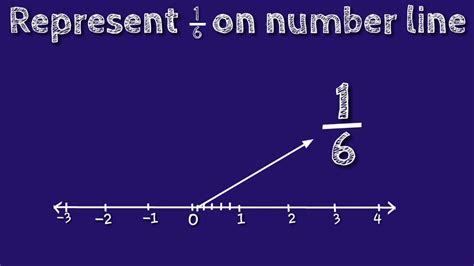
Table of Contents
Understanding 1/6 on a Number Line: A Comprehensive Guide
The number line is a fundamental tool in mathematics, providing a visual representation of numbers and their relationships. Understanding how to place fractions, like 1/6, on a number line is crucial for developing a strong grasp of numerical concepts. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of representing 1/6 on a number line, exploring various methods and applications. We'll cover everything from basic understanding to more advanced concepts, ensuring a thorough comprehension for learners of all levels.
What is a Number Line?
A number line is a straight line extending infinitely in both directions, used to represent numbers visually. It typically includes marked points representing integers (whole numbers), but can also accommodate fractions, decimals, and even irrational numbers. The key is that each point on the line corresponds to a unique number, and the distance between points reflects the difference between the numbers they represent.
Key Features of a Number Line
- Zero Point: The central point, representing the number zero.
- Positive Numbers: Located to the right of zero.
- Negative Numbers: Located to the left of zero.
- Equal Intervals: The distance between consecutive integers is consistent throughout the line. This uniformity is crucial for accurately plotting fractions.
Representing 1/6 on a Number Line
Representing 1/6 on a number line involves understanding that it's a fraction, representing one part out of six equal parts of a whole. To accurately plot it, we need to divide the space between two consecutive integers (e.g., 0 and 1) into six equal segments.
Step-by-Step Guide:
-
Draw a Number Line: Start by drawing a straight line and marking a zero point.
-
Choose an Interval: Select two consecutive integers, preferably 0 and 1, for simplicity.
-
Divide the Interval: Divide the space between 0 and 1 into six equal parts. This can be done by using a ruler or by visually estimating equal segments.
-
Label the Segments: Label each of the six segments with the corresponding fraction: 1/6, 2/6 (which simplifies to 1/3), 3/6 (which simplifies to 1/2), 4/6 (which simplifies to 2/3), 5/6, and 1.
-
Locate 1/6: The first mark after zero represents 1/6. Mark this point clearly.
Visual Representation:
Imagine the number line:
0 ---|---|---|---|---|--- 1
The vertical lines represent the divisions into six equal parts. The first mark after 0 is 1/6.
Understanding Fractions and Their Representation
Fractions represent parts of a whole. The numerator (top number) indicates the number of parts being considered, while the denominator (bottom number) indicates the total number of equal parts the whole is divided into. In 1/6, the numerator is 1 (one part) and the denominator is 6 (six equal parts).
Different Representations of Fractions:
Fractions can be represented in various ways:
- As a part of a whole: Imagine a pizza sliced into six equal pieces. 1/6 represents one slice of that pizza.
- As a decimal: 1/6 is approximately 0.1667.
- As a percentage: 1/6 is approximately 16.67%.
All these representations relate to the same value and can be plotted at the same point on the number line.
Applications of Representing Fractions on a Number Line
The ability to accurately place fractions on a number line is essential for various mathematical applications:
1. Comparing Fractions:
The number line provides a clear visual comparison of fractions. For instance, by observing the positions of 1/6 and 1/2 on the number line, it's immediately apparent that 1/2 is greater than 1/6.
2. Addition and Subtraction of Fractions:
Adding and subtracting fractions can be visualized on the number line. For example, adding 1/6 and 2/6 can be done by starting at 1/6 and moving two more segments to the right, arriving at 3/6 (or 1/2).
3. Understanding Equivalent Fractions:
The number line helps visualize equivalent fractions. For example, 2/6 and 1/3 occupy the same point on the number line, demonstrating their equivalence.
4. Solving Word Problems:
Many word problems involving fractions require visualization. The number line can aid in understanding and solving these problems. For example, a problem involving dividing a piece of rope into six equal parts and using one part can be easily visualized on the number line.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
1. Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions:
The number line can also accommodate mixed numbers (e.g., 1 1/6) and improper fractions (e.g., 7/6). Mixed numbers represent a whole number plus a fraction, while improper fractions have a numerator larger than the denominator.
2. Decimals and Number Lines:
Decimals can also be easily plotted on a number line. This allows for comparing and contrasting fractions and decimals. For example, you can plot 0.1667 (the decimal approximation of 1/6) alongside 1/6 on the number line, showing their close proximity.
3. Negative Fractions:
The number line extends to negative numbers, enabling the representation of negative fractions. -1/6 would be located to the left of zero, mirroring the location of 1/6 on the positive side.
4. Irrational Numbers:
While representing irrational numbers (like π or √2) precisely on a number line is impossible due to their infinite decimal expansions, their approximate positions can be shown, illustrating their placement relative to other numbers.
Practical Activities and Exercises
To reinforce understanding, consider these activities:
-
Creating Number Lines: Have students create their own number lines, plotting various fractions, including 1/6 and related fractions.
-
Fraction Comparison Games: Design games where students compare the positions of different fractions on the number line.
-
Real-World Applications: Pose word problems requiring the use of a number line to visualize and solve the problem. For example: "John ate 1/6 of a pizza. How much is left?"
Conclusion: Mastering 1/6 and Beyond
Mastering the representation of 1/6 on a number line lays a crucial foundation for a deeper understanding of fractions, decimals, and more advanced mathematical concepts. Through consistent practice and visualization, students can develop a strong intuitive grasp of these numerical relationships, paving the way for success in mathematics. The number line serves as a versatile tool that aids in comparison, addition, subtraction, and the overall comprehension of fractional values, making it an invaluable resource for both students and educators alike. Remember, the key is to break down the task into smaller, manageable steps, focusing on understanding the underlying concepts rather than just memorizing procedures. By applying the techniques outlined in this guide, you'll be well on your way to mastering the representation of fractions, starting with the seemingly simple yet profoundly important 1/6.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Protons Does Neon Have
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Organelle Is Responsible For Cellular Respiration
Mar 21, 2025
-
Convert 42 Degrees Celsius To Fahrenheit
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 1 3 8 In Decimal Form
Mar 21, 2025
-
Is Water Freezing Exothermic Or Endothermic
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 6 On A Number Line . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
