0.4 Miles Is How Many Feet
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
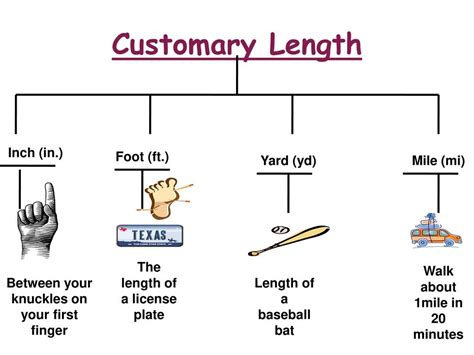
Table of Contents
0.4 Miles is How Many Feet: A Comprehensive Guide to Unit Conversions
Knowing how to convert units is a fundamental skill, useful in various aspects of life, from everyday tasks to complex scientific calculations. This comprehensive guide delves into the conversion of 0.4 miles to feet, exploring the process, providing the answer, and extending the knowledge to encompass related unit conversions. We'll also explore practical applications and common pitfalls to avoid.
Understanding Units of Measurement: Miles and Feet
Before diving into the conversion, let's establish a clear understanding of the units involved: miles and feet. Both are units of length within the imperial system of measurement, predominantly used in the United States.
-
Miles (mi): A larger unit of length, historically defined as 5,280 feet. It's commonly used for measuring longer distances, such as the distance between cities or the length of a road trip.
-
Feet (ft): A smaller unit of length. There are 12 inches in a foot. It's frequently used for measuring shorter distances, such as the dimensions of a room or the height of a person.
Converting 0.4 Miles to Feet: The Calculation
The conversion from miles to feet is straightforward. Since 1 mile equals 5,280 feet, we simply multiply the number of miles by this conversion factor.
Here's the calculation:
0.4 miles * 5,280 feet/mile = 2,112 feet
Therefore, 0.4 miles is equal to 2,112 feet.
Understanding the Conversion Factor: 5,280 feet/mile
The conversion factor, 5,280 feet/mile, is crucial to understanding the relationship between miles and feet. It represents the ratio between the two units. This factor is a constant and remains consistent regardless of the number of miles you're converting.
This ratio stems from historical definitions of these units. The precise origins are somewhat debated, but the connection is firmly established within the imperial system.
Practical Applications of Mile-to-Foot Conversions
The ability to convert miles to feet, and vice-versa, has numerous practical applications in various fields:
1. Real Estate and Construction:
- Land Surveying: Determining property boundaries and area calculations often require converting between miles and feet for accurate measurements.
- Construction Planning: Converting distances from blueprints (often in feet) to real-world distances (potentially in miles) helps in large-scale construction projects.
- Estimating Material Needs: Calculating the amount of materials needed for projects, such as fencing or paving, requires precise length measurements, often requiring unit conversion.
2. Transportation and Logistics:
- Route Planning: GPS systems and mapping software often display distances in miles, but precise navigation might require converting these distances to feet for specific maneuvers.
- Logistics and Delivery: Optimizing delivery routes and tracking shipment progress frequently involves calculating distances in feet, especially in complex urban environments.
- Traffic Management: Traffic engineers use precise measurements, including foot-based units, for efficient traffic flow analysis and signal timing.
3. Sports and Recreation:
- Running and Cycling: Many running and cycling routes are measured in miles, but tracking progress and analyzing performance often involves smaller unit measurements in feet.
- Track and Field: Track and field events frequently use precise measurements in feet and meters for accurate timing and scoring.
- Golf: Distance calculations in golf are often critical for shot selection and strategy, sometimes requiring converting between miles and feet.
4. Science and Engineering:
- Mapping and Cartography: Creating accurate maps and geographical data often requires converting between miles and feet for precise representation of distances.
- Civil Engineering: Building roads, bridges, and other infrastructure necessitates accurate length measurements, often requiring conversions between miles and feet.
- Environmental Science: Monitoring environmental changes, such as measuring the flow rate of rivers or tracking wildlife movements, often necessitates precise measurements using a range of units.
Beyond Miles and Feet: Expanding Unit Conversion Skills
Mastering the mile-to-foot conversion is a stepping stone to a broader understanding of unit conversions. This skill is vital for working with other units of length within the imperial system and the metric system.
Converting to Inches:
Since there are 12 inches in a foot, you can easily extend the conversion to find the equivalent length in inches:
- Convert miles to feet: 0.4 miles * 5,280 feet/mile = 2,112 feet
- Convert feet to inches: 2,112 feet * 12 inches/foot = 25,344 inches
Therefore, 0.4 miles is equal to 25,344 inches.
Converting to Yards:
There are 3 feet in a yard. The conversion would proceed as follows:
- Convert miles to feet: 0.4 miles * 5,280 feet/mile = 2,112 feet
- Convert feet to yards: 2,112 feet / 3 feet/yard = 704 yards
Therefore, 0.4 miles is equal to 704 yards.
Working with the Metric System:
While the imperial system is used in the example, it's essential to be familiar with metric units. Converting miles to meters or kilometers requires using appropriate conversion factors. These conversion factors are readily available online or in reference books.
For example, to convert 0.4 miles to kilometers:
- Convert miles to feet: 0.4 miles * 5,280 feet/mile = 2112 feet
- Convert feet to meters: 2112 feet * 0.3048 meters/foot ≈ 643.7376 meters
- Convert meters to kilometers: 643.7376 meters / 1000 meters/kilometer ≈ 0.6437 kilometers
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Unit Conversions
Several common mistakes can occur during unit conversions:
- Incorrect Conversion Factors: Using the wrong conversion factor is a significant error. Always double-check your conversion factors before performing any calculations.
- Mixing Units: Avoid mixing units during calculations. Ensure all your measurements are in the same unit before performing operations.
- Significant Figures: Pay attention to significant figures, especially in scientific and engineering contexts. Rounding errors can accumulate and affect the accuracy of the final result.
- Unit Cancellation: Ensure that units cancel out correctly during the calculation. The final result should be in the desired unit.
Conclusion: Mastering Unit Conversions for Everyday Success
Converting 0.4 miles to feet, and understanding the broader context of unit conversions, is a valuable skill with wide-ranging applications. From everyday tasks to complex engineering projects, the ability to accurately convert between different units is crucial for precision, efficiency, and avoiding errors. By understanding the process, utilizing appropriate conversion factors, and avoiding common pitfalls, you can confidently tackle any unit conversion challenge. Remember to always double-check your work and use reliable resources for conversion factors to ensure accuracy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Type Of Bond Holds Dna Together
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is A 12 Out Of 18
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Do You Find Magnitude Of Displacement
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Neon
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Photons Are Produced In A Laser Pulse
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 0.4 Miles Is How Many Feet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
