X 4 X 2 3x 2
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
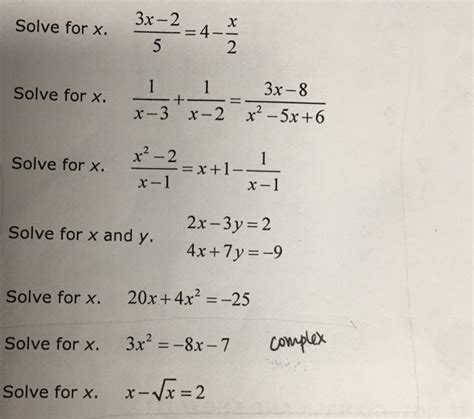
Table of Contents
Decoding the Enigma: A Deep Dive into x⁴ + 2x³ + 2x²
The seemingly simple expression x⁴ + 2x³ + 2x² might appear innocuous at first glance. However, a deeper exploration reveals a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts, applications, and potential avenues for further investigation. This article will dissect this polynomial expression, exploring its factorization, roots, graphical representation, and implications within broader mathematical contexts. We'll go beyond a simple solution and delve into the analytical and computational methods that underpin its understanding.
Understanding the Polynomial's Structure
At its core, x⁴ + 2x³ + 2x² is a quartic polynomial – a polynomial of degree four. This means the highest power of the variable 'x' is 4. The coefficients are integers: 1, 2, and 2. The lack of a linear (x) and constant term is a noteworthy feature, shaping its behavior and properties.
The absence of a constant term immediately tells us something crucial: x = 0 is a root of the polynomial. This is because if we substitute x = 0 into the expression, we get 0⁴ + 2(0)³ + 2(0)² = 0. Therefore, x = 0 is a factor of the polynomial. This allows us to begin factoring the expression.
Factorization Techniques
We can factor out x² from the expression:
x²(x² + 2x + 2)
This simplifies the problem considerably. We now have a quadratic expression within the parentheses: x² + 2x + 2. Let's analyze this quadratic.
We can attempt to factor it using the standard method of finding two numbers that add up to the coefficient of x (2) and multiply to the constant term (2). However, no such real numbers exist. This indicates that the roots of the quadratic are complex numbers.
To find the roots of x² + 2x + 2, we can use the quadratic formula:
x = (-b ± √(b² - 4ac)) / 2a
Where a = 1, b = 2, and c = 2. Substituting these values, we get:
x = (-2 ± √(2² - 4 * 1 * 2)) / 2 * 1
x = (-2 ± √(-4)) / 2
x = (-2 ± 2i) / 2
x = -1 ± i
Therefore, the roots of the quadratic are x = -1 + i and x = -1 - i, where 'i' is the imaginary unit (√-1).
This gives us the complete factorization of the original quartic polynomial:
x²(x - (-1 + i))(x - (-1 - i))
or
x²(x + 1 - i)(x + 1 + i)
Graphical Representation and Behavior
The graphical representation of x⁴ + 2x³ + 2x² provides valuable insights into its behavior. Since the leading coefficient (1) is positive and the degree is even, the graph will open upwards. The double root at x = 0 indicates that the graph touches the x-axis at the origin but doesn't cross it. The complex roots (-1 + i) and (-1 - i) mean that the graph doesn't intersect the x-axis at any other points. It remains entirely above the x-axis except at the origin.
The graph will show a relatively flat region around x = 0 due to the double root, then increase steeply as x moves further away from the origin in both positive and negative directions.
Applications and Extensions
While this specific polynomial might not have immediate, obvious applications in a real-world scenario like modeling physical phenomena, understanding its properties is crucial for grasping more complex mathematical concepts.
1. Foundation for Higher-Order Polynomials: Analyzing quartic polynomials like this one lays the groundwork for understanding higher-order polynomials (quintics, sextics, etc.), which can model more complex systems and phenomena.
2. Complex Numbers and their Significance: The presence of complex roots highlights the importance of complex numbers in algebra and their role in solving equations that don't have real solutions. Complex numbers are fundamental in fields like electrical engineering, quantum mechanics, and signal processing.
3. Numerical Methods: For more complex polynomials where analytical solutions are difficult or impossible to find, numerical methods like Newton-Raphson or the bisection method are used to approximate the roots. This polynomial, though solvable analytically, provides a simplified context to understand the principles behind these numerical techniques.
Further Explorations and Related Concepts
-
Partial Fraction Decomposition: While not directly applicable in this case (due to the presence of complex roots), the concept of partial fraction decomposition is relevant when dealing with rational functions (ratios of polynomials). This technique is widely used in calculus and engineering.
-
Polynomial Long Division: This method could have been used to explore the polynomial's factors but was bypassed due to the easier initial extraction of x². This is still a relevant tool for manipulating and simplifying polynomials.
-
Relationship to Differential Equations: Polynomials often arise as solutions to differential equations, especially in modeling physical processes. This particular polynomial, while not a direct solution to any commonly encountered differential equation, offers an illustrative example of the type of functions involved in such solutions.
-
Taylor and Maclaurin Series: These series expansions allow the representation of functions as infinite sums of polynomial terms. Understanding polynomials is essential to grasping the foundations of these powerful tools in calculus.
Conclusion: Beyond the Surface
The seemingly simple expression x⁴ + 2x³ + 2x² offers a gateway to exploring a wide range of mathematical concepts. Its complete factorization, the analysis of its roots (both real and complex), and its graphical representation reveal fundamental principles of algebra and analysis. While the immediate practical application might not be apparent, its pedagogical value is immense, serving as a stepping stone towards a deeper understanding of higher-order polynomials, complex numbers, and numerical methods. Further exploration of the topics mentioned above will solidify the foundations of mathematical knowledge and facilitate tackling more advanced mathematical problems in various scientific and engineering disciplines. The journey from a simple polynomial to these broader concepts underscores the interconnectedness and beauty of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Si Unit For Power Is The
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Much Is 1 4 Lb
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Quarts In 40 Gallons
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Atoms Are In Carbon
Mar 20, 2025
-
In Which Organelle Does Photosynthesis Take Place
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about X 4 X 2 3x 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
