Which Subshell Is Represented By The Actinides Series
listenit
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
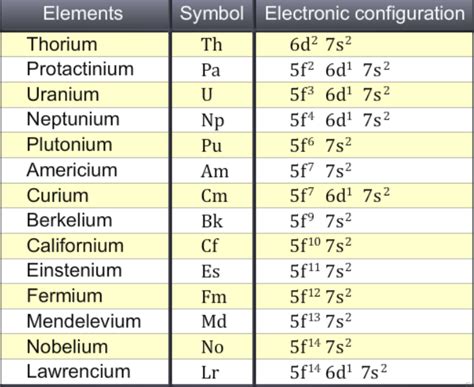
Table of Contents
Which Subshell is Represented by the Actinide Series? Understanding the f-Block Elements
The actinide series, a fascinating group of elements crucial to nuclear technology and various scientific applications, holds a unique position in the periodic table. Understanding their electronic configuration is key to comprehending their properties and behavior. This comprehensive article delves deep into the question: which subshell is represented by the actinide series? The answer, as we'll explore, is the 5f subshell. But let's unpack this further, exploring the intricacies of electron configuration, the periodic table's structure, and the distinctive characteristics of the actinides.
The Periodic Table: A Roadmap to Electron Configuration
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, arranges elements based on their atomic number (number of protons) and recurring chemical properties. This arrangement isn't arbitrary; it reflects the underlying pattern of electron configuration, which dictates an element's chemical behavior. Electrons, negatively charged particles, orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels, or shells. Each shell is further subdivided into subshells, denoted by the letters s, p, d, and f. These subshells can hold a specific number of electrons:
- s subshell: Holds a maximum of 2 electrons
- p subshell: Holds a maximum of 6 electrons
- d subshell: Holds a maximum of 10 electrons
- f subshell: Holds a maximum of 14 electrons
The filling of these subshells follows the Aufbau principle, which dictates that electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. However, exceptions exist due to factors like electron-electron repulsion and orbital stability.
Locating the Actinides: The f-Block Elements
The periodic table's organization reveals the subshell associated with each element series. The actinide series belongs to the f-block, specifically occupying the 5f subshell. This placement is crucial because the 5f electrons are primarily responsible for the unique chemical and physical properties of these elements. The f-block elements are characterized by the filling of the f subshells. The lanthanides (rare earth elements) fill the 4f subshell, while the actinides fill the 5f subshell.
The Significance of the 5f Subshell
The 5f subshell's involvement in actinide chemistry is profound. The electrons in this subshell are relatively loosely held, leading to:
- Variable oxidation states: Actinides exhibit a wide range of oxidation states, unlike many other elements. This is because the energy difference between the 5f, 6d, and 7s orbitals is small, allowing electrons to be readily excited and participate in bonding.
- Complex coordination chemistry: The 5f orbitals are able to participate in bonding with ligands (molecules or ions that bind to a central metal atom), resulting in a rich and diverse coordination chemistry.
- Radioactivity: Many actinides are radioactive, meaning their nuclei are unstable and decay over time, emitting particles and energy. This is a direct consequence of their complex nuclear structures.
- Metallic character: Actinides are typically metals, possessing high density and metallic luster. The delocalized 5f electrons contribute to their metallic bonding.
Understanding Electron Configurations of Actinides
Let's examine the electron configurations of some actinides to solidify the concept of 5f subshell filling:
- Actinium (Ac): [Rn] 6d<sup>1</sup> 7s<sup>2</sup> (Note: While Actinium starts the series, the 5f subshell begins to fill in the subsequent elements)
- Thorium (Th): [Rn] 6d<sup>2</sup> 7s<sup>2</sup>
- Protactinium (Pa): [Rn] 5f<sup>2</sup> 6d<sup>1</sup> 7s<sup>2</sup> (Here, the 5f subshell starts to fill)
- Uranium (U): [Rn] 5f<sup>3</sup> 6d<sup>1</sup> 7s<sup>2</sup>
- Neptunium (Np): [Rn] 5f<sup>4</sup> 6d<sup>1</sup> 7s<sup>2</sup>
- Plutonium (Pu): [Rn] 5f<sup>6</sup> 7s<sup>2</sup> (Variations in configurations are possible for later actinides due to subtle energy level differences)
It's important to note that the electron configurations of heavier actinides become increasingly complex, with variations and exceptions to the general filling order due to relativistic effects and electron-electron interactions. These relativistic effects significantly impact the energies of the orbitals, leading to irregularities in electron configuration.
Distinguishing Actinides from Lanthanides: Subtle but Significant Differences
While both actinides and lanthanides are f-block elements, they differ in several key aspects:
- Subshell: Actinides fill the 5f subshell, while lanthanides fill the 4f subshell.
- Radioactivity: Many actinides are radioactive, whereas lanthanides are largely non-radioactive.
- Oxidation States: Actinides generally exhibit a wider range of oxidation states than lanthanides.
- Reactivity: Actinides are generally more reactive than lanthanides.
- Applications: Actinides find primary applications in nuclear technology and energy production, whereas lanthanides are used in various technological applications like magnets, catalysts, and lighting.
These differences arise from the relative energies of the f-orbitals and their interaction with other orbitals. The 5f orbitals in actinides are more diffuse and less shielded from the nucleus than the 4f orbitals in lanthanides. This leads to greater participation of 5f electrons in chemical bonding.
Applications of Actinides: A Glimpse into Their Significance
The unique properties of actinides, primarily driven by their 5f electron configuration, lead to several critical applications:
- Nuclear Fuel: Elements like uranium and plutonium are essential components in nuclear reactors for generating electricity. Their ability to undergo nuclear fission releases vast amounts of energy.
- Nuclear Weapons: Unfortunately, some actinides are also used in the production of nuclear weapons, highlighting the dual-use nature of these elements.
- Radioactive Tracers: Certain actinides are utilized as radioactive tracers in various scientific research, including medical imaging and environmental monitoring.
- Radiation Therapy: Specific actinides and their decay products find applications in cancer radiation therapy.
The potential benefits and risks associated with actinides underscore the importance of understanding their properties and handling them responsibly.
Conclusion: The 5f Subshell and Beyond
In conclusion, the actinide series is definitively represented by the 5f subshell. The filling of this subshell is the defining characteristic of these elements, dictating their unique chemical and physical properties. From their variable oxidation states and complex coordination chemistry to their role in nuclear technology, the 5f electrons are fundamental to understanding the actinides' behavior and applications. Further research continues to unveil the intricacies of these fascinating elements, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge in chemistry, physics, and nuclear science. Understanding the 5f subshell is crucial for further advancements in these fields, bringing us closer to responsible and innovative applications of these powerful elements while mitigating the associated risks. The complexity of the actinides, particularly the relativistic effects influencing their electronic structure, demands continuous investigation to fully exploit their potential and manage their inherent challenges.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Derivative Of Ln 1 X 2
Mar 14, 2025
-
A Square Is A Rectangle
Mar 14, 2025
-
Does A Trapezoid Have Right Angles
Mar 14, 2025
-
Calculate The Product Of 8 15 6 5 And 1 3
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is 45 In A Fraction
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Subshell Is Represented By The Actinides Series . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
