Which Electromagnetic Has The Longest Wavelength
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
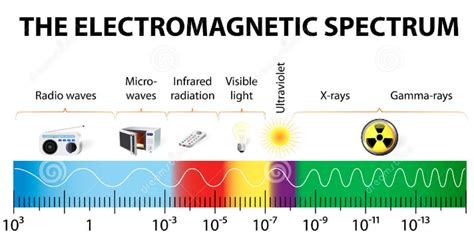
Table of Contents
Which Electromagnetic Wave Has the Longest Wavelength?
Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum is crucial in various fields, from astronomy and telecommunications to medical imaging and material science. This vast spectrum encompasses a range of waves, each characterized by its unique wavelength and frequency. But which electromagnetic wave boasts the longest wavelength? The answer, simply put, is radio waves. This article delves into the specifics of radio waves, comparing them to other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum and exploring their diverse applications.
Understanding the Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is a continuous distribution of electromagnetic radiation, arranged in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength. This spectrum includes, from longest wavelength to shortest:
- Radio waves: These waves possess the longest wavelengths, ranging from millimeters to kilometers.
- Microwaves: Shorter than radio waves, microwaves are used in various applications, including cooking and communication.
- Infrared radiation: Infrared waves are felt as heat and are used in thermal imaging and remote controls.
- Visible light: This is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that our eyes can detect, encompassing the colors of the rainbow.
- Ultraviolet radiation: UV radiation is invisible to the human eye and can cause sunburn.
- X-rays: X-rays have even shorter wavelengths and are used in medical imaging.
- Gamma rays: These waves possess the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies, making them extremely energetic and potentially harmful.
Radio Waves: The Champions of Wavelength
Radio waves, as previously stated, hold the title of having the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum. Their wavelengths can stretch from just a few millimeters to several kilometers. This vast range allows for a wide variety of applications, catering to different communication needs and scientific explorations.
The Range of Radio Wave Wavelengths: A Closer Look
The sheer range of radio wave wavelengths is a key factor in their versatility. Different portions of the radio wave spectrum are assigned to specific uses due to their differing propagation characteristics. For example:
-
Extremely Low Frequency (ELF): These waves have wavelengths exceeding 100 kilometers and are used in communication with submarines. Their ability to penetrate water makes them ideal for underwater communication despite their low frequency and energy.
-
Super Low Frequency (SLF): With wavelengths ranging from 10 to 100 kilometers, SLF waves also find applications in submarine communication and other long-range communication systems.
-
Ultra Low Frequency (ULF): Wavelengths extend from 1 to 10 kilometers. ULF waves are used in studies of the Earth's magnetic field and for detecting lightning strikes across vast distances.
-
Very Low Frequency (VLF): Wavelengths range from 100 meters to 10 kilometers. VLF radio waves are used in navigation systems and long-range communications, including some military applications.
-
Low Frequency (LF): With wavelengths between 1 and 10 kilometers, LF radio waves are used in maritime navigation systems and long-range broadcasting.
-
Medium Frequency (MF): Wavelengths range from 100 meters to 1 kilometer. MF waves are commonly used in AM radio broadcasting.
-
High Frequency (HF): These waves have wavelengths between 10 meters and 100 meters. HF radio waves are known for their ability to reflect off the ionosphere, allowing for long-distance communication beyond the horizon, often used in shortwave radio.
-
Very High Frequency (VHF): Wavelengths range from 1 to 10 meters. VHF is used in FM radio broadcasting, television broadcasting, and some two-way radio communications.
-
Ultra High Frequency (UHF): These waves have wavelengths between 10 centimeters and 1 meter. UHF is widely used in television broadcasting, cellular communications, and satellite communications.
-
Super High Frequency (SHF): Wavelengths range from 1 millimeter to 10 centimeters. SHF waves are used in radar systems, satellite communications, and microwave ovens.
-
Extremely High Frequency (EHF): These waves have the shortest wavelengths within the radio spectrum, typically ranging from 1 millimeter to 10 millimeters. EHF is used in some specialized radar systems and high-speed data transmission.
The Significance of Wavelength in Radio Wave Applications
The wavelength of a radio wave directly impacts its propagation characteristics, influencing its ability to travel long distances, penetrate obstacles, and undergo diffraction. Longer wavelengths, like those found in ELF and VLF waves, are better at penetrating obstacles such as seawater and the Earth's crust. Shorter wavelengths, on the other hand, are more easily absorbed by atmospheric gases. This explains why different frequencies are chosen for different purposes.
Comparison with Other Electromagnetic Waves
To solidify the understanding of why radio waves have the longest wavelengths, let's briefly compare them to other parts of the electromagnetic spectrum:
-
Microwaves: Although they have shorter wavelengths than radio waves, microwaves still share some similarities in their applications, especially in communication. However, their shorter wavelengths limit their ability to penetrate obstacles as effectively as radio waves.
-
Infrared, Visible Light, Ultraviolet, X-rays, and Gamma rays: These forms of electromagnetic radiation have significantly shorter wavelengths than radio waves. Their higher frequencies correspond to higher energy levels, making them suitable for different applications, but they are less effective for long-range communication.
Applications of Radio Waves: A Diverse Landscape
The diverse applications of radio waves highlight their importance in modern society. Here are some prominent examples:
-
Broadcasting: Radio waves are fundamental to radio and television broadcasting, enabling transmission of audio and visual information over long distances.
-
Navigation: Various navigation systems, including GPS and maritime navigation, rely heavily on radio wave technology.
-
Communication: From cell phones to satellite communication, radio waves are the backbone of our global communication infrastructure.
-
Astronomy: Radio astronomy utilizes radio telescopes to detect radio waves emitted by celestial objects, providing invaluable insights into the universe.
-
Medical Imaging: While not as prominent as X-rays or MRI, some radio wave-based medical imaging techniques exist, although their applications are more limited.
-
Remote Sensing: Radio waves are used in remote sensing applications to gather information about the Earth's surface from a distance, for example in weather forecasting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, radio waves definitively hold the title for the longest wavelength in the electromagnetic spectrum. Their extensive wavelength range, from millimeters to kilometers, allows for a vast array of applications that are crucial to modern technology and scientific exploration. Understanding the properties and applications of radio waves, along with the entire electromagnetic spectrum, is essential for comprehending the vastness and interconnectedness of our physical world. The unique characteristics of radio waves—their ability to penetrate various media and travel great distances—make them indispensable tools in numerous fields, underscoring their importance in our technological advancement and scientific understanding of the universe. The remarkable versatility of radio waves is a testament to the power of electromagnetic radiation and its profound influence on our lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
12 Is What Percent Of 200
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is A Kit And Kaboodle
Mar 26, 2025
-
Weight Of 1 Cubic Meter Water
Mar 26, 2025
-
How To Find A One Sided Limit
Mar 26, 2025
-
Convert 4 1 2 To A Decimal
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Electromagnetic Has The Longest Wavelength . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
