Where Do Decomposers Go On A Food Web
listenit
Mar 27, 2025 · 6 min read
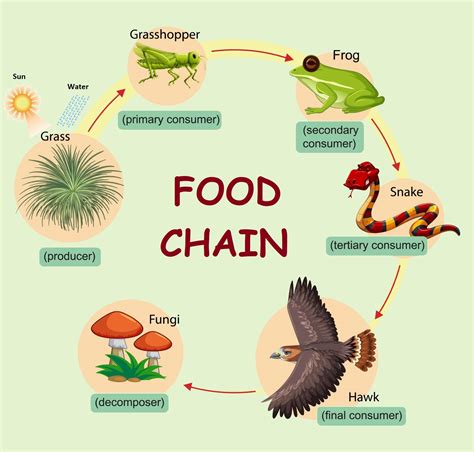
Table of Contents
Where Do Decomposers Go on a Food Web? Understanding Their Crucial Role
Decomposers, those unsung heroes of the ecosystem, play a vital role in the intricate dance of life known as the food web. Unlike producers and consumers that directly participate in the linear flow of energy, decomposers operate in a crucial, often overlooked, cycle of nutrient recycling. But where exactly do they fit into the visual representation of this complex system – the food web? The answer is: everywhere. They’re not neatly placed in a specific box, but rather interwoven throughout, connecting all levels and completing the circle of life.
The Food Web: A Network of Interdependencies
Before delving into the role of decomposers, let's briefly review the structure of a food web. It's a complex network illustrating the feeding relationships between different organisms in an ecosystem. At its base are the producers, primarily plants and algae, which convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. These producers form the foundation of the food web, providing energy for all other organisms.
Next come the consumers, which are categorized into different levels:
- Primary Consumers (Herbivores): These animals feed directly on producers. Examples include rabbits, deer, and grasshoppers.
- Secondary Consumers (Carnivores): These animals prey on primary consumers. Examples include foxes, snakes, and owls.
- Tertiary Consumers (Apex Predators): These are top predators, often at the highest trophic level, with few or no natural predators. Examples include lions, wolves, and sharks.
This linear progression, from producers to top consumers, is a simplification. In reality, food webs are far more complex, with organisms often occupying multiple trophic levels. A fox, for example, might eat rabbits (primary consumers) and mice (secondary consumers), making it both a secondary and tertiary consumer. This complexity is further amplified by the omnivores, which consume both plants and animals.
Decomposers: The Recyclers of Life
This is where decomposers enter the picture. They are the unsung heroes, the cleanup crew, and the essential recyclers of the ecosystem. Unlike producers and consumers that participate in the linear transfer of energy, decomposers break down organic matter, recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem, making them available for producers. This process is essential for the continued functioning of the food web. Without decomposers, nutrients would remain locked within dead organisms, eventually leading to a depletion of resources and ecosystem collapse.
What exactly do decomposers do? They break down complex organic compounds – like proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids – into simpler inorganic substances, including carbon dioxide, water, and mineral nutrients. This process, known as decomposition, releases these nutrients back into the soil, water, and air, making them available for uptake by producers. This completes the nutrient cycle, ensuring the continuous flow of energy and nutrients within the ecosystem.
Types of Decomposers and Their Roles
Several different types of organisms play crucial roles in decomposition:
1. Bacteria: The Microscopic Powerhouses
Bacteria are among the most important decomposers, particularly in breaking down organic matter in soil and water. They are incredibly diverse, with different species specialized in breaking down specific types of organic compounds. Some bacteria are aerobic, requiring oxygen for respiration, while others are anaerobic, thriving in oxygen-deficient environments. This diversity allows them to efficiently decompose a wide range of organic materials.
2. Fungi: Masters of Decomposition
Fungi are also crucial decomposers, particularly in terrestrial environments. Their extensive network of hyphae (thread-like structures) allows them to penetrate and break down large amounts of organic matter, including wood, leaves, and other plant material. Fungi secrete enzymes that break down complex organic molecules, making them accessible for absorption. Mycorrhizal fungi, which form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, also play a critical role in nutrient cycling, facilitating the uptake of nutrients by plants.
3. Detritivores: The Scavengers
Detritivores, unlike bacteria and fungi that directly decompose organic matter, consume dead organic matter and waste products, accelerating the decomposition process. Detritivores play a crucial role in fragmenting organic materials, making them more accessible to bacteria and fungi. Examples of detritivores include earthworms, millipedes, woodlice, and dung beetles. These organisms physically break down large organic particles into smaller pieces, increasing the surface area available for bacterial and fungal decomposition.
4. Other Decomposers
Various other organisms contribute to decomposition, albeit to a lesser extent than bacteria, fungi, and detritivores. This includes some protists, insects, and even some vertebrates like vultures and hyenas. These organisms play a complementary role, speeding up the breakdown of organic matter and aiding in the recycling of nutrients.
Decomposers' Place in the Food Web: A Holistic Perspective
Understanding where decomposers fit in the food web requires moving beyond a simple linear representation. They are not at a specific trophic level but rather operate on a different plane. They are not consumers, as they don't directly ingest other organisms for energy. Instead, they obtain energy by breaking down organic matter. Their role is not to directly compete for energy, but to recycle it.
Think of the food web as a circle, not a straight line. Producers capture energy from the sun, consumers utilize this energy through consumption, and finally, decomposers return nutrients to the environment, closing the loop and making resources available for producers again. Decomposers are part of all trophic levels, acting as a bridge between all links in the food chain. Every dead organism, every fallen leaf, every waste product, provides the decomposers with the resources they need.
The Importance of Decomposers in Ecosystem Health
The role of decomposers is crucial for maintaining ecosystem health and stability. Their efficient breakdown of organic matter is essential for:
- Nutrient Cycling: Decomposers release essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium back into the soil, making them available for plants. This nutrient cycling is essential for plant growth and the overall productivity of the ecosystem.
- Soil Formation: The decomposition of organic matter contributes to soil formation and improves soil structure. The organic matter produced by decomposers improves soil water retention and aeration.
- Waste Management: Decomposers break down waste products, preventing the accumulation of organic waste, which can negatively impact ecosystem health.
- Disease Prevention: Efficient decomposition can help to control the spread of disease by quickly breaking down dead organisms and waste products.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Decomposers
Decomposers are not simply at one place on the food web; they are integral to its functionality. They are essential players in the cyclical nature of energy flow and nutrient cycling, connecting all levels of the food web. They ensure that nutrients are constantly recycled, supporting the growth of producers and, ultimately, the entire ecosystem. Without these unsung heroes, life as we know it would cease to exist. Their presence is not confined to one trophic level but rather permeates the entire web, underscoring their irreplaceable role in the delicate balance of nature. Their continuous work ensures the sustainability and productivity of ecosystems worldwide. They are the silent keepers of the cycle, ensuring the continuity of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does Mass Affect The Period Of A Pendulum
Mar 30, 2025
-
Abiotic Factors In The Temperate Grassland
Mar 30, 2025
-
Are Frequency And Wavelength Directly Proportional
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is The Fraction For 40
Mar 30, 2025
-
What Is 8 Divided By 7
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Where Do Decomposers Go On A Food Web . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
