What Type Of Bond Holds Water Molecules Together
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
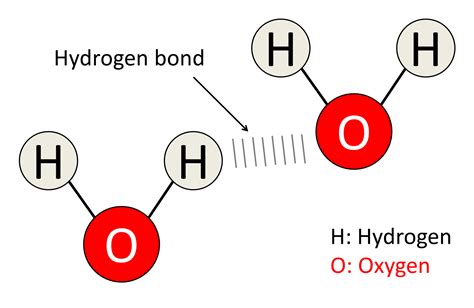
Table of Contents
What Type of Bond Holds Water Molecules Together? A Deep Dive into Hydrogen Bonding
Water. It's the elixir of life, the ubiquitous solvent, and the very foundation of our planet's ecosystems. But what makes this seemingly simple molecule so unique and crucial to life as we know it? The answer lies in the type of bond that holds water molecules together: hydrogen bonds. This article will delve deep into the nature of hydrogen bonding in water, exploring its properties, implications, and significance in various scientific fields.
Understanding the Water Molecule: H₂O
Before we dive into hydrogen bonding, let's refresh our understanding of the water molecule itself. Water (H₂O) consists of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to two hydrogen atoms. This covalent bond involves the sharing of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms. However, oxygen is significantly more electronegative than hydrogen. This means oxygen attracts the shared electrons more strongly, creating a polar molecule.
Electronegativity and Polarity: The Key to Hydrogen Bonding
Oxygen's higher electronegativity results in an uneven distribution of charge within the water molecule. The oxygen atom carries a partial negative charge (δ-), while each hydrogen atom carries a partial positive charge (δ+). This polarity is crucial because it allows for the formation of hydrogen bonds between water molecules.
Hydrogen Bonds: The Special Interaction
A hydrogen bond is a special type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs between a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (like oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) and another electronegative atom in a different molecule. In water, the partially positive hydrogen atom of one water molecule is attracted to the partially negative oxygen atom of another water molecule.
Strength of Hydrogen Bonds: A Delicate Balance
It's important to distinguish between hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds. Hydrogen bonds are significantly weaker than covalent bonds. However, their collective strength is substantial, especially in water where numerous hydrogen bonds exist simultaneously. This network of hydrogen bonds is responsible for many of water's unique properties.
Unique Properties of Water Attributed to Hydrogen Bonding
The network of hydrogen bonds in water gives rise to a plethora of unusual properties that are essential for life:
1. High Surface Tension: A Resilient Surface
Water's high surface tension is a direct consequence of the strong cohesive forces between water molecules due to hydrogen bonding. These forces create a "skin" on the water's surface, allowing certain insects to walk on water.
2. High Boiling Point: A Stable Liquid
Water has an unusually high boiling point compared to other similar-sized molecules. This is because a considerable amount of energy is required to break the numerous hydrogen bonds holding the water molecules together before they can transition to the gaseous phase.
3. High Specific Heat Capacity: Temperature Regulation
Water's high specific heat capacity means it can absorb a large amount of heat energy with a relatively small temperature change. This property is vital for regulating temperature in organisms and in the environment. Large bodies of water act as temperature buffers, moderating climate fluctuations.
4. High Heat of Vaporization: Evaporative Cooling
Water's high heat of vaporization means it requires a significant amount of energy to change from a liquid to a gas. This is why sweating is an effective cooling mechanism: the evaporation of sweat absorbs a considerable amount of heat from the body.
5. Density Anomaly: Ice Floats
Unlike most substances, ice is less dense than liquid water. This is because the hydrogen bonds in ice form a rigid, open crystalline structure, creating more space between the molecules. This unique property ensures that ice floats, insulating aquatic life during winter.
6. Excellent Solvent: The Universal Solvent
Water's polarity and ability to form hydrogen bonds make it an excellent solvent for many ionic and polar substances. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of compounds is crucial for biological processes, as it facilitates the transport of nutrients and the removal of waste products.
The Role of Hydrogen Bonding in Biological Systems
The significance of hydrogen bonding extends far beyond the properties of pure water. Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in a vast array of biological processes and structures:
1. Protein Structure: The Foundation of Life's Machinery
Hydrogen bonds are essential for maintaining the three-dimensional structures of proteins. These bonds stabilize the secondary structures (alpha-helices and beta-sheets) and contribute to the overall tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins. The disruption of hydrogen bonds can lead to protein denaturation, affecting their function.
2. DNA Structure: The Blueprint of Life
The double helix structure of DNA is stabilized by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs (adenine with thymine, and guanine with cytosine). These bonds are crucial for the accurate replication and transcription of genetic information.
3. Enzyme-Substrate Interactions: Catalysis and Regulation
Hydrogen bonds are involved in the binding of substrates to enzymes, facilitating enzymatic reactions. These interactions are often crucial for regulating enzyme activity.
4. Cell Membranes: Structure and Function
Hydrogen bonds contribute to the stability and fluidity of cell membranes. They are involved in the interactions between lipid molecules and membrane proteins.
5. Water's Role in Cellular Processes: Transport and Reaction Medium
Water acts as a solvent and transport medium within cells, facilitating various biochemical reactions. Its ability to form hydrogen bonds allows it to interact with many biomolecules, playing a crucial role in cellular processes.
Hydrogen Bonding Beyond Biology: Applications in Materials Science
The importance of hydrogen bonding is not confined to biological systems. It plays a significant role in various materials science applications:
1. Polymer Science: Controlling Material Properties
Hydrogen bonds influence the properties of many polymers, affecting their strength, flexibility, and solubility. The presence and strength of hydrogen bonds can be manipulated to tailor the properties of polymeric materials for specific applications.
2. Crystal Engineering: Designing Functional Materials
Hydrogen bonds are utilized in crystal engineering to design and synthesize crystalline materials with specific properties and functionalities. The precise control of hydrogen bonding networks allows for the creation of materials with tailored optical, electronic, and magnetic properties.
3. Drug Design: Targeting Specific Interactions
Hydrogen bonds play a vital role in drug design. Understanding the hydrogen bonding interactions between drugs and their target biomolecules is crucial for developing effective pharmaceuticals. The design of drugs often involves optimizing hydrogen bonding interactions to enhance their affinity and selectivity for specific targets.
Conclusion: The Profound Impact of a Weak Bond
While individually weak, the collective strength of hydrogen bonds in water is remarkable, underpinning many of its unique and essential properties. From the stability of biological macromolecules to the regulation of Earth's climate, hydrogen bonding's impact is profound and far-reaching. Its influence extends across multiple scientific disciplines, highlighting its importance in understanding the natural world and developing new technologies. The seemingly simple water molecule, held together by these relatively weak yet powerful bonds, is a testament to the intricate beauty and elegant design of the universe. Further research into hydrogen bonding will undoubtedly continue to unveil its diverse roles and potential applications in various fields, enhancing our understanding of the world around us and paving the way for innovative advancements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Much Is 1 4 Lb
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Quarts In 40 Gallons
Mar 20, 2025
-
How Many Atoms Are In Carbon
Mar 20, 2025
-
In Which Organelle Does Photosynthesis Take Place
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Percentage Of 55 Is 34
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Type Of Bond Holds Water Molecules Together . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
