What The Square Root Of 15
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
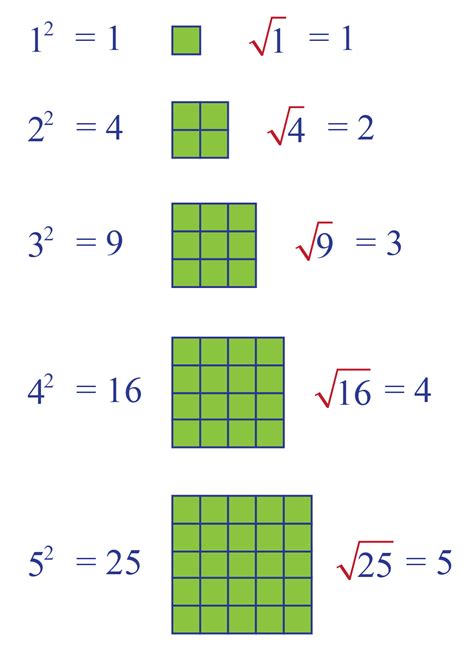
Table of Contents
What is the Square Root of 15? A Deep Dive into Irrational Numbers
The square root of 15, denoted as √15, is a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 15. While it might seem simple at first glance, exploring this seemingly straightforward mathematical concept opens doors to a fascinating world of irrational numbers, approximation techniques, and their applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of √15, providing you with a solid understanding of its nature, calculation methods, and real-world significance.
Understanding the Square Root
Before we delve into the specifics of √15, let's establish a foundational understanding of square roots. A square root of a number x is a value that, when multiplied by itself, results in x. For example, the square root of 9 (√9) is 3 because 3 * 3 = 9. Square roots are the inverse operation of squaring a number.
Key Characteristics of Square Roots:
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: a positive and a negative. For instance, √9 = ±3 (positive 3 and negative 3). However, when we talk about the principal square root (often denoted simply as √x), we refer to the positive root.
- Square Roots of Perfect Squares: Numbers that are perfect squares (e.g., 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, etc.) have whole number square roots.
- Square Roots of Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers that are not perfect squares have square roots that are irrational numbers—numbers that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. This is where √15 falls.
The Irrational Nature of √15
The square root of 15 is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction (a ratio of two integers). Its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating, extending infinitely without a predictable pattern. This is a fundamental property that distinguishes it from rational numbers like 1/2 or 3/4.
Proof of Irrationality:
While a rigorous mathematical proof requires techniques beyond the scope of this introductory article, we can intuitively understand the irrationality of √15 by considering its prime factorization. 15 = 3 x 5. Since the prime factors 3 and 5 appear only once, their square roots cannot be simplified to a rational number. This lack of perfect square factors results in an irrational square root.
Approximating √15
Since we cannot express √15 as a simple fraction or a terminating decimal, we rely on approximation methods to obtain its numerical value. Several techniques can be used, including:
1. Using a Calculator: The simplest approach is to use a calculator. Most scientific calculators will provide a decimal approximation of √15, typically accurate to several decimal places (around 3.87298).
2. Linear Approximation: This method uses the concept of linear functions to estimate the square root. We can find two perfect squares that bound 15: 16 (4²) and 9 (3²). Since 15 is closer to 16, we might approximate √15 as slightly less than 4. This gives a rough estimation but lacks precision.
3. Babylonian Method (Heron's Method): This iterative method provides increasingly accurate approximations with each iteration. It involves the following steps:
- Start with an initial guess: Let's start with 4 as our initial guess.
- Iterative formula: The next approximation is calculated using the formula:
x_(n+1) = 0.5 * (x_n + 15/x_n)wherex_nis the current approximation andx_(n+1)is the next approximation. - Repeat: Repeat this process until the desired level of accuracy is achieved.
Let's perform a few iterations:
- Iteration 1: x₁ = 0.5 * (4 + 15/4) = 3.875
- Iteration 2: x₂ = 0.5 * (3.875 + 15/3.875) ≈ 3.87298
- Iteration 3: Further iterations will yield even more precise approximations.
4. Taylor Series Expansion: For higher precision, advanced mathematical techniques like Taylor series expansion can be used. This method involves representing the square root function as an infinite sum of terms, allowing for arbitrarily accurate approximations. However, this method is computationally more intensive.
Applications of √15
While √15 might seem like an abstract mathematical concept, it finds practical applications in various fields:
1. Geometry: In geometry, √15 can represent the length of a diagonal in a rectangle or the length of a side in a triangle, depending on the given dimensions. For example, if a rectangle has sides of length 3 and 5, then the length of its diagonal would be √(3² + 5²) = √34, which although different from √15 demonstrates the principle.
2. Physics: Square roots frequently appear in physics formulas related to motion, energy, and other phenomena. Situations involving vector calculations, especially those dealing with right-angled triangles, might necessitate the use of √15 or similar irrational numbers.
3. Engineering: Similar to physics, engineering calculations often require the use of square roots to solve problems related to mechanics, electricity, and other fields. Applications can range from structural analysis to circuit design.
4. Computer Graphics: In computer graphics, calculations involving distances and scaling often involve square roots. Rendering 3D models and creating realistic simulations require precise calculations of distances and positions, which use √15-like irrational numbers.
5. Statistics and Probability: Standard deviation calculations, used to measure the dispersion of data, often involve square roots. The square root of the variance is the standard deviation, a crucial metric in statistical analysis.
Conclusion: The Significance of √15 and Irrational Numbers
The square root of 15, despite its seemingly simple definition, represents a fundamental concept in mathematics. Its irrational nature highlights the rich complexity of the number system. Understanding its properties and approximation methods is crucial for anyone working in fields where mathematical precision is paramount. While we cannot express √15 exactly as a fraction or terminating decimal, we can obtain highly accurate approximations using various techniques, enabling us to apply this irrational number in diverse practical applications across various scientific and technological disciplines. The exploration of √15 serves as a gateway to a deeper appreciation of irrational numbers and their integral role in mathematics and the physical world. Furthermore, the diverse approximation methods provide a testament to the power and elegance of mathematical tools used to solve real-world problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
25 Out Of 31 As A Percentage
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Do Pulleys Make Work Easier
Mar 25, 2025
-
Which Has The Largest Atomic Radius
Mar 25, 2025
-
Why Do Noble Gasses Not Have Electronegativity Values
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Chambers Does The Frog Heart Have
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What The Square Root Of 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
