What Percent Of 50 Is 3
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 4 min read
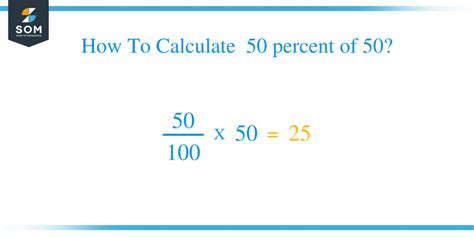
Table of Contents
What Percent of 50 is 3? A Comprehensive Guide to Percentage Calculations
Understanding percentages is a fundamental skill applicable across numerous fields, from everyday budgeting and shopping to complex scientific calculations and financial analysis. This article delves deep into the seemingly simple question: "What percent of 50 is 3?" We'll not only solve this specific problem but also equip you with the tools and understanding to tackle any percentage calculation with confidence.
Understanding Percentages: The Basics
Before we tackle the specific problem, let's establish a firm understanding of what percentages represent. A percentage is simply a fraction expressed as a number out of 100. The symbol "%" represents "per hundred" or "out of 100." For instance, 50% means 50 out of 100, which is equivalent to the fraction 50/100 or the decimal 0.5.
Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial for solving percentage problems. We often encounter percentages in various contexts:
- Discounts: A 20% discount on a $100 item.
- Taxes: A 6% sales tax on a purchase.
- Interest Rates: A 5% interest rate on a loan.
- Statistics: The percentage of people who prefer a certain product.
- Data Analysis: Percentage change in stock prices or sales figures.
Solving "What Percent of 50 is 3?"
Now, let's address the central question: What percent of 50 is 3? We can solve this using several methods:
Method 1: Using Proportions
This method involves setting up a proportion, where we equate two ratios:
- Ratio 1: The given percentage (x) over 100 (representing the whole).
- Ratio 2: The part (3) over the whole (50).
The proportion looks like this:
x/100 = 3/50
To solve for x, we cross-multiply:
50x = 300
Then, we divide both sides by 50:
x = 300/50 = 6
Therefore, 3 is 6% of 50.
Method 2: Using the Formula
We can also solve this using a formula:
(Part / Whole) * 100 = Percentage
In this case:
(3 / 50) * 100 = 6%
This formula directly calculates the percentage by dividing the part by the whole and then multiplying by 100.
Method 3: Decimal Conversion
Another approach involves converting the fraction 3/50 into a decimal and then multiplying by 100 to get the percentage:
3/50 = 0.06
0.06 * 100 = 6%
This method emphasizes the relationship between fractions, decimals, and percentages.
Expanding Your Percentage Calculation Skills
Understanding the fundamental methods above allows you to solve a wide range of percentage problems. Let's explore some variations and related concepts:
Finding the Part
If you know the percentage and the whole, you can find the part. For example:
"What is 25% of 80?"
Using the formula:
(25/100) * 80 = 20
Therefore, 25% of 80 is 20.
Finding the Whole
If you know the percentage and the part, you can find the whole. For instance:
"15 is 30% of what number?"
Let's use 'x' to represent the unknown whole:
15 = (30/100) * x
Solving for x:
x = (15 * 100) / 30 = 50
Therefore, 15 is 30% of 50.
Percentage Increase and Decrease
Calculating percentage increase or decrease is also a common application. The formula for percentage increase is:
[(New Value - Old Value) / Old Value] * 100
The formula for percentage decrease is:
[(Old Value - New Value) / Old Value] * 100
For example, if a price increases from $50 to $60:
Percentage increase = [(60 - 50) / 50] * 100 = 20%
Real-World Applications: Examples
Let's explore some practical applications to solidify your understanding:
-
Shopping Discounts: A store offers a 15% discount on a $75 item. The discount amount is (15/100) * $75 = $11.25. The final price is $75 - $11.25 = $63.75.
-
Sales Tax: A 6% sales tax is added to a $100 purchase. The tax amount is (6/100) * $100 = $6. The total cost is $100 + $6 = $106.
-
Investment Returns: An investment grows from $1,000 to $1,200. The percentage increase is [(1200 - 1000) / 1000] * 100 = 20%.
-
Grade Calculation: A student scores 27 out of 30 on a test. Their percentage score is (27/30) * 100 = 90%.
Advanced Percentage Concepts: Compound Interest
Compound interest is a more complex application of percentages where interest is earned not only on the principal amount but also on accumulated interest. Understanding this concept is crucial for financial planning and investment strategies. The formula for compound interest is:
A = P (1 + r/n)^(nt)
Where:
- A = the future value of the investment/loan, including interest
- P = the principal investment amount (the initial deposit or loan amount)
- r = the annual interest rate (decimal)
- n = the number of times that interest is compounded per year
- t = the number of years the money is invested or borrowed for
Conclusion: Mastering Percentage Calculations
Mastering percentage calculations is essential for success in various aspects of life. From daily budgeting to complex financial analysis, a strong understanding of percentages is invaluable. By understanding the fundamental methods, formulas, and variations discussed in this article, you can confidently tackle any percentage problem and apply this knowledge to real-world situations. Remember to practice regularly, using diverse examples and problems to reinforce your understanding. This will not only improve your mathematical skills but also enhance your ability to analyze data and make informed decisions in various contexts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Is Bigger 2 3 Or 3 4
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Do Chemical Equations Need To Be Balanced
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Does The Cell Membrane Help Maintain Homeostasis
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are Columns Of The Periodic Table Called
Mar 19, 2025
-
X 4 X 2 3x 2
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Percent Of 50 Is 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
