What Is The Relationship Between The Diameter And The Circumference
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
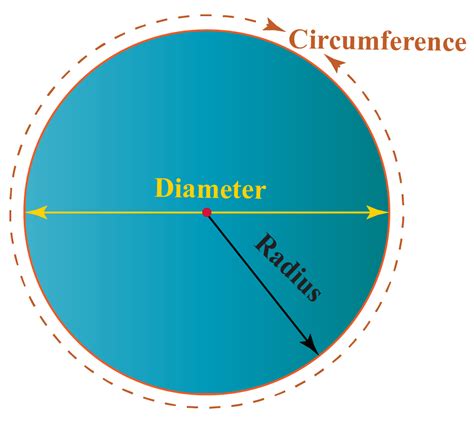
Table of Contents
The Enduring Relationship Between Diameter and Circumference: A Deep Dive
The relationship between a circle's diameter and its circumference is a fundamental concept in mathematics, geometry, and even physics. It's a cornerstone of understanding circles and their properties, and its implications reach far beyond the classroom. This article delves into this relationship, exploring its historical context, mathematical formulation, applications, and even some unexpected connections.
Understanding the Basics: Diameter and Circumference Defined
Before exploring the relationship, let's clearly define the key terms:
-
Diameter: The diameter of a circle is the straight line passing through the center of the circle and connecting two points on the circumference. It's the longest chord of a circle. Think of it as the widest part of the circle.
-
Circumference: The circumference of a circle is the distance around the circle. It's essentially the perimeter of the circle.
The Constant Connection: Pi (π)
The crucial link between a circle's diameter and circumference is the mathematical constant π (pi). Pi represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. This means:
Circumference / Diameter = π
This ratio holds true for any circle, regardless of its size. Whether you're dealing with a tiny button or a gigantic planet, the circumference divided by the diameter will always equal pi. This remarkable consistency makes pi one of the most important constants in mathematics.
The Value of Pi: An Irrational Number
The value of pi is approximately 3.14159, but it's important to understand that pi is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating. While we often use approximations like 3.14 or 22/7, these are just estimations. The true value of pi is infinitely precise, a fascinating fact that has captivated mathematicians for centuries.
Calculating Circumference: Using the Formula
The relationship between diameter and circumference allows us to calculate the circumference of a circle if we know its diameter (or vice-versa). The formula is derived directly from the definition of pi:
Circumference = π * Diameter
Or, if we know the radius (half the diameter), we can use:
Circumference = 2 * π * Radius
Historical Context: The Quest to Understand Pi
The understanding and calculation of pi has a rich history, stretching back thousands of years. Ancient civilizations, including the Babylonians and Egyptians, made surprisingly accurate estimations of pi, though their methods were often geometrical approximations. The Greek mathematician Archimedes made significant advancements by using polygons inscribed and circumscribed around a circle to refine the approximation of pi. Over the centuries, the quest to determine pi with increasing accuracy has driven mathematical innovation, leading to the development of new computational methods and algorithms.
Beyond the Formula: Applications of the Diameter-Circumference Relationship
The relationship between diameter and circumference is far more than a simple mathematical formula; it has far-reaching applications in numerous fields:
1. Engineering and Design:
-
Wheel Design: The diameter of a wheel directly determines its circumference, crucial for calculating distance traveled, gear ratios, and rotational speed in vehicles and machinery.
-
Pipe Sizing: In plumbing and engineering, pipe diameters are critical in determining flow rates and pressure. The circumference impacts the material needed and surface area for heat transfer.
-
Circular Structures: In architecture and construction, understanding the relationship between diameter and circumference is essential for designing and building circular structures like domes, towers, and stadiums.
2. Science and Physics:
-
Orbital Mechanics: The circumference of a planet's orbit, related to its diameter, is a key factor in calculating orbital periods and velocities.
-
Circular Motion: In physics, the circumference is essential for understanding angular velocity and centripetal force in circular motion.
-
Wave Phenomena: The wavelength of circular waves (like ripples in water) is directly related to their diameter.
3. Everyday Life:
-
Baking and Cooking: The diameter of a pie pan determines the circumference of the crust, influencing baking time and ingredient amounts.
-
Gardening and Landscaping: Calculating the circumference of circular flowerbeds or garden features helps determine the amount of materials needed for edging or planting.
-
Sports and Games: The diameter of a ball (basketball, soccer ball, etc.) affects its circumference, influencing its handling and trajectory.
Advanced Concepts: Exploring Beyond the Basics
While the basic formula is straightforward, there are more sophisticated aspects to explore:
1. Approximating Pi: Different Methods
Throughout history, mathematicians have employed various methods to approximate pi, including:
-
Infinite Series: These mathematical series provide increasingly accurate approximations of pi as more terms are added.
-
Monte Carlo Methods: These probabilistic methods use random sampling to estimate pi by simulating points within a circle inscribed within a square.
-
Continued Fractions: Representing pi as a continued fraction provides another way to approximate its value.
2. The Transcendence of Pi:
Pi is not only irrational; it's also transcendental. This means it's not the root of any polynomial equation with rational coefficients. This property has profound implications in various mathematical fields.
3. Pi in Higher Dimensions:
The concept of pi extends beyond two-dimensional circles. In higher dimensions, analogous constants exist, representing the ratio of a hypersphere's surface area or volume to its diameter.
Conclusion: The Ever-Present Pi
The relationship between a circle's diameter and circumference, embodied by the constant pi, is a fundamental concept with far-reaching implications. From ancient mathematical explorations to modern engineering marvels, the understanding of this relationship underpins a vast array of fields. Its seemingly simple formula belies a deep mathematical richness, with ongoing explorations and discoveries continuing to reveal the multifaceted nature of this remarkable constant. The enduring legacy of pi is a testament to the beauty and power of mathematical principles. It serves as a reminder that even the most fundamental concepts can hold surprising depth and profound applications across diverse disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does Australia Use Fahrenheit Or Celsius
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are The Rows On The Periodic Table Called
Mar 16, 2025
-
Words That Start With The Same Letter
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Derivative Of 3 X
Mar 16, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple For 4 And 7
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Relationship Between The Diameter And The Circumference . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
