What Is The Relationship Between The Diameter And Circumference
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
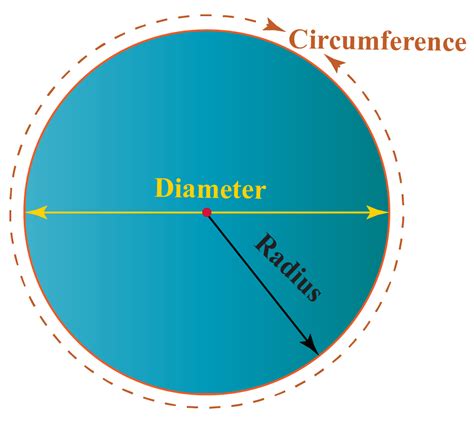
Table of Contents
The Enduring Relationship Between Diameter and Circumference: A Deep Dive
The relationship between a circle's diameter and its circumference is one of the most fundamental concepts in mathematics and geometry. It forms the basis for understanding many aspects of circles, spheres, and even more complex geometrical shapes. This article explores this relationship in detail, delving into its history, mathematical formulation, applications, and its significance in various fields.
Understanding the Basics: Diameter and Circumference
Before we delve into the intricate relationship, let's define our key terms:
-
Diameter: The diameter of a circle is a straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It's essentially the longest chord of the circle. We often represent the diameter using the symbol 'd'.
-
Circumference: The circumference of a circle is the linear distance around the circle. It's the perimeter of the circle. We typically denote the circumference using the symbol 'C'.
The Constant of Pi (π): The Heart of the Relationship
The fundamental relationship between the diameter and circumference lies in the mathematical constant Pi (π). Pi represents the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter. This ratio is constant for all circles, regardless of their size. Mathematically, this is expressed as:
C = πd
or, equivalently, since the radius (r) is half the diameter (d = 2r):
C = 2πr
This seemingly simple equation encapsulates a profound mathematical truth: the circumference is always a fixed multiple of the diameter, that multiple being Pi.
The History of Pi: A Journey Through Time
The understanding and calculation of Pi has captivated mathematicians for millennia. Evidence suggests that ancient civilizations, including the Babylonians and Egyptians, had approximations of Pi. The Rhind Papyrus, an ancient Egyptian mathematical text, contains a calculation that yields a value of approximately 3.16 for Pi.
The Greek mathematician Archimedes (c. 287 – c. 212 BC) made a significant contribution by using the method of exhaustion to approximate Pi. He inscribed and circumscribed regular polygons around a circle, systematically increasing the number of sides to refine the approximation. His method yielded a value of Pi between 3.1408 and 3.1429.
Over the centuries, mathematicians continued to refine the calculation of Pi, using increasingly sophisticated techniques. The invention of calculus and infinite series led to even more accurate estimations. Today, Pi has been calculated to trillions of digits, though only a relatively small number of digits are needed for most practical applications.
Applications of the Diameter-Circumference Relationship
The relationship between diameter and circumference is not merely a theoretical concept; it finds extensive practical applications in diverse fields:
1. Engineering and Design:
- Wheel Design: In designing wheels for vehicles, the diameter determines the circumference, which is crucial for calculating speed, gear ratios, and tire rotation.
- Circular Structures: The construction of circular structures like bridges, tunnels, and stadiums relies heavily on understanding the relationship between diameter and circumference for accurate measurements and material estimations.
- Machining and Manufacturing: In manufacturing processes, precise calculations of circumference are essential for creating circular components of specific sizes.
2. Surveying and Mapping:
- Land Measurement: Surveyors use the diameter-circumference relationship to determine the area of circular land parcels or to calculate distances based on the curvature of the Earth.
- Cartography: Mapping accurately involves understanding the relationship between distances on a map and the corresponding actual distances on the ground, often involving circular projections.
3. Physics and Astronomy:
- Orbital Mechanics: Calculating the orbital paths of celestial bodies often involves using the circumference of their orbits, which is directly related to their orbital diameter.
- Circular Motion: In physics, understanding the circumference is crucial for analyzing the motion of objects moving in circular paths.
4. Everyday Life:
- Baking: The diameter of a cake pan determines the circumference, which affects baking time and the overall shape of the cake.
- Gardening: The diameter of a circular garden bed helps determine the amount of fencing or edging required.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
The relationship between diameter and circumference opens the door to understanding more advanced concepts:
1. Area of a Circle:
The area (A) of a circle is given by the formula:
A = πr²
Notice the presence of Pi again. The area is directly related to the square of the radius, and therefore indirectly related to the diameter.
2. Circumference of an Ellipse:
While the relationship between diameter and circumference is straightforward for circles, it becomes more complex for ellipses. The circumference of an ellipse doesn't have a simple closed-form expression, requiring the use of elliptic integrals or approximation techniques.
3. Higher Dimensions:
The concept extends to higher dimensions. For instance, the circumference of a circle is analogous to the surface area of a sphere, and the diameter is analogous to the sphere's diameter.
Approximations of Pi: Accuracy and Practicality
While the exact value of Pi is an irrational number with infinitely many decimal places, for most practical purposes, approximations are sufficient. Common approximations include:
- 3.14: A simple and widely used approximation.
- 22/7: A rational approximation, offering a reasonable level of accuracy.
- 355/113: A more accurate rational approximation.
The choice of approximation depends on the required level of accuracy for the specific application. For most everyday calculations, 3.14 is more than adequate. However, for highly precise engineering or scientific applications, more accurate approximations are necessary.
Conclusion: The Universal Significance of Pi and the Diameter-Circumference Relationship
The relationship between the diameter and circumference of a circle, governed by the constant Pi, is a cornerstone of mathematics and geometry. Its importance extends far beyond theoretical concepts, finding practical applications in numerous fields. From engineering marvels to everyday tasks, the understanding of this fundamental relationship is essential for solving problems and developing innovative solutions across a wide spectrum of disciplines. The continuing exploration of Pi and its properties reflects the enduring fascination and the profound significance of this mathematical constant in our understanding of the world around us. The simple equation C = πd encapsulates a powerful and ubiquitous truth about the nature of circles and their relationship to the universe itself. This timeless relationship continues to inspire mathematical exploration and holds immeasurable value in our technological and scientific advancements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Water A Good Leaving Group
Mar 17, 2025
-
480 Cm Equals How Many M
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 8 In Fraction Form
Mar 17, 2025
-
The Elbow Is Proximal To The Shoulder
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Many Radians In A Revolution
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Relationship Between The Diameter And Circumference . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
