What Is The Prime Factorization Of 104
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
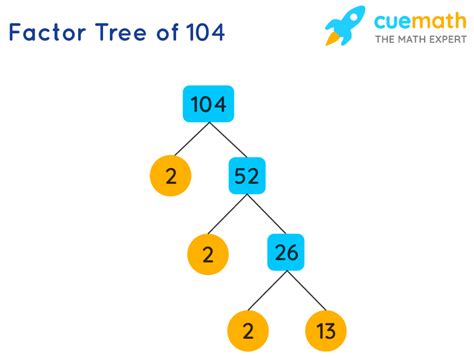
Table of Contents
What is the Prime Factorization of 104? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
Finding the prime factorization of a number might seem like a simple mathematical exercise, but it's a fundamental concept with far-reaching implications in number theory and cryptography. This article will delve into the process of finding the prime factorization of 104, explaining the underlying principles and showcasing different methods to achieve the result. We'll also explore the broader significance of prime factorization and its applications in various fields.
Understanding Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 104, let's clarify some key terms:
-
Prime Number: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on.
-
Composite Number: A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one divisor other than 1 and itself. Essentially, it can be factored into smaller positive integers. For instance, 12 is a composite number because it's divisible by 2, 3, 4, and 6.
-
Prime Factorization: Prime factorization (or integer factorization) is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, result in the original number. This factorization is unique for every composite number. It's a fundamental concept in number theory.
Methods for Finding the Prime Factorization of 104
There are several approaches to determine the prime factorization of 104. Let's explore two common methods:
Method 1: Repeated Division by Prime Numbers
This is a straightforward method. We start by dividing the number by the smallest prime number (2) and continue dividing the result by prime numbers until we're left with 1.
- Divide by 2: 104 divided by 2 is 52.
- Divide by 2 again: 52 divided by 2 is 26.
- Divide by 2 again: 26 divided by 2 is 13.
- Divide by 13: 13 divided by 13 is 1.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 104 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 13, or 2³ x 13.
Method 2: Factor Tree
A factor tree is a visual representation of the factorization process. It's particularly helpful for visualizing the steps involved.
104
/ \
2 52
/ \
2 26
/ \
2 13
We start with 104 and find two factors (2 and 52). We continue breaking down the factors until we reach only prime numbers. The prime factors at the end of the branches are 2, 2, 2, and 13. This confirms that the prime factorization of 104 is 2³ x 13.
The Uniqueness of Prime Factorization: The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This theorem is fundamental to many areas of mathematics. The prime factorization of 104, 2³ x 13, is unique; there's no other way to express 104 as a product of prime numbers.
Applications of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple process of prime factorization has significant applications in various fields:
1. Cryptography: RSA Algorithm
The RSA algorithm, a widely used public-key cryptosystem, relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime factors. The security of RSA depends on the computational infeasibility of factoring extremely large numbers (hundreds or thousands of digits) into their prime components. Even with powerful computers, factoring such large numbers takes an impractical amount of time.
2. Number Theory: Solving Diophantine Equations
Prime factorization plays a crucial role in solving Diophantine equations, which are polynomial equations where the solutions are restricted to integers. Many number theory problems involve understanding the prime factors of numbers to find solutions.
3. Computer Science: Hashing Algorithms
Some hashing algorithms use prime numbers in their calculations to minimize collisions and improve the efficiency of data retrieval. Prime numbers provide a good distribution of hash values, reducing the likelihood of different inputs producing the same hash output.
4. Abstract Algebra: Ring Theory and Field Theory
Prime numbers and factorization are fundamental concepts in abstract algebra, specifically in ring theory and field theory. These areas of mathematics deal with abstract algebraic structures and use prime numbers to understand their properties and relationships.
Beyond 104: Exploring Larger Numbers and Factorization Algorithms
While the prime factorization of 104 is relatively straightforward to compute, factoring much larger numbers is a significantly more challenging task. For very large numbers, sophisticated algorithms are required, such as:
- Trial Division: A basic method, but inefficient for large numbers.
- Pollard's rho algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm that's effective for finding small prime factors.
- Quadratic sieve: A deterministic algorithm used for factoring numbers with hundreds of digits.
- General number field sieve: The fastest known algorithm for factoring very large numbers.
These algorithms utilize advanced mathematical techniques and are crucial for cryptography and other computationally intensive tasks.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple concept of prime factorization underpins many advanced mathematical concepts and has significant practical applications, particularly in cryptography and computer science. Understanding the methods for determining the prime factorization of numbers, like 104 in this case, provides a foundational understanding of number theory and its importance in various fields. While finding the prime factorization of small numbers is relatively easy, the challenge of factoring extremely large numbers forms the basis of many secure cryptographic systems. This exploration demonstrates the power and elegance of seemingly simple mathematical concepts and their vast implications in the modern world. The prime factorization of 104 – 2³ x 13 – is more than just a numerical result; it's a gateway to understanding a fundamental concept that shapes our digital world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Gcf Of 28 And 24
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 1 7 As A Fraction
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Squar Root Of 81
Mar 26, 2025
-
14 Is 20 Of What Number
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Level Of Taxonomy Has The Fewest Organisms
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Prime Factorization Of 104 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
