What Is The Number Of Protons For Silver
listenit
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
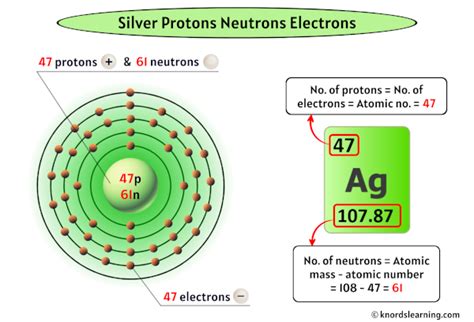
Table of Contents
What is the Number of Protons for Silver? Understanding Atomic Structure and Silver's Properties
Silver, a lustrous, white metal known for its conductivity and antimicrobial properties, holds a fascinating place in chemistry and beyond. A key aspect of understanding silver, and indeed any element, lies in its atomic structure, specifically the number of protons within its nucleus. This article will delve deep into the answer to the question: what is the number of protons for silver? We'll explore the concept of atomic number, its significance, and how it relates to silver's unique characteristics. We'll also look at related concepts, including isotopes and the periodic table, to provide a comprehensive understanding.
The Atomic Number: Defining an Element
The defining characteristic of an element is its atomic number, which represents the number of protons found in the nucleus of a single atom of that element. Protons, positively charged particles, are fundamental building blocks of all matter. The atomic number is unique to each element; no two elements have the same number of protons. This number dictates the element's chemical properties and its position on the periodic table.
Silver's Atomic Number: The Answer
The atomic number for silver (Ag) is 47. This means that every atom of silver contains 47 protons in its nucleus. This fundamental number governs silver's chemical behavior and its physical properties, differentiating it from all other elements. Understanding this simple number unlocks a deeper appreciation for silver's role in various applications.
The Periodic Table: Organizing the Elements
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, organizes elements based on their atomic numbers and recurring chemical properties. Silver (Ag) is located in Group 11, Period 5, reflecting its electronic configuration and properties. Its position in the periodic table provides valuable insights into its reactivity and behavior. The table itself is a powerful tool for predicting the properties of elements based on their position and trends within the table.
Silver's Position and Properties: Implications of Atomic Number
Silver's position in the periodic table, determined by its atomic number, directly influences its properties. Its high electrical and thermal conductivity, for example, is a result of its electronic configuration – a direct consequence of having 47 protons. The arrangement of electrons in its outer shells dictates its reactivity and its ability to form various chemical compounds. Its location also indicates its relationship to other elements in Group 11 (copper and gold), highlighting similarities and differences in their properties.
Isotopes: Variations in Neutron Number
While the number of protons defines an element, the number of neutrons can vary. Isotopes are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with different numbers of neutrons. This variation affects the atom's mass but not its chemical properties significantly. Silver has two naturally occurring isotopes: Silver-107 (¹⁰⁷Ag) and Silver-109 (¹⁰⁹Ag). Both isotopes have 47 protons, but they differ in their neutron count: ¹⁰⁷Ag has 60 neutrons, while ¹⁰⁹Ag has 62 neutrons. The weighted average of the atomic masses of these isotopes gives silver its standard atomic weight of approximately 107.87 amu (atomic mass units).
Implications of Isotopes: Abundance and Applications
The relative abundance of silver isotopes (about 51.8% ¹⁰⁷Ag and 48.2% ¹⁰⁹Ag) impacts various applications of silver. While the chemical properties are essentially the same, the difference in mass can be significant in certain applications, such as mass spectrometry and nuclear physics research. Understanding the isotopic composition of silver is crucial for precise measurements and analysis in specific fields.
Silver's Chemical Properties: A Deeper Dive
The number of protons in silver dictates its chemical behavior. Silver is a relatively unreactive metal, displaying a low tendency to oxidize or corrode in the air. This is due to the arrangement of its electrons, making it resistant to reactions with many substances. However, it does react with certain chemicals, especially oxidizing agents like nitric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid.
Reactivity and Compound Formation
Silver's reactivity is influenced by its electronic configuration and the stability of its filled d-orbitals. While it doesn't readily react with oxygen or water at room temperature, it can form various compounds, such as silver oxide (Ag₂O), silver sulfide (Ag₂S), and silver halides (AgCl, AgBr, AgI). These compounds have various applications in photography, medicine, and industry.
Silver's Physical Properties: Conductivity and More
Silver's excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, its malleability, and its ductility are all linked to its atomic structure and, ultimately, its 47 protons. These properties make it a valuable material in various applications.
Applications of Silver's Properties
- Electrical Conductivity: Silver is the best electrical conductor among all metals, finding use in electronics, circuits, and electrical contacts.
- Thermal Conductivity: Its high thermal conductivity makes it useful in heat exchangers and thermal management applications.
- Malleability and Ductility: These properties allow silver to be easily shaped into wires, sheets, and various forms, making it versatile for manufacturing.
- Reflectivity: Silver's high reflectivity makes it suitable for mirrors and optical devices.
- Antimicrobial Properties: Silver ions exhibit potent antimicrobial properties, utilized in wound dressings, water purification, and antimicrobial coatings.
Conclusion: The Significance of Silver's 47 Protons
The number of protons in a silver atom, 47, is not just a number; it's the fundamental identifier of this element, dictating all its physical and chemical properties. From its excellent conductivity to its antimicrobial effects, silver's unique characteristics are a direct consequence of this atomic number. Understanding the atomic structure of silver, its isotopes, and its position on the periodic table provides a comprehensive appreciation for its diverse applications and its significant role in science and technology. The seemingly simple number 47 holds the key to understanding a rich and complex element with wide-ranging applications. This deep dive into silver's atomic structure highlights the power of fundamental concepts in chemistry and their far-reaching implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Calculate Molarity In Titration
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Do You Write 5 As A Decimal
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many Inches Is 6 Meters
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Is The Cell Membrane Related To Homeostasis
Apr 05, 2025
-
100 Cm Is Equal To How Many Meters
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Number Of Protons For Silver . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
