What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 4
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
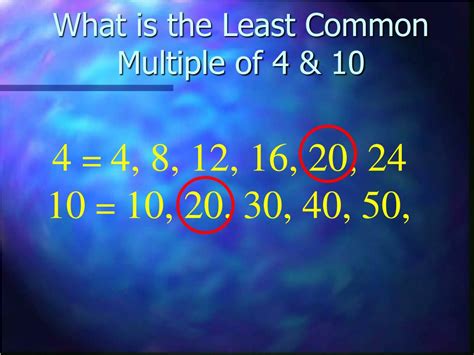
Table of Contents
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 10 and 4? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic problem, but understanding the underlying concepts opens up a fascinating world of number theory with practical applications in various fields. This article will not only answer the question "What is the least common multiple of 10 and 4?" but also delve into the methods for calculating the LCM, explore its significance, and uncover its uses in diverse areas like scheduling, music theory, and even computer science.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the integers as factors. For instance, if we consider the numbers 2 and 3, their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30...
The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, 24, and so on. The smallest of these common multiples is 6. Therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Calculating the LCM of 10 and 4
Now, let's address the central question: What is the least common multiple of 10 and 4? We can employ several methods to determine this.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is the most straightforward method, particularly for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40...
By comparing the lists, we see that the smallest common multiple is 20. Therefore, the LCM of 10 and 4 is 20.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor.
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
- Prime factorization of 4: 2 x 2 = 2²
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 2: 2² = 4
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
Multiplying these together: 4 x 5 = 20. Therefore, the LCM of 10 and 4 is 20.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) are closely related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is always equal to the product of the two numbers. This relationship provides another method for calculating the LCM.
First, we find the GCD of 10 and 4 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- Divide the larger number (10) by the smaller number (4): 10 ÷ 4 = 2 with a remainder of 2.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (4) and the smaller number with the remainder (2).
- Repeat: 4 ÷ 2 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
- The GCD is the last non-zero remainder, which is 2.
Now, we use the relationship: LCM(a, b) = (a x b) / GCD(a, b)
LCM(10, 4) = (10 x 4) / 2 = 40 / 2 = 20
Therefore, the LCM of 10 and 4 is again 20.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM extends far beyond simple arithmetic problems. Its applications span numerous fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have two tasks that need to be performed regularly: Task A every 10 days and Task B every 4 days. To find the next time both tasks coincide, you need to find the LCM of 10 and 4. Since the LCM is 20, both tasks will coincide every 20 days. This principle is crucial in scheduling meetings, production cycles, and other repetitive tasks.
2. Music Theory
LCM plays a role in understanding musical harmony and rhythm. Finding the LCM of different note durations helps determine when rhythms synchronize. For example, the LCM helps determine the shortest period where two musical phrases with different note durations will align rhythmically.
3. Computer Science
In computer programming, especially in areas dealing with synchronization and concurrency, LCM is used to determine the optimal intervals for updating or refreshing data.
4. Gear Ratios and Mechanical Engineering
The LCM helps in calculating gear ratios and finding the optimal combination of gears to achieve a desired speed or torque. Understanding the LCM is fundamental in mechanical design to ensure smooth and efficient operation of machines.
5. Abstract Algebra
The concept of LCM extends to more abstract mathematical structures in abstract algebra, where the notion of least common multiple is generalized to other algebraic systems.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further Concepts
This exploration of the LCM of 10 and 4 has provided a solid foundation, but we can extend our understanding further:
- LCM of more than two numbers: The principles remain the same; however, you need to consider all the numbers involved. Prime factorization becomes especially helpful in these cases.
- LCM and fractions: The LCM is essential when adding or subtracting fractions. Finding the LCM of the denominators allows for a common denominator, simplifying the calculation.
- Euclidean Algorithm for GCD: The Euclidean algorithm, used to find the GCD, is a highly efficient algorithm with wide applications in number theory and cryptography.
- Applications in cryptography: The concepts of GCD and LCM underpin many cryptographic algorithms.
Conclusion
The seemingly simple question of finding the least common multiple of 10 and 4 has opened a door to a rich world of mathematical concepts with diverse practical applications. Understanding LCM is not just about solving arithmetic problems; it's about mastering a fundamental concept that underlies various aspects of our world, from scheduling tasks to building complex machines and understanding musical harmonies. By grasping the principles and methods discussed here, you are well-equipped to tackle more complex problems involving LCM and appreciate its significance in different fields. The journey into the realm of number theory is just beginning.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Top Of A Wave Called
Mar 15, 2025
-
Log X 3 Log X 1
Mar 15, 2025
-
8x 4 4x 3 4 6x 4 4
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Do The Arrows On A Food Chain Represent
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is Salt An Element Compound Or Mixture
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
