What Is The Lcm Of 3 8
listenit
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
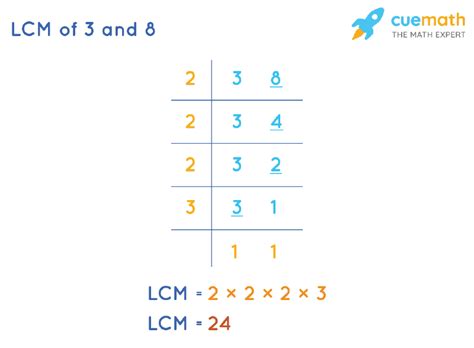
Table of Contents
What is the LCM of 3 and 8? A Deep Dive into Least Common Multiples
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly crucial in arithmetic, algebra, and even more advanced fields. This article provides a comprehensive explanation of how to determine the LCM of 3 and 8, exploring various methods and delving into the underlying principles. We'll also explore the broader context of LCMs, including their applications and relevance in different mathematical scenarios.
Understanding Least Common Multiples (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the integers as factors. This concept is distinct from the greatest common divisor (GCD), which is the largest integer that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder.
Key Characteristics of LCM:
- Positive Integer: The LCM is always a positive integer.
- Divisibility: The LCM is divisible by all the numbers in the set.
- Smallest: It is the smallest positive integer possessing this divisibility property.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 3 and 8
Several methods can be used to calculate the LCM of 3 and 8. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We simply list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30...
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest number appearing in both lists is 24. Therefore, the LCM of 3 and 8 is 24.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
- Prime Factorization of 3: 3 (3 is a prime number)
- Prime Factorization of 8: 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 2: 2³ = 8
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
Multiplying these together gives us: 8 x 3 = 24. Therefore, the LCM of 3 and 8 is 24.
3. Formula using GCD
The LCM and GCD of two numbers are related by the following formula:
LCM(a, b) = (|a * b|) / GCD(a, b)
where |a * b| represents the absolute value of the product of a and b.
First, let's find the GCD of 3 and 8 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- Divide 8 by 3: 8 = 2 * 3 + 2
- Divide 3 by 2: 3 = 1 * 2 + 1
- Divide 2 by 1: 2 = 2 * 1 + 0
The GCD is the last non-zero remainder, which is 1.
Now, using the formula:
LCM(3, 8) = (|3 * 8|) / GCD(3, 8) = 24 / 1 = 24
This confirms that the LCM of 3 and 8 is indeed 24.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM has a wide range of applications in various areas:
1. Fraction Operations
LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To add or subtract fractions, we need to find a common denominator, and the LCM of the denominators is the most efficient common denominator to use.
For example, to add 1/3 and 1/8, we find the LCM of 3 and 8 (which is 24). We then rewrite the fractions with the common denominator of 24:
1/3 = 8/24 1/8 = 3/24
Now, we can easily add the fractions: 8/24 + 3/24 = 11/24
2. Scheduling Problems
LCM is essential for solving problems involving cyclical events that repeat at different intervals. Consider the following:
- Two buses depart from a station at different intervals. Bus A departs every 3 hours, and Bus B departs every 8 hours. When will both buses depart at the same time again?
The answer is the LCM of 3 and 8, which is 24. Both buses will depart together again after 24 hours.
3. Gear Ratios and Rotational Mechanics
In engineering and physics, LCM is used to calculate gear ratios and analyze rotational speeds. When gears mesh, the rotational speeds are related by the ratio of their teeth numbers. The LCM helps determine when the gears will return to their starting positions simultaneously.
4. Music Theory
LCM plays a role in music theory, particularly when dealing with rhythmic patterns and finding the least common multiple of the note durations.
Further Exploration: LCM for More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, we simply consider all the prime factors of all the numbers and take the highest power of each. For the listing multiples method, the process becomes more complex, but conceptually, it remains the same. The GCD-based formula can also be extended using iterative approaches.
Conclusion
Determining the LCM of 3 and 8, whether through listing multiples, prime factorization, or the GCD formula, consistently yields the result of 24. This seemingly simple calculation underscores a fundamental mathematical concept with broad-reaching applications across various fields. Understanding LCM is crucial not only for solving mathematical problems but also for tackling real-world scenarios involving repetitive cycles, fractions, and ratios. By mastering this concept, one gains a deeper appreciation of the interconnectedness and practical utility of seemingly abstract mathematical ideas. The diverse applications of LCM highlight its importance in various disciplines, emphasizing its value beyond the classroom.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Of 36 Is 18
Mar 28, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 6 And 18
Mar 28, 2025
-
Do You Have To Add Water To Acid
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Fraction Of 70
Mar 28, 2025
-
Light Is A Transverse Or Longitudinal Wave
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Lcm Of 3 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
