What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 56 And 42
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
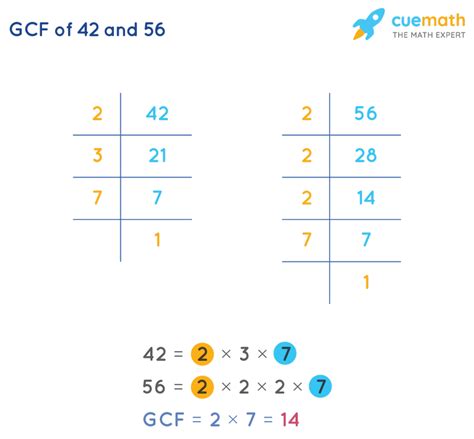
Table of Contents
What is the Greatest Common Factor of 56 and 42? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task. However, understanding the underlying principles and exploring different methods for calculating the GCF reveals a fascinating glimpse into number theory and its applications. This article will delve into various ways to determine the GCF of 56 and 42, explaining the concepts involved and offering a broader perspective on their significance in mathematics.
Understanding the Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
The GCF of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that goes into both numbers evenly. This concept is fundamental in simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and understanding modular arithmetic.
For example, let's consider the numbers 12 and 18. The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. The factors of 18 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18. The common factors are 1, 2, 3, and 6. The greatest among these common factors is 6; therefore, the GCF of 12 and 18 is 6.
Methods for Finding the GCF of 56 and 42
Several methods exist to calculate the GCF, each offering a different approach and level of complexity. Let's apply these methods to find the GCF of 56 and 42:
1. Listing Factors Method
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list all the factors of each number and identify the largest common factor.
Factors of 56: 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 14, 28, 56 Factors of 42: 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21, 42
Comparing the two lists, we find the common factors: 1, 2, 7, and 14. The greatest among them is 14.
Therefore, the GCF of 56 and 42 is 14.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method leverages the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be represented uniquely as a product of prime numbers. We find the prime factorization of each number, and then the GCF is the product of the common prime factors raised to the lowest power.
Prime factorization of 56: 2 x 2 x 2 x 7 = 2³ x 7 Prime factorization of 42: 2 x 3 x 7
The common prime factors are 2 and 7. The lowest power of 2 is 2¹ (or simply 2), and the lowest power of 7 is 7¹. Therefore, the GCF is 2 x 7 = 14.
3. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCF, especially for larger numbers. It's based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers does not change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal, and that number is the GCF.
- Divide the larger number (56) by the smaller number (42): 56 ÷ 42 = 1 with a remainder of 14.
- Replace the larger number (56) with the remainder (14): Now we find the GCF of 42 and 14.
- Divide the larger number (42) by the smaller number (14): 42 ÷ 14 = 3 with a remainder of 0.
- Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the last non-zero remainder, which is 14.
Therefore, the GCF of 56 and 42 using the Euclidean algorithm is 14.
The Significance of the GCF
The GCF is far more than just a mathematical curiosity. It plays a crucial role in various areas:
1. Simplifying Fractions
The GCF is essential for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. To simplify a fraction, we divide both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF. For example, if we have the fraction 56/42, we can simplify it by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCF, which is 14:
56/42 = (56 ÷ 14) / (42 ÷ 14) = 4/3
2. Solving Algebraic Equations
The GCF is sometimes used in solving algebraic equations, particularly those involving polynomials. Factoring out the GCF can simplify the equation and make it easier to solve.
3. Modular Arithmetic
Modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus), relies heavily on the concept of the GCF. The GCF helps determine the solutions to congruence equations.
4. Cryptography
Interestingly, the GCF plays a subtle but important role in certain cryptographic algorithms. The Euclidean algorithm, used to efficiently find the GCF, is fundamental in RSA cryptography, a widely used public-key cryptosystem.
5. Geometry and Measurement
The GCF is useful in geometry problems involving finding the largest possible square tile that can cover a rectangular area without any gaps or overlaps. The side length of the square tile will be the GCF of the dimensions of the rectangle.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further
The concept of the GCF extends beyond just two numbers. We can find the GCF of more than two numbers by applying the same methods repeatedly. For example, to find the GCF of 56, 42, and 28, we can first find the GCF of 56 and 42 (which is 14), and then find the GCF of 14 and 28 (which is 14). Therefore, the GCF of 56, 42, and 28 is 14.
Moreover, the GCF concept forms the basis for understanding the least common multiple (LCM). The LCM of two numbers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of both numbers. There's a relationship between the GCF and LCM: For any two positive integers a and b, the product of their GCF and LCM is equal to the product of the two numbers (GCF(a, b) x LCM(a, b) = a x b).
Conclusion: The GCF – A Cornerstone of Number Theory
In conclusion, finding the greatest common factor of 56 and 42, while seemingly simple, unlocks a deeper understanding of fundamental mathematical concepts. From simplifying fractions to its role in advanced cryptographic algorithms, the GCF demonstrates the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas and its surprising impact on diverse fields. Understanding the different methods for calculating the GCF not only enhances arithmetic skills but also provides a gateway into the fascinating world of number theory and its vast applications. The seemingly simple question of “What is the greatest common factor of 56 and 42?” leads to a rich and rewarding exploration of mathematical principles and their practical significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm For 10 And 8
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Many Quarts Is 7 Pints
Mar 24, 2025
-
Molar Concentration Of Concentrated Sulfuric Acid
Mar 24, 2025
-
132 Lbs Is How Many Kg
Mar 24, 2025
-
Is The Outer Core Solid Or Liquid
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 56 And 42 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
