What Is The Gcf Of 36 And 90
listenit
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
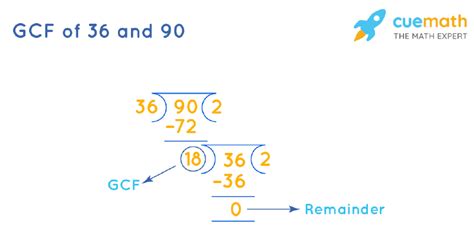
Table of Contents
What is the GCF of 36 and 90? A Deep Dive into Greatest Common Factors
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and different methods for calculating it opens up a world of mathematical possibilities. This article delves deep into determining the GCF of 36 and 90, exploring various techniques and highlighting their applications in broader mathematical contexts. We'll go beyond a simple answer and unpack the significance of GCF in various fields.
Understanding Greatest Common Factors (GCF)
The greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that can perfectly divide both numbers. This concept is fundamental to many areas of mathematics, including simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and even in more advanced fields like cryptography.
Methods for Finding the GCF of 36 and 90
Several methods can be used to determine the GCF of 36 and 90. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Listing Factors Method
This method involves listing all the factors of each number and then identifying the largest factor common to both.
- Factors of 36: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36
- Factors of 90: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 15, 18, 30, 45, 90
Comparing the two lists, we see that the common factors are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18. The greatest common factor is therefore 18.
This method is straightforward for smaller numbers but can become cumbersome with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method utilizes the prime factorization of each number. The prime factorization is the expression of a number as a product of its prime numbers (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
- Prime factorization of 36: 2² x 3²
- Prime factorization of 90: 2 x 3² x 5
To find the GCF, we identify the common prime factors and their lowest powers. Both numbers share 2¹ and 3². Therefore, the GCF is 2¹ x 3² = 2 x 9 = 18.
This method is generally more efficient for larger numbers, as it systematically breaks down the numbers into their fundamental components.
3. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method, particularly useful for large numbers. It's based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers doesn't change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal, and that number is the GCF.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to 36 and 90:
- 90 = 2 x 36 + 18
- 36 = 2 x 18 + 0
Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the last non-zero remainder, which is 18.
The Euclidean algorithm is computationally efficient and forms the basis of many advanced algorithms in computer science and cryptography.
Applications of GCF
The concept of GCF extends far beyond simple arithmetic exercises. Its applications are widespread across various mathematical and real-world scenarios:
1. Simplifying Fractions
GCF plays a crucial role in simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. To simplify a fraction, we divide both the numerator and denominator by their GCF. For example, consider the fraction 36/90. Since the GCF of 36 and 90 is 18, we can simplify the fraction as follows:
36/90 = (36 ÷ 18) / (90 ÷ 18) = 2/5
This simplification makes fractions easier to understand and work with.
2. Solving Algebraic Equations
GCF is often used in factoring algebraic expressions. Factoring involves expressing an algebraic expression as a product of simpler expressions. Finding the GCF of the terms in an expression allows for efficient factoring. For example, consider the expression 36x + 90y. The GCF of 36 and 90 is 18. Therefore, we can factor the expression as:
36x + 90y = 18(2x + 5y)
3. Geometry and Measurement
GCF is utilized in solving geometric problems related to areas and volumes. For instance, when determining the largest square tile that can perfectly cover a rectangular floor of dimensions 36 units by 90 units, the GCF (18) represents the side length of the largest square tile.
4. Number Theory and Cryptography
GCF is fundamental in number theory, a branch of mathematics focusing on the properties of integers. It's also a cornerstone of modern cryptography, particularly in algorithms like the RSA algorithm, which is widely used for secure data transmission. The efficiency of GCF algorithms is critical for the security of these cryptographic systems.
5. Data Analysis and Computer Science
In data analysis, GCF can be useful in simplifying data representations and identifying patterns. In computer science, efficient GCF algorithms are crucial for various tasks, including optimizing code and managing data structures.
Beyond the GCF of 36 and 90: Exploring Further
While we've focused on finding the GCF of 36 and 90, the principles and methods discussed apply universally to any pair of integers. Understanding the concept of GCF and its various computational approaches lays a solid foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. The Euclidean algorithm, in particular, serves as a testament to the elegance and power of mathematical algorithms. Its simplicity belies its profound impact on various fields.
Furthermore, exploring the relationship between GCF and the least common multiple (LCM) reveals another layer of mathematical interconnectedness. The product of the GCF and LCM of two numbers always equals the product of the two numbers themselves. This relationship provides a powerful tool for solving problems involving both GCF and LCM simultaneously.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding GCF
The seemingly simple question of finding the GCF of 36 and 90 opens doors to a rich understanding of fundamental mathematical concepts and their applications. Mastering various methods for calculating GCF not only enhances arithmetic skills but also provides a solid base for tackling more complex mathematical problems in algebra, number theory, geometry, and even computer science. The GCF, therefore, is not merely a mathematical concept; it's a key that unlocks deeper insights into the structure and interconnectedness of numbers. By understanding its significance and various applications, we can appreciate its importance in various mathematical and real-world scenarios.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 35 In Fraction Form
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is 1 20 In Decimal Form
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 39
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Percent Of 400 Is 20
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 4 And 16
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Gcf Of 36 And 90 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
