What Is The Gcf Of 36 And 54
listenit
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
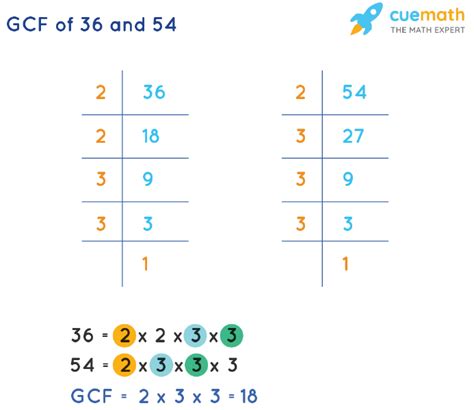
Table of Contents
What is the GCF of 36 and 54? A Deep Dive into Finding the Greatest Common Factor
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and different methods involved is crucial for a solid foundation in mathematics. This article delves deep into determining the GCF of 36 and 54, exploring various techniques and highlighting their practical applications. We'll move beyond simply finding the answer and unpack the broader mathematical principles at play.
Understanding the Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the GCF of 36 and 54, let's define what the GCF actually is. The greatest common factor (also known as the greatest common divisor or GCD) of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that goes evenly into both numbers.
This concept is fundamental in various areas of mathematics, including:
- Simplifying fractions: Finding the GCF allows us to reduce fractions to their simplest form.
- Algebraic manipulations: GCF is essential when factoring polynomials.
- Number theory: GCF plays a critical role in understanding the properties of integers.
- Real-world applications: GCF finds applications in solving problems related to division, sharing, and grouping.
Method 1: Prime Factorization
The prime factorization method is a systematic approach to finding the GCF. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors—numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves.
Steps:
-
Find the prime factorization of each number:
- 36 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 2² x 3²
- 54 = 2 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 2 x 3³
-
Identify common prime factors: Both 36 and 54 share a 2 and two 3s.
-
Multiply the common prime factors: The GCF is the product of the common prime factors raised to the lowest power. In this case, it's 2¹ x 3² = 2 x 9 = 18.
Therefore, the GCF of 36 and 54 is 18.
Method 2: Listing Factors
This method is more intuitive but can be less efficient for larger numbers. It involves listing all the factors of each number and then identifying the largest common factor.
Steps:
-
List the factors of 36: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36
-
List the factors of 54: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, 54
-
Identify common factors: The common factors of 36 and 54 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18.
-
Determine the greatest common factor: The largest of these common factors is 18.
Again, the GCF of 36 and 54 is 18.
Method 3: Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCF, especially for larger numbers. It's based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers doesn't change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal.
Steps:
-
Start with the two numbers: 36 and 54.
-
Subtract the smaller number from the larger number: 54 - 36 = 18
-
Replace the larger number with the result: Now we have 18 and 36.
-
Repeat the process: 36 - 18 = 18.
-
The process stops when both numbers are equal: Both numbers are now 18.
Therefore, the GCF of 36 and 54 is 18.
Applications of Finding the GCF
The ability to find the GCF isn't just a theoretical exercise; it has practical applications across numerous fields:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Consider the fraction 36/54. By finding the GCF (18), we can simplify the fraction to 2/3. This simplifies calculations and makes understanding proportions easier.
-
Dividing Objects: Imagine you have 36 apples and 54 oranges, and you want to divide them into equal groups with the largest possible number of items per group. The GCF (18) tells you that you can create 18 groups, each with 2 apples and 3 oranges.
-
Geometry: In geometry, the GCF can help determine the dimensions of the largest possible square that can tile a rectangle with dimensions 36 units by 54 units. The side length of this square would be 18 units.
-
Music Theory: Understanding GCF is helpful in music theory for finding the greatest common divisor of two note frequencies, aiding in harmonic analysis.
Beyond the Basics: GCF and LCM
The GCF is closely related to the least common multiple (LCM). The LCM of two numbers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both numbers. There's a useful relationship between the GCF and LCM:
For any two integers 'a' and 'b': GCF(a, b) * LCM(a, b) = a * b
Knowing the GCF of 36 and 54 (which is 18), we can easily calculate their LCM:
LCM(36, 54) = (36 * 54) / 18 = 108
This relationship provides a quick way to find the LCM if the GCF is already known.
Extending the Concept: More than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the GCF of more than two numbers. For prime factorization, you would find the prime factorization of each number and then identify the common prime factors raised to the lowest power. The Euclidean algorithm can also be adapted for multiple numbers.
Conclusion: Mastering the GCF
Finding the greatest common factor is a fundamental skill with widespread applications. While the simple method of listing factors might suffice for small numbers, understanding the prime factorization method and the efficient Euclidean algorithm provides a powerful toolkit for tackling more complex problems. Mastering these techniques not only strengthens your mathematical understanding but also opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts and real-world problem-solving. Remember the key takeaways: the GCF represents the largest shared divisor, and various efficient methods exist for its calculation, each with its unique advantages. Understanding the relationship between GCF and LCM further broadens your mathematical capabilities. By understanding the 'why' behind the calculations, you elevate your understanding beyond rote memorization and unlock a deeper appreciation for the beauty and utility of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Symbol For Sample Standard Deviation Is
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Product Of 7 16 4 3 And 1 2
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is 4 A Rational Number Or Irrational
Mar 15, 2025
-
Salad Dressing Homogeneous Heterogeneous Solution Colloid Suspension
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is Lcm Of 3 And 8
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Gcf Of 36 And 54 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
