What Is The Diploid Number Of Chromosomes In Corn
listenit
Apr 03, 2025 · 6 min read
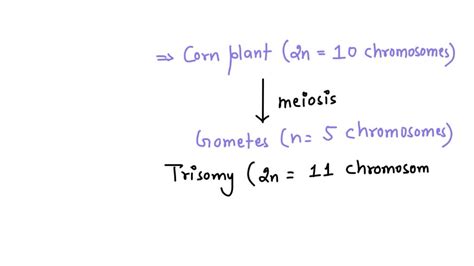
Table of Contents
What is the Diploid Number of Chromosomes in Corn? A Deep Dive into Maize Genetics
Corn, also known as maize (Zea mays), is a staple crop globally, providing a significant portion of the world's food and feed. Understanding its genetics is crucial for improving yield, disease resistance, and overall agricultural efficiency. A fundamental aspect of corn genetics is its chromosome number, specifically the diploid number. This article delves deep into the diploid chromosome number of corn, exploring its significance in various genetic contexts and its implications for research and agricultural practices.
Understanding Diploid Chromosome Number
Before diving into the specifics of corn, let's establish a foundational understanding of diploid chromosome numbers. The diploid number (2n) represents the total number of chromosomes found in a somatic (non-reproductive) cell of an organism. This number is typically an even number because organisms inherit one set of chromosomes from each parent. These sets are called homologous chromosomes, meaning they carry the same genes but may have different alleles (variations of those genes).
During sexual reproduction, the diploid number is halved through meiosis, resulting in haploid gametes (sperm and egg cells) with half the number of chromosomes (n). When fertilization occurs, the haploid gametes fuse, restoring the diploid number in the zygote, which then develops into a new organism.
The Diploid Chromosome Number of Corn: 2n = 20
The diploid chromosome number in corn is 2n = 20. This means that each somatic cell in a corn plant contains 20 chromosomes, organized into 10 homologous pairs. Each pair comprises one chromosome inherited from the maternal parent and one from the paternal parent. These chromosomes carry the genetic information responsible for all the traits of the corn plant, from its height and leaf structure to its kernel characteristics and disease resistance.
Significance of the Diploid Number in Corn Genetics
The knowledge that corn has 20 chromosomes is fundamental to various aspects of corn genetics and research:
1. Karyotyping and Cytogenetic Analysis:
The diploid number is crucial for karyotyping, a technique used to visualize and analyze the chromosomes of an organism. By identifying the number, size, and shape of chromosomes, researchers can detect chromosomal abnormalities, such as deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. These abnormalities can impact the phenotype (observable characteristics) of the plant and can be associated with decreased yield or disease susceptibility. Understanding the expected 20 chromosomes allows for quick identification of any deviations.
2. Genetic Mapping and Breeding:
The diploid number is essential for genetic mapping, a process used to determine the relative positions of genes on chromosomes. This information is critical in plant breeding programs aimed at improving desirable traits. By knowing the chromosome number, breeders can more efficiently track and select for specific genes linked to advantageous characteristics, leading to the development of high-yielding, disease-resistant, and stress-tolerant corn varieties.
3. Genome Sequencing and Analysis:
The diploid chromosome number provides a framework for genome sequencing projects. Knowing the number of chromosomes helps researchers assemble and interpret the massive amount of genomic data generated during sequencing. This information facilitates a deeper understanding of corn's genetic architecture, identifying genes responsible for specific traits and pathways crucial for growth and development.
4. Polyploidy and its Impact:
While corn's natural diploid number is 20, polyploidy (having more than two sets of chromosomes) can occur. Polyploid corn plants may exhibit altered phenotypes, such as increased size or altered fertility. Understanding the basic diploid number allows researchers to study the effects of polyploidy and explore its potential in breeding programs.
5. Genetic Engineering and Transformation:
The diploid number is important for genetic engineering techniques, such as gene transformation. Researchers often introduce new genes into the corn genome to improve certain traits. Knowing the chromosome number assists in targeting specific genes and evaluating the success of transformation events.
Beyond the Diploid Number: Exploring the Corn Genome
While the diploid number (2n = 20) provides a crucial starting point, understanding corn's genetics requires delving deeper into the structure and function of its individual chromosomes. The corn genome is vast and complex, containing a significant amount of genetic information.
Chromosome Structure and Gene Organization:
Each of the 10 chromosome pairs in corn carries thousands of genes. These genes are arranged along the chromosome in a linear fashion and are often clustered into gene families with related functions. The physical organization of these genes plays a vital role in gene regulation and expression, affecting the corn plant's overall phenotype.
Repetitive DNA and Transposable Elements:
A significant portion of the corn genome consists of repetitive DNA sequences and transposable elements (transposons or "jumping genes"). These sequences can move within the genome, potentially causing mutations and influencing gene expression. Understanding the distribution and impact of these elements is crucial for comprehending the complexity of the corn genome and its evolutionary dynamics.
Applications of Corn Genetics Research: Improving Crop Production
Research on corn genetics, including its diploid number and genome structure, has significant implications for improving crop production:
1. Enhanced Yield:
By identifying genes associated with yield components such as kernel number, kernel size, and plant height, breeders can develop corn varieties with higher yields. This is crucial for ensuring food security and meeting the increasing global demand for corn.
2. Disease Resistance:
Understanding the genetic basis of disease resistance allows breeders to develop corn varieties resistant to various pathogens and pests. This reduces the need for pesticides and improves the sustainability of corn production.
3. Stress Tolerance:
Research on corn genetics can lead to the development of varieties tolerant to various environmental stresses, including drought, salinity, and extreme temperatures. This is essential for ensuring stable corn production in challenging environments.
4. Nutritional Enhancement:
Genetic modification of corn can lead to the enhancement of its nutritional value, increasing the levels of essential vitamins and minerals. This can contribute to improving human health and nutrition, particularly in regions with nutritional deficiencies.
Conclusion: The Diploid Number – A Cornerstone of Corn Genetics
The diploid chromosome number of corn (2n = 20) serves as a fundamental cornerstone in the field of maize genetics. This seemingly simple number underpins countless research endeavors, breeding programs, and agricultural advancements. From karyotyping to genome sequencing, understanding the diploid number is essential for unraveling the complexities of corn genetics and harnessing its potential for improving crop production and food security worldwide. Continued research in this area will undoubtedly lead to further breakthroughs in our understanding of this crucial crop and its role in feeding a growing global population. Future research will likely focus on even finer details of the genome, including epigenetic modifications and the complex interplay between genes and environment that influence corn's overall phenotype and productivity. The 20 chromosomes hold the key to unlocking even greater potential in this vital agricultural resource.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Does A Higher Specific Heat Mean
Apr 04, 2025
-
Question Plane Draw The Skeletal Structures
Apr 04, 2025
-
100 Yards On A Football Field
Apr 04, 2025
-
A Consumer That Eats Only Plants
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Amount Of Energy Required To Raise The Temperature
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Diploid Number Of Chromosomes In Corn . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
