What Is The Correct Formula For Potassium Sulfite
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
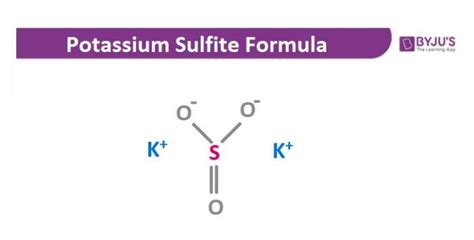
Table of Contents
What is the Correct Formula for Potassium Sulfite? Understanding Chemical Nomenclature and Applications
Potassium sulfite, a chemical compound with various industrial and even culinary applications, often sparks confusion regarding its precise chemical formula. This article delves deep into understanding the correct formula, its properties, production methods, safety precautions, and its diverse applications across different sectors. We'll also address common misconceptions and provide a comprehensive overview of this important chemical.
Understanding Chemical Formulas: A Quick Primer
Before diving into the specifics of potassium sulfite, let's establish a basic understanding of chemical formulas. A chemical formula uses symbols and numbers to represent the types and number of atoms present in a molecule of a compound. For instance, H₂O represents water, indicating two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. The subscripts denote the number of atoms of each element.
The Correct Formula for Potassium Sulfite: K₂SO₃
The correct chemical formula for potassium sulfite is K₂SO₃. This formula signifies that one molecule of potassium sulfite contains:
- Two (2) potassium (K) atoms: Potassium is an alkali metal, known for its reactivity and its presence in numerous biological processes.
- One (1) sulfur (S) atom: Sulfur is a nonmetal vital in various organic and inorganic compounds.
- Three (3) oxygen (O) atoms: Oxygen is a highly reactive nonmetal, crucial for respiration and combustion.
The arrangement of these atoms within the molecule forms a specific structure, contributing to its unique chemical and physical properties. The sulfite ion (SO₃²⁻) carries a negative charge, balanced by the two positive charges of the potassium ions (K⁺).
Common Misconceptions and Alternative Names
It's crucial to distinguish potassium sulfite from other related compounds:
- Potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄): This compound contains the sulfate ion (SO₄²⁻), possessing one extra oxygen atom compared to sulfite. This subtle difference drastically alters its properties and applications. Confusing these two is a common mistake.
- Potassium bisulfite (KHSO₃): This compound is also known as potassium hydrogen sulfite. It contains only one potassium atom bonded to the bisulfite ion (HSO₃⁻). Again, its properties differ significantly from potassium sulfite.
- Potassium metabisulfite (K₂S₂O₅): This is a dimer of potassium bisulfite and shares some similar properties, but its chemical structure and reactivity are distinct.
Using the incorrect name or formula can lead to significant errors, especially in chemical reactions and industrial processes. Always ensure you are using the precise and accurate name and formula – K₂SO₃ – to avoid confusion.
Properties of Potassium Sulfite: A Detailed Look
Potassium sulfite exists as a white, crystalline solid at room temperature. Its properties are:
- Molar Mass: Approximately 158.26 g/mol
- Density: Approximately 2.42 g/cm³
- Melting Point: Decomposes before melting
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water, but less so in alcohol
- Reactivity: It's a reducing agent, readily reacting with oxidizing agents like oxygen in the air. This reactivity is crucial to its preservative properties.
- pH: Aqueous solutions of potassium sulfite are alkaline (basic), meaning they have a pH greater than 7.
Understanding these properties is vital for its safe handling and effective utilization in various applications.
Production of Potassium Sulfite
Potassium sulfite is typically produced through the reaction of potassium hydroxide (KOH) with sulfur dioxide (SO₂):
2KOH + SO₂ → K₂SO₃ + H₂O
This reaction involves dissolving sulfur dioxide gas in a potassium hydroxide solution. The resulting potassium sulfite solution is then purified and crystallized to obtain the final product.
The precise conditions of the reaction, including temperature and pressure, affect the yield and purity of the final product. Industrial production employs sophisticated techniques to ensure high purity and efficient output.
Safety Precautions: Handling Potassium Sulfite Responsibly
While potassium sulfite is widely used, it's crucial to handle it with care due to its potential hazards:
- Irritation: Contact with skin, eyes, or mucous membranes can cause irritation. Appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, goggles, and lab coats are necessary when handling it.
- Respiratory Irritation: Inhalation of potassium sulfite dust can cause respiratory irritation. Well-ventilated areas are essential for its handling.
- Reaction with Acids: It reacts with acids to produce sulfur dioxide gas, which is a respiratory irritant. Therefore, contact with acids must be avoided.
- Oxidizing Agents: It reacts with strong oxidizing agents, which can lead to hazardous reactions.
Always follow safety data sheets (SDS) and appropriate laboratory safety protocols when handling potassium sulfite.
Applications of Potassium Sulfite: A Wide Range of Uses
Potassium sulfite's versatility makes it valuable in various industries:
1. Food Industry: Preservative and Antioxidant
Its primary application is as a preservative and antioxidant in the food industry. It prevents enzymatic browning in fruits and vegetables and inhibits the growth of microorganisms, extending the shelf life of food products. It's commonly used in:
- Dried fruits: To maintain their color and prevent spoilage.
- Winemaking: As a stabilizer and antioxidant, helping to preserve the wine's flavor and color.
- Processed foods: In certain canned or bottled foods, preventing microbial growth.
2. Chemical Industry: Reducing Agent and Reagent
Potassium sulfite's reducing properties make it a valuable reducing agent in various chemical processes. It is used in:
- Chemical synthesis: As a reagent in the production of other chemicals.
- Photography: In the developing process of photographic films.
- Pulp and paper industry: As a bleaching agent and reducing agent.
3. Water Treatment: Oxygen Scavenger
Potassium sulfite is employed in water treatment to remove dissolved oxygen. This is crucial in certain industrial processes that require oxygen-free water, such as boiler water treatment to prevent corrosion.
4. Other Applications
It finds applications in various niche industries, including:
- Textile industry: As a bleaching agent and reducing agent.
- Leather tanning: In the tanning process of leather.
Conclusion: A Crucial Compound with Wide-Ranging Applications
Potassium sulfite, with its chemical formula K₂SO₃, plays a significant role in various industries. Its preservative, reducing, and oxygen-scavenging properties make it an indispensable compound. However, its safe handling requires adherence to safety protocols and awareness of its potential hazards. Understanding the correct formula and properties of potassium sulfite is essential for its proper use and handling in various applications. This article aimed to provide a comprehensive overview of this critical chemical compound, clarifying its formula, properties, applications, and safety aspects. Always consult relevant safety data sheets (SDS) before handling this chemical.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Highest Common Factor Of 30 And 75
Mar 23, 2025
-
Ln X Ln X 2 5
Mar 23, 2025
-
Where Is The Electron Transport Chain Located In Prokaryotes
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is 170 C In F
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is A Match Burning A Chemical Change
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Correct Formula For Potassium Sulfite . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
