What Is The Correct Formula For Barium Phosphate
listenit
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
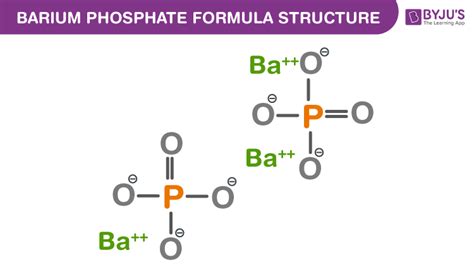
Table of Contents
What is the Correct Formula for Barium Phosphate?
Determining the correct chemical formula for any compound requires understanding the charges of the constituent ions and applying the principle of charge neutrality. This principle dictates that the overall charge of a stable compound must be zero; the positive charges from the cations must balance the negative charges from the anions. Let's explore how this applies to barium phosphate.
Understanding the Ions Involved
Before we can determine the formula for barium phosphate, we need to identify the ions involved and their respective charges:
-
Barium (Ba): Barium is an alkaline earth metal located in Group 2 of the periodic table. Alkaline earth metals consistently form +2 cations, meaning they lose two electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Therefore, the barium ion is written as Ba²⁺.
-
Phosphate (PO₄): Phosphate is a polyatomic anion, meaning it's a group of atoms carrying a net negative charge. It consists of one phosphorus atom (P) and four oxygen atoms (O). The phosphorus atom shares electrons with the oxygen atoms, resulting in a stable arrangement with a net charge of -3. The phosphate ion is represented as PO₄³⁻.
Applying Charge Neutrality to Determine the Formula
To achieve charge neutrality in barium phosphate, the positive charges from the barium ions must exactly cancel out the negative charges from the phosphate ions. We can achieve this by using the lowest common multiple of the charges, which is 6 (2 x 3 = 6).
This means we need:
- 3 Ba²⁺ ions (3 x +2 = +6) to balance
- 2 PO₄³⁻ ions (2 x -3 = -6)
Therefore, the correct chemical formula for barium phosphate is Ba₃(PO₄)₂. The parentheses around (PO₄) indicate that the entire phosphate group is present twice in the formula unit.
Why Other Formulas Are Incorrect
It's crucial to understand why other potential formulas are incorrect. For instance, simply combining the symbols without considering charges (e.g., BaPO₄) would result in an unbalanced charge and an unstable compound. This violates the fundamental principle of charge neutrality.
Further Exploration of Barium Phosphate Properties
Now that we've established the correct formula, let's delve deeper into some of its properties and applications.
Physical Properties
Barium phosphate, Ba₃(PO₄)₂, is a white crystalline solid. Its physical properties include:
- Insolubility: Barium phosphate is largely insoluble in water, meaning it doesn't readily dissolve. This property is often exploited in various applications.
- High Melting Point: It possesses a high melting point, indicating strong ionic bonds between the barium and phosphate ions.
- Density: It has a relatively high density compared to other similar compounds.
Chemical Properties
The chemical properties of barium phosphate are largely governed by its ionic nature and the reactivity of both barium and phosphate ions.
- Reactivity with Acids: Barium phosphate reacts with strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid (HCl) or nitric acid (HNO₃), to form soluble barium salts and phosphoric acid. This reaction is often used to dissolve barium phosphate in laboratory settings.
- Thermal Stability: It's relatively thermally stable, meaning it doesn't readily decompose at moderate temperatures. However, at very high temperatures, it can decompose.
- Reactions with other salts: It can participate in double displacement reactions under specific conditions.
Applications of Barium Phosphate
Barium phosphate finds applications in several areas due to its unique properties:
- Phosphor: It is a component in some phosphors, materials that emit light when exposed to radiation. This application leverages its ability to interact with electromagnetic radiation.
- Coatings: Its insolubility makes it a suitable component in certain coatings where resistance to water is crucial.
- Ceramic Industry: It can be used as an additive in the ceramic industry to alter properties such as melting point and hardness.
- Flame Retardants: The presence of phosphate contributes to its potential use in flame retardant materials. This is an area of ongoing research and development.
- Medical Applications: While research is still ongoing, some studies explore its potential role in biomedicine due to its interaction with phosphate systems in the body, but caution is required as barium compounds can be toxic.
Safety Considerations
It's crucial to handle barium phosphate with care, as barium compounds are generally considered toxic. Appropriate safety precautions, including wearing protective gloves and eye protection, should always be taken when handling this substance. Inhalation or ingestion should be avoided.
Distinguishing Barium Phosphate from Other Barium Compounds
It's important to differentiate barium phosphate from other barium compounds. The phosphate ion gives it distinct properties compared to barium chloride (BaCl₂), barium sulfate (BaSO₄), or barium nitrate (Ba(NO₃)₂). These compounds exhibit different solubilities, reactivities, and applications. The phosphate ion’s presence plays a key role in its unique characteristics.
Synthesis of Barium Phosphate
Barium phosphate can be synthesized through various methods, typically involving the reaction of soluble barium salts with soluble phosphate salts. A precipitation reaction occurs, resulting in the formation of the insoluble barium phosphate, which can then be separated and purified. The exact method and conditions used will depend on the desired purity and scale of production.
Conclusion
The correct formula for barium phosphate is unequivocally Ba₃(PO₄)₂. Understanding the charges of the constituent ions (Ba²⁺ and PO₄³⁻) and applying the principle of charge neutrality are fundamental to determining the correct formula. Barium phosphate possesses unique physical and chemical properties that lead to its applications in various fields. However, it's vital to handle it cautiously due to its toxicity. Further research and development continue to explore its potential uses across a range of industries. Remember that meticulous attention to detail and understanding fundamental chemical principles are crucial in correctly identifying and working with chemical compounds.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple 2 And 8
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 24 And 4
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Light Years Away Is Mars From Earth
Mar 29, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 23
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Decimal For 6 10
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Correct Formula For Barium Phosphate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
