What Is The Bottom Number In A Fraction Called
listenit
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
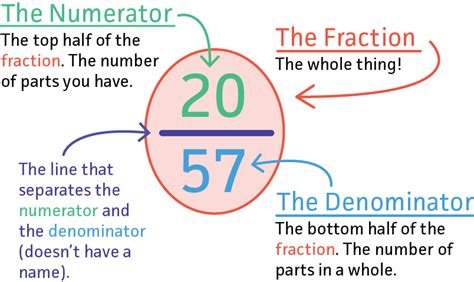
Table of Contents
What is the Bottom Number in a Fraction Called? A Deep Dive into Denominators
Understanding fractions is fundamental to mathematics, and a key component of that understanding is knowing the names of the parts of a fraction. While many grasp the concept of fractions intuitively, knowing the precise terminology is crucial for effective communication and advanced mathematical operations. This comprehensive guide delves into the meaning and significance of the bottom number in a fraction, exploring its various aspects and applications.
Understanding Fractions: A Quick Recap
Before diving into the specifics of the bottom number, let's briefly review what fractions represent. A fraction is a way of expressing a part of a whole. It shows the ratio of one quantity to another. For example, 1/2 represents one out of two equal parts of a whole.
A fraction consists of two main components:
- Numerator: The top number in a fraction. It represents the number of parts you have.
- Denominator: The bottom number in a fraction. This is what we'll be focusing on in this article.
The Denominator: The Unsung Hero of Fractions
The bottom number in a fraction is called the denominator. Its primary role is to indicate the total number of equal parts into which a whole is divided. It represents the size or magnitude of each part. The larger the denominator, the smaller each individual part becomes.
Think of slicing a pizza:
- 1/2: You've divided the pizza into 2 equal slices, and the denominator (2) tells us this.
- 1/4: You've divided the pizza into 4 equal slices, indicating a smaller slice size than the 1/2.
- 1/8: Here, the pizza is divided into 8 equal slices, resulting in even smaller slices.
The denominator provides essential context to the numerator. Without the denominator, the numerator is meaningless. For instance, the number "1" by itself doesn't tell us much, but "1/4" clearly specifies one part out of four equal parts.
The Denominator's Influence on Fraction Value
The denominator has a significant impact on the overall value of the fraction. As mentioned earlier, a larger denominator results in a smaller fraction value. This is because the whole is divided into more parts, making each individual part smaller.
Conversely, a smaller denominator implies a larger fraction value because the whole is divided into fewer parts, resulting in larger individual parts.
Consider these examples:
- 1/2 > 1/4: One-half is greater than one-fourth.
- 1/4 < 1/2: One-fourth is less than one-half.
- 3/8 < 3/4: Three-eighths is less than three-quarters.
This demonstrates the crucial role the denominator plays in determining the relative size and value of fractions.
Types of Denominators
While all denominators represent the total number of equal parts, they can be categorized further:
1. Common Denominators
When comparing or performing operations (like addition and subtraction) on fractions, we often need common denominators. This is a denominator shared by two or more fractions. Finding a common denominator is essential for performing calculations accurately.
For example, to add 1/2 and 1/4, we need to find a common denominator, which in this case is 4. We rewrite 1/2 as 2/4, and then we can add 2/4 + 1/4 = 3/4.
2. Unlike Denominators
Fractions with different denominators are said to have unlike denominators. Before performing operations on fractions with unlike denominators, you must convert them into equivalent fractions with common denominators.
3. Proper and Improper Fractions
The denominator also plays a role in classifying fractions:
-
Proper Fractions: In proper fractions, the numerator is smaller than the denominator. Examples include 1/2, 2/5, and 3/8. These fractions represent a value less than 1.
-
Improper Fractions: In improper fractions, the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. Examples include 5/4, 7/3, and 8/8. These fractions represent a value greater than or equal to 1. Improper fractions can be converted into mixed numbers (a whole number and a proper fraction). For example, 5/4 is equal to 1 and 1/4.
Denominators in Real-World Applications
The concept of denominators isn't confined to the classroom; it permeates various aspects of daily life:
-
Cooking: Recipes frequently use fractions to specify ingredient amounts (e.g., 1/2 cup of sugar, 2/3 cup of flour). The denominator here tells us how many equal parts the cup is divided into.
-
Measurements: We use fractions in measurements of length (e.g., 3/4 inch), weight (e.g., 1/2 pound), and volume (e.g., 1/4 liter).
-
Time: Telling time involves fractions of an hour (e.g., a quarter past the hour is 15 minutes, or 1/4 of an hour).
-
Finance: Percentages are essentially fractions with a denominator of 100 (e.g., 50% is equivalent to 50/100).
-
Data Analysis: In statistics and probability, fractions are commonly used to represent proportions and probabilities. The denominator represents the total number of possible outcomes.
Beyond Basic Fractions: Denominators in Advanced Concepts
The importance of the denominator extends far beyond basic fraction arithmetic. Let's briefly explore some more advanced concepts:
1. Decimal Representation
Any fraction can be expressed as a decimal. This is done by dividing the numerator by the denominator. The denominator plays a key role in determining the precision and length of the decimal representation. For instance, 1/2 is 0.5, while 1/3 is 0.3333... (a repeating decimal). The denominator affects whether the decimal is terminating (ends) or repeating.
2. Rational and Irrational Numbers
Fractions, by definition, represent rational numbers - numbers that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers (numerator and denominator). Numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction are called irrational numbers (e.g., π and √2). The concept of the denominator is fundamental to the definition of rational numbers.
3. Algebraic Fractions
In algebra, we encounter algebraic fractions, which are fractions where the numerator and denominator contain variables. The same principles regarding the denominator apply, even though we're working with variables instead of just numbers. Manipulating algebraic fractions involves techniques like finding common denominators and simplifying expressions.
Common Misconceptions about Denominators
Several common misconceptions surround denominators:
-
Confusing Numerator and Denominator: This is the most prevalent mistake. Always remember the denominator is the bottom number, representing the total parts.
-
Ignoring the Importance of the Denominator: Some students focus solely on the numerator, neglecting the crucial context provided by the denominator. Understanding the relationship between the numerator and denominator is key to comprehending fractions.
-
Difficulty with Common Denominators: Finding a common denominator can be challenging for some, but mastering this skill is essential for fraction operations.
Conclusion: Mastering the Denominator
The denominator, the bottom number in a fraction, is a fundamental concept in mathematics with widespread real-world applications. Understanding its role in representing the total number of equal parts, its impact on the fraction's value, and its involvement in various mathematical operations is crucial for building a strong foundation in mathematics. By overcoming common misconceptions and mastering the concepts outlined in this article, you'll gain a deeper appreciation for the importance and versatility of the denominator. From basic arithmetic to advanced algebraic manipulations, the denominator remains a cornerstone of fractional understanding. Therefore, a thorough grasp of its meaning and function is essential for success in various mathematical endeavors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 4 Times 3 4
Mar 23, 2025
-
Use Pascals Triangle To Expand The Binomial
Mar 23, 2025
-
Square Root Of 3 Times Square Root Of 5
Mar 23, 2025
-
How To Find Charge Of Transition Metals
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Many Strings On A Cello
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Bottom Number In A Fraction Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
