What Do The Arrows In The Food Web Represent
listenit
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
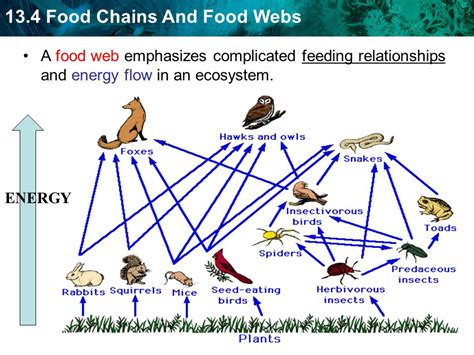
Table of Contents
What Do the Arrows in a Food Web Represent? Unlocking the Secrets of Ecological Relationships
Food webs are intricate diagrams depicting the interconnected feeding relationships within an ecosystem. Understanding these webs is crucial to comprehending the delicate balance of nature and the impact of environmental changes. A key element in interpreting these diagrams lies in understanding the meaning of the arrows. This article delves deep into the significance of arrows in food webs, explaining what they represent, the different types of relationships they illustrate, and their importance in ecological studies.
Decoding the Arrow: The Direction of Energy Flow
At its most fundamental level, the arrow in a food web represents the flow of energy. It points from the organism being consumed (the prey) to the organism doing the consuming (the predator). This signifies that the energy stored within the prey's tissues is transferred to the predator through the act of predation. This energy transfer is the driving force behind all life in an ecosystem.
Beyond Simple Predation: Exploring Different Relationships
While predation is the most common relationship depicted by arrows, food webs also represent other crucial interactions, all indicated by the direction of the arrow:
-
Herbivory: Arrows pointing from plants to herbivores illustrate the transfer of energy from plants to animals that consume them. For instance, an arrow pointing from grass to a rabbit indicates the rabbit's consumption of grass for energy.
-
Parasitism: Arrows can represent parasitic relationships where one organism (the parasite) benefits at the expense of another (the host). The arrow points from the host to the parasite, indicating the flow of energy and nutrients from the host to the parasite. For example, an arrow from a tree to a parasitic vine showcases the vine drawing nutrients from the tree.
-
Decomposition: Arrows pointing from dead organisms (plants or animals) to decomposers (bacteria and fungi) depict the transfer of energy as decomposers break down organic matter, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem. This crucial process recycles nutrients, making them available for producers.
-
Detritivory: Arrows illustrate the flow of energy from dead organic matter (detritus) to detritivores (organisms that feed on detritus). This includes earthworms, millipedes, and dung beetles, which play a significant role in nutrient cycling.
-
Mutualism: While less directly represented by a single arrow, mutualistic relationships, where both organisms benefit, can be implied through a network of interconnected arrows. For instance, the interconnected feeding relationships between pollinators and flowering plants are implied through several linked arrows.
The Importance of Arrows in Understanding Ecosystem Dynamics
The arrows in a food web aren't merely lines on a diagram; they're powerful tools for understanding several aspects of ecosystem dynamics:
1. Energy Transfer and Trophic Levels
Arrows clearly illustrate the movement of energy through trophic levels. Producers (plants) form the base, followed by primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores that eat herbivores), and tertiary consumers (carnivores that eat other carnivores). By tracing the arrows, we can easily visualize the energy flow from one trophic level to the next. This helps us understand the energy pyramid, where energy decreases as we move up the trophic levels due to energy loss at each stage.
2. Biodiversity and Species Interactions
Food webs reveal the complexity of biodiversity and the intricate relationships between species. A web with numerous arrows and interconnected species indicates high biodiversity and a more resilient ecosystem. Conversely, a simplified web with fewer arrows might suggest lower biodiversity and vulnerability to disruptions. The arrows highlight keystone species, those whose removal would dramatically alter the entire web.
3. Impact of Environmental Changes
Analyzing food webs allows scientists to predict the potential impact of environmental changes. For example, the removal of a key predator (due to habitat loss or hunting) can be visualized by removing the arrows associated with that predator. This allows us to model the cascading effects on other species within the ecosystem, helping to assess the vulnerability of the entire ecosystem.
4. Conservation Efforts
Food webs are invaluable tools for conservation biology. By understanding the interconnectedness of species, conservation efforts can be targeted towards protecting keystone species or restoring damaged food webs. This allows for more effective management of natural resources and the preservation of biodiversity.
Limitations of Food Web Representations
While food webs are powerful tools, they have limitations:
-
Simplification: Real-world ecosystems are far more complex than any single food web can depict. Food webs are simplifications that often omit many species and interactions for the sake of clarity.
-
Dynamic Nature: Food webs are not static; they change over time due to seasonal variations, environmental changes, and species interactions. A food web represents a snapshot in time, not a complete picture of ecological dynamics.
-
Incomplete Knowledge: Our understanding of many ecosystems remains incomplete. Therefore, food webs are often incomplete and might not capture all existing relationships.
Advanced Concepts and Applications
The study of food webs has expanded beyond simple graphical representations. Researchers utilize advanced techniques such as network analysis and mathematical modeling to gain a deeper understanding of ecosystem complexity. These techniques help quantify the strength of interactions, identify key players, and predict the effects of environmental perturbations.
These advanced approaches are applied in various fields:
-
Ecosystem Management: Predicting the impact of human activities, such as deforestation or pollution, on ecosystem stability.
-
Conservation Planning: Identifying species that play crucial roles in maintaining ecosystem function and prioritizing conservation efforts.
-
Climate Change Research: Assessing the vulnerability of ecosystems to climate change and developing strategies for mitigation and adaptation.
-
Invasive Species Management: Understanding how invasive species can disrupt existing food webs and develop strategies to control their spread.
Conclusion: Arrows as Keystones to Understanding Ecological Relationships
The humble arrow in a food web, seemingly simple, holds immense power in unraveling the intricacies of ecological relationships. It’s the key to understanding energy flow, species interactions, ecosystem stability, and the consequences of environmental changes. From simple classroom diagrams to sophisticated mathematical models, the arrows in a food web continue to be essential tools for ecologists and conservationists, providing insights into the delicate balance of nature and informing strategies for its preservation. Through a deeper understanding of these directional indicators, we gain a more profound appreciation for the interconnectedness of life and the vital role each species plays within its ecosystem. Further exploration into these representations will undoubtedly uncover more secrets of the natural world and strengthen our efforts towards ecological sustainability.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
2 Log 4 Log 2 Log 2
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is The Charge On Cobalt
Apr 04, 2025
-
What Is A Person From Wales Called
Apr 04, 2025
-
Lead Ii Nitrate And Sodium Iodide
Apr 04, 2025
-
5 X 4 25 X 6
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Do The Arrows In The Food Web Represent . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
