What Are The Factors Of 43
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
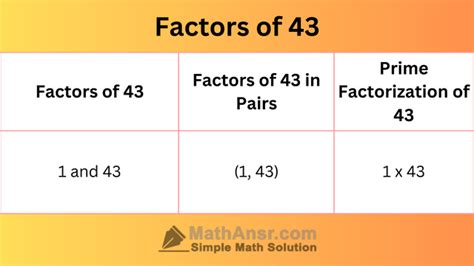
Table of Contents
- What Are The Factors Of 43
- Table of Contents
- What are the Factors of 43? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Divisibility
- Understanding Factors and Divisibility
- Identifying Factors: A Systematic Approach
- Prime Numbers: The Building Blocks of Numbers
- Identifying Prime Numbers: Simple Tests and Algorithms
- The Unique Factorization of 43
- 43: A Prime Number
- The Significance of Prime Numbers
- Exploring Related Concepts: Divisibility Rules and Factorization Techniques
- Divisibility Rules: Quick Checks for Divisibility
- Factorization Techniques: Beyond Trial Division
- Conclusion: The Significance of Simplicity
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What are the Factors of 43? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Divisibility
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 43?" opens a door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, prime numbers, and the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, understanding the underlying concepts provides a richer appreciation of mathematical principles and their applications.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we delve into the specifics of 43, let's clarify the fundamental concepts. A factor (or divisor) of a number is any integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. Divisibility is the property of one number being completely divisible by another without any remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Identifying Factors: A Systematic Approach
Finding the factors of a number involves systematically checking each integer from 1 up to the number itself. While this is feasible for smaller numbers, it becomes computationally intensive for larger numbers. However, understanding prime factorization provides a more efficient approach.
Prime Numbers: The Building Blocks of Numbers
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other numbers, as every composite number (a number that is not prime) can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers (this is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic).
Some examples of prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The sequence of prime numbers is infinite, meaning there is no largest prime number. The distribution of prime numbers among integers is a topic of ongoing mathematical research.
Identifying Prime Numbers: Simple Tests and Algorithms
Determining whether a number is prime can be accomplished through various methods. For smaller numbers, trial division (checking for divisibility by all prime numbers up to the square root of the number) is a relatively efficient method. For larger numbers, more sophisticated algorithms like the Miller-Rabin primality test are employed.
The Unique Factorization of 43
Now, let's return to the central question: What are the factors of 43? By applying the concepts we've discussed, we can easily determine the factors of 43.
To find the factors, we systematically check integers:
- 1: 43 divided by 1 is 43, with no remainder.
- 43: 43 divided by 43 is 1, with no remainder.
Therefore, the factors of 43 are 1 and 43.
43: A Prime Number
The fact that the only factors of 43 are 1 and itself signifies that 43 is a prime number. This means it cannot be expressed as a product of smaller integers other than 1 and itself. This characteristic makes 43 a fundamental building block in the construction of larger numbers.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers hold immense importance in various fields, including:
-
Cryptography: The security of many modern encryption systems relies on the difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime factors. The larger the prime numbers involved, the more secure the encryption.
-
Number Theory: Prime numbers are central to numerous theorems and conjectures in number theory, driving ongoing mathematical research and discoveries.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms for finding prime numbers and factoring large numbers are fundamental to computer science and cryptography.
Exploring Related Concepts: Divisibility Rules and Factorization Techniques
While we've established that 43 is a prime number and its factors are 1 and 43, let's explore some related concepts to enhance our understanding of number theory.
Divisibility Rules: Quick Checks for Divisibility
Divisibility rules are shortcuts to determine whether a number is divisible by certain integers without performing long division. For example:
- A number is divisible by 2 if its last digit is even (0, 2, 4, 6, 8).
- A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3.
- A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is 0 or 5.
- A number is divisible by 10 if its last digit is 0.
While these rules don't directly apply to determining whether a number is prime, they can be helpful in preliminary checks for factoring larger numbers.
Factorization Techniques: Beyond Trial Division
For larger numbers, trial division becomes less efficient. More advanced factorization techniques are employed, including:
- Pollard's rho algorithm: A probabilistic algorithm used to find factors of a composite number.
- Sieve of Eratosthenes: An ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer.
- General Number Field Sieve (GNFS): The most efficient known algorithm for factoring very large integers.
These algorithms are computationally intensive and are crucial in cryptography and other areas requiring efficient factorization.
Conclusion: The Significance of Simplicity
The factors of 43 – 1 and 43 – might seem deceptively simple. However, the exploration of this seemingly straightforward question has provided us with a deeper understanding of fundamental concepts in number theory, including prime numbers, divisibility, and factorization techniques. The simplicity of the answer belies the rich mathematical landscape it reveals. Understanding prime numbers and their properties is crucial for numerous applications, particularly in cryptography and computer science. The ongoing quest to understand the distribution and properties of prime numbers continues to drive mathematical research, highlighting their enduring importance in the world of mathematics. The seemingly simple number 43 serves as a microcosm of this vast and fascinating field.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Integration Of 1 X 2 3 2
Mar 18, 2025
-
Power Series For Ln 1 X
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Are The Five Properties Of A Mineral
Mar 18, 2025
-
7 Out Of 10 As A Percentage
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Gcf Of 12 And 15
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 43 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
