What Are The Factors For 44
listenit
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
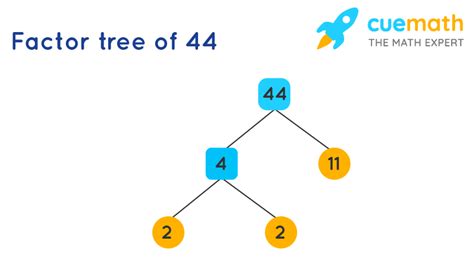
Table of Contents
Decomposing 44: A Deep Dive into its Factors and Mathematical Significance
The seemingly simple number 44 holds a surprising depth when explored through the lens of its factors and mathematical properties. Understanding the factors of a number is fundamental to various mathematical concepts, from prime factorization to algebraic manipulations. This comprehensive exploration delves into the factors of 44, examining their properties, their relevance in different mathematical contexts, and their broader implications within number theory.
Understanding Factors: The Building Blocks of Numbers
Before diving into the specifics of 44, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes a factor. A factor, or divisor, of a number is a whole number that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Finding all the factors of a number is a crucial step in many mathematical operations. It's the foundation for simplifying fractions, solving equations, and understanding the structure of numbers themselves.
Identifying the Factors of 44
Now, let's pinpoint the factors of 44. We can approach this systematically:
- 1: Every number is divisible by 1.
- 2: 44 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2 (44/2 = 22).
- 4: 44 is divisible by 4 (44/4 = 11).
- 11: 44 is divisible by 11 (44/11 = 4).
- 22: As seen earlier, 22 is a factor.
- 44: Every number is divisible by itself.
Therefore, the complete set of factors for 44 is 1, 2, 4, 11, 22, and 44.
Prime Factorization: Unpacking the Building Blocks
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. Prime numbers are whole numbers greater than 1 that have only two divisors: 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Prime factorization provides a unique representation of any number, much like a fingerprint.
To find the prime factorization of 44, we can use a factor tree:
44
/ \
2 22
/ \
2 11
This shows that 44 can be expressed as 2 x 2 x 11, or 2² x 11. This prime factorization is unique to 44 and is a fundamental representation of the number.
The Significance of Factors in Various Mathematical Contexts
The factors of a number are not just a simple list; they hold significant weight in many mathematical areas:
1. Number Theory: Exploring the Properties of Numbers
Number theory delves into the properties of integers and their relationships. Factors play a central role in understanding concepts like:
- Divisibility Rules: Understanding factors allows us to determine divisibility by specific numbers. For instance, since 44 is divisible by 2 and 11, it follows the divisibility rules for both.
- Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. Finding the GCD often involves finding the factors of the numbers involved. For example, if we want to find the GCD of 44 and 88, we would examine their factors and find that the GCD is 44.
- Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. Factors are used in calculating the LCM, often through prime factorization.
2. Algebra: Simplifying Expressions and Solving Equations
Factors are essential for simplifying algebraic expressions and solving equations:
- Factoring Polynomials: Factoring involves breaking down a polynomial expression into simpler factors. This is crucial for solving polynomial equations and simplifying complex expressions. The concept of factors is directly related to finding the roots or zeros of a polynomial.
- Simplifying Fractions: Finding common factors in the numerator and denominator of a fraction allows us to simplify the fraction to its lowest terms. This simplification is vital in various mathematical and scientific calculations.
3. Geometry and Measurement: Area, Volume, and More
Factors appear subtly in geometric contexts:
- Area and Volume Calculations: Finding the dimensions of a rectangle or a cube often involves working with factors. For instance, if the area of a rectangle is 44 square units, we might explore factor pairs (e.g., 4 x 11, 2 x 22) to determine possible dimensions.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Deeper Mathematical Concepts Related to 44
The number 44, while seemingly unremarkable at first glance, opens doors to more complex mathematical ideas:
1. Perfect Numbers and Abundant Numbers
A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (divisors excluding the number itself). 44 is not a perfect number; the sum of its proper divisors (1 + 2 + 4 + 11 + 22 = 40) is less than 44. Numbers like 44, where the sum of proper divisors is less than the number itself, are called deficient numbers. Conversely, abundant numbers have a sum of proper divisors greater than the number itself.
2. Number Patterns and Sequences
44 can be a part of various number sequences and patterns. Exploring these sequences can reveal interesting mathematical relationships and properties. For example, 44 is part of the sequence of even numbers, but it's also part of more specialized sequences defined by specific mathematical rules.
3. Modular Arithmetic and Congruences
In modular arithmetic, we consider remainders after division. The properties of 44 in modular arithmetic, its remainders when divided by different numbers, can be explored. For example, 44 is congruent to 0 (mod 2), 0 (mod 4), and 0 (mod 11).
4. Number Bases and Representation
The representation of 44 varies depending on the number base used. In base 10 (decimal), it's 44. In base 2 (binary), it's 101100. Exploring different number bases provides a broader understanding of the number's structure.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Factors
The seemingly simple task of finding the factors of 44 unveils a surprisingly rich tapestry of mathematical concepts. From the basic understanding of divisibility to the more sophisticated realms of number theory and algebra, the factors of a number form the cornerstone of many mathematical explorations. This in-depth analysis highlights the interconnectedness of various mathematical disciplines and emphasizes the importance of understanding the fundamental building blocks of numbers. By exploring the factors of a number, we not only gain a deeper appreciation for its properties but also gain valuable insights into the broader world of mathematics. The seemingly straightforward number 44 serves as a compelling example of how seemingly simple concepts can lead to intricate and fascinating mathematical discoveries.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Ground State Electron Configuration For Bromine
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Times Does 2 Go Into 19
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Opposite Of Condensation
Mar 26, 2025
-
9 Oz Is Equal To How Many Cups
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Liters Is In 1500 Ml
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors For 44 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
