What Are The Common Factors Of 36 And 90
listenit
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
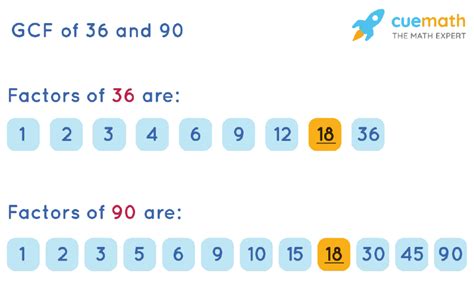
Table of Contents
What are the Common Factors of 36 and 90? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common factors of two numbers might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but it opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, with implications reaching far beyond basic calculations. This article delves into the common factors of 36 and 90, exploring various methods to find them, understanding their significance, and expanding upon related mathematical concepts. We'll move beyond a simple answer and illuminate the underlying principles, making this exploration valuable for students, math enthusiasts, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of numbers.
Understanding Factors and Common Factors
Before we tackle the specific problem of 36 and 90, let's define our key terms.
-
Factor: A factor of a number is any integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
-
Common Factor: A common factor of two or more numbers is a factor that is shared by all of them. For instance, the common factors of 12 and 18 are 1, 2, 3, and 6.
-
Greatest Common Factor (GCF) or Highest Common Factor (HCF): The greatest common factor is the largest common factor among a set of numbers. For 12 and 18, the GCF is 6.
Method 1: Listing Factors
The most straightforward method to find the common factors of 36 and 90 is to list all the factors of each number and then identify the ones they have in common.
Factors of 36: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36
Factors of 90: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 15, 18, 30, 45, 90
Common Factors of 36 and 90: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18
Therefore, the common factors of 36 and 90 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18. The greatest common factor (GCF) is 18.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a more powerful and efficient method, particularly when dealing with larger numbers. It involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself.
Prime Factorization of 36:
36 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 2² x 3²
Prime Factorization of 90:
90 = 2 x 3 x 3 x 5 = 2 x 3² x 5
To find the common factors using prime factorization, we identify the prime factors that appear in both factorizations. We then take the lowest power of each common prime factor.
Both 36 and 90 share a factor of 2 (to the power of 1) and a factor of 3 (to the power of 2).
Therefore, the GCF is 2¹ x 3² = 2 x 9 = 18. Any combination of these prime factors (including 1, representing 2⁰ x 3⁰) will be a common factor. This gives us the same set of common factors as Method 1: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18.
Method 3: Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of two numbers, especially useful for larger numbers where listing factors becomes cumbersome. This algorithm is based on the principle that the GCF of two numbers does not change if the larger number is replaced by its difference with the smaller number. This process is repeated until the two numbers are equal.
Let's apply the Euclidean algorithm to 36 and 90:
- 90 = 2 x 36 + 18
- 36 = 2 x 18 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is 18, which is the GCF of 36 and 90. Once we have the GCF, we can easily derive all other common factors.
Significance of Common Factors
Understanding common factors has numerous applications in mathematics and beyond:
-
Simplification of Fractions: Finding the GCF is crucial for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 36/90 can be simplified to 2/5 by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCF (18).
-
Solving Equations: Common factors play a role in solving algebraic equations, particularly in factoring polynomials.
-
Geometry: Common factors are used in determining the dimensions of objects with common factors in their measurements. For instance, if you have tiles that are 36 units by 18 units, you might need to find the greatest common divisor (GCD) to determine the size of the largest square tile you could use to cover the area evenly.
-
Real-world Applications: Common factors appear in various real-world scenarios involving grouping or division. For example, consider dividing 36 apples and 90 oranges into identical bags with the maximum number of items in each bag. The solution will be related to the greatest common factor.
Expanding on Related Concepts
Let's explore some closely related mathematical concepts:
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The least common multiple is the smallest number that is a multiple of both numbers. For 36 and 90, the LCM is 180. The relationship between the GCF and LCM is given by the formula: GCF(a, b) x LCM(a, b) = a x b. In our case, 18 x 180 = 3240, and 36 x 90 = 3240, verifying the formula.
-
Modular Arithmetic: Common factors play a crucial role in modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value, called the modulus.
-
Number Theory: The study of common factors is a fundamental aspect of number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of integers.
Conclusion
Finding the common factors of 36 and 90, while seemingly straightforward, provides a valuable entry point into the fascinating world of number theory. We explored various methods—listing factors, prime factorization, and the Euclidean algorithm—each offering unique insights and efficiency depending on the context. Understanding common factors is essential not only for simplifying calculations but also for solving more complex mathematical problems and tackling real-world applications. This exploration highlights the interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and the importance of understanding fundamental principles to unlock a deeper appreciation of numbers and their properties. The exploration of common factors is a stepping stone to a more profound comprehension of the elegance and intricacy of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Derivative Of Ln 1 X
Mar 17, 2025
-
Which Type Of Molecule Is Shown Below
Mar 17, 2025
-
How To Find The Domain Of F O G
Mar 17, 2025
-
Amino Acids Are The Monomers For
Mar 17, 2025
-
Why Cant Ions Pass Through The Membrane
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Common Factors Of 36 And 90 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
