What Are All The Factors Of 70
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
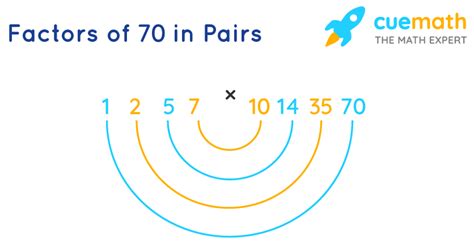
Table of Contents
What Are All the Factors of 70? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding all the factors of a number might seem like a simple task, especially for smaller numbers like 70. However, understanding the process thoroughly reveals fundamental concepts in number theory, laying a groundwork for more complex mathematical explorations. This article delves into the factors of 70, explaining the methods involved, and expanding upon related mathematical ideas.
Understanding Factors
Before we dive into the specific factors of 70, let's define what a factor is. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides evenly into that number without leaving a remainder. In other words, if 'a' is a factor of 'b', then b/a results in a whole number.
Finding the Factors of 70: A Step-by-Step Approach
There are several ways to find the factors of 70. Let's explore the most common methods:
Method 1: Systematic Listing
The simplest approach is to systematically list all the whole numbers that divide 70 without leaving a remainder. We start with 1 (as 1 is a factor of every number) and work our way up:
- 1: 70 ÷ 1 = 70
- 2: 70 ÷ 2 = 35
- 5: 70 ÷ 5 = 14
- 7: 70 ÷ 7 = 10
- 10: 70 ÷ 10 = 7
- 14: 70 ÷ 14 = 5
- 35: 70 ÷ 35 = 2
- 70: 70 ÷ 70 = 1
Notice that after we reach 10, the factors begin to repeat in reverse order (14, 35, 70 mirror 5, 2, 1). This is a characteristic of factor pairs; for every factor, there's a corresponding factor that, when multiplied together, equals the original number.
Therefore, the factors of 70 are 1, 2, 5, 7, 10, 14, 35, and 70.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method leverages the concept of prime numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
Let's find the prime factorization of 70:
- Start by dividing 70 by the smallest prime number, 2: 70 ÷ 2 = 35.
- Now, divide 35 by the next prime number, 5: 35 ÷ 5 = 7.
- 7 is itself a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 70 is 2 x 5 x 7.
From the prime factorization, we can easily find all the factors. We systematically combine the prime factors in various ways:
- Using only one prime factor: 2, 5, 7
- Using two prime factors: 2 x 5 = 10, 2 x 7 = 14, 5 x 7 = 35
- Using all three prime factors: 2 x 5 x 7 = 70
- And finally, including 1 as a factor: 1
This method yields the same set of factors: 1, 2, 5, 7, 10, 14, 35, and 70.
Beyond the Factors: Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding the factors of 70 opens doors to a deeper exploration of number theory. Let's explore some related concepts:
1. Divisibility Rules:
Divisibility rules are shortcuts to determine if a number is divisible by another number without performing the actual division. For 70, we can see the divisibility rules in action:
- Divisible by 2: 70 is an even number, hence divisible by 2.
- Divisible by 5: 70 ends in 0 or 5, hence divisible by 5.
- Divisible by 7: This requires a bit more calculation, but we've already established that 70 is divisible by 7.
- Divisible by 10: 70 ends in 0, thus divisible by 10.
2. Greatest Common Factor (GCF) and Least Common Multiple (LCM):
These concepts are crucial in simplifying fractions and solving various mathematical problems.
-
GCF: The greatest common factor is the largest number that divides evenly into two or more numbers. Let's say we want to find the GCF of 70 and another number, say 42. The factors of 42 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 14, 21, and 42. The common factors of 70 and 42 are 1, 2, 7, and 14. Therefore, the GCF(70, 42) is 14.
-
LCM: The least common multiple is the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers. To find the LCM(70, 42), we can list multiples of both numbers until we find the smallest common one. Or we can use the prime factorization method: 70 = 2 x 5 x 7 and 42 = 2 x 3 x 7. The LCM is found by taking the highest power of each prime factor present in either number: 2 x 3 x 5 x 7 = 210. Therefore, LCM(70, 42) = 210.
3. Perfect Numbers and Abundant Numbers:
-
Perfect Number: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (divisors excluding the number itself). 70 is not a perfect number because the sum of its proper divisors (1 + 2 + 5 + 7 + 10 + 14 + 35 = 74) is greater than 70.
-
Abundant Number: An abundant number is a positive integer that is less than the sum of its proper divisors. Since the sum of the proper divisors of 70 (74) is greater than 70, 70 is an abundant number.
4. Number of Factors:
A formula exists to calculate the number of factors of any given number based on its prime factorization. If the prime factorization of a number N is given by N = p₁^a₁ * p₂^a₂ * ... * pₙ^aₙ, where pᵢ are distinct prime numbers and aᵢ are their respective exponents, then the number of factors of N is given by:
(a₁ + 1)(a₂ + 1)...(aₙ + 1)
For 70 (2¹ x 5¹ x 7¹), the number of factors is (1+1)(1+1)(1+1) = 8. This confirms our earlier findings that 70 has 8 factors.
Conclusion: The Significance of Factorization
Finding the factors of 70, while seemingly a basic arithmetic exercise, unveils fundamental concepts within number theory. Understanding factorization methods, divisibility rules, GCF, LCM, and related concepts provides a solid foundation for further mathematical exploration. This knowledge is not only important for academic pursuits but also finds practical applications in various fields like cryptography, computer science, and even music theory. The seemingly simple act of finding the factors of 70 opens up a world of mathematical possibilities. The application of this knowledge extends far beyond simple number crunching. It acts as a stepping stone for understanding more complex mathematical structures and algorithms. By appreciating the building blocks of number theory, we can unlock a deeper understanding of the world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Are Temperature And Pressure Directly Proportional
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Find If The Limit Exists
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Is Bigger 2 3 Or 3 4
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Do Chemical Equations Need To Be Balanced
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Does The Cell Membrane Help Maintain Homeostasis
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are All The Factors Of 70 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
