Sum Of Interior Angles In A Heptagon
listenit
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
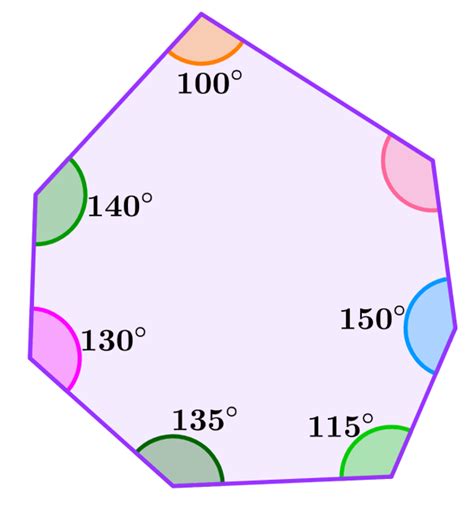
Table of Contents
Sum of Interior Angles in a Heptagon: A Comprehensive Guide
The heptagon, a captivating polygon with seven sides and seven angles, holds a unique place in geometry. Understanding its properties, particularly the sum of its interior angles, opens doors to a deeper appreciation of shapes and their mathematical relationships. This comprehensive guide will delve into the sum of interior angles in a heptagon, exploring various methods of calculation, real-world applications, and related geometrical concepts.
Understanding Polygons and Their Angles
Before we focus specifically on heptagons, let's establish a foundational understanding of polygons and their angles. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting straight line segments. These segments are called the sides of the polygon, and the points where the sides meet are called vertices. Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they possess:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon (or Septagon): 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
- and so on...
Each polygon possesses both interior angles (angles formed inside the polygon by its sides) and exterior angles (angles formed by extending one side of the polygon). The sum of these angles is governed by specific mathematical relationships.
Calculating the Sum of Interior Angles in a Heptagon: The Formula Approach
The most efficient method for determining the sum of interior angles in any polygon, including a heptagon, involves a simple formula. This formula is derived from the concept of triangulation, which involves dividing a polygon into a series of triangles.
The formula for the sum of interior angles (S) of an n-sided polygon is:
S = (n - 2) × 180°
Where 'n' represents the number of sides of the polygon.
For a heptagon, n = 7. Substituting this value into the formula, we get:
S = (7 - 2) × 180° = 5 × 180° = 900°
Therefore, the sum of the interior angles in any heptagon is always 900 degrees. This holds true regardless of the heptagon's shape or size; whether it's a regular heptagon (with all sides and angles equal) or an irregular heptagon (with varying side lengths and angles), the sum of its interior angles will always be 900°.
Triangulation Method: A Visual Approach
While the formula provides a quick and accurate solution, understanding the underlying principle of triangulation is crucial for a deeper grasp of the concept. Let's visualize this method:
-
Choose a vertex: Select any vertex of the heptagon as a starting point.
-
Draw diagonals: From the chosen vertex, draw diagonals to all other non-adjacent vertices. This will divide the heptagon into five triangles. Note that the number of triangles formed is always two less than the number of sides (n-2).
-
Sum of angles in triangles: Each triangle has an interior angle sum of 180°. Since we have five triangles, the total sum of the angles in these triangles is 5 × 180° = 900°.
-
Interior angles of the heptagon: These angles of the triangles precisely constitute the interior angles of the heptagon. Therefore, the sum of the interior angles of the heptagon is 900°.
Regular Heptagon: A Special Case
A regular heptagon is a heptagon where all sides are of equal length, and all interior angles are equal. In a regular heptagon, each interior angle can be calculated by dividing the total sum of interior angles by the number of angles (which is equal to the number of sides):
Each interior angle = 900° / 7 ≈ 128.57°
This means each interior angle in a regular heptagon measures approximately 128.57 degrees. This value is crucial in various applications, particularly in design and architecture where precise angular measurements are essential.
Irregular Heptagons: Variety in Angle Measures
Unlike a regular heptagon, an irregular heptagon has sides of varying lengths and angles of different measures. However, the fundamental principle remains: the sum of its interior angles will always be 900°. The individual angles will vary, but their sum will consistently add up to 900°. This property makes the sum of interior angles a robust and reliable characteristic of any heptagon, irrespective of its shape.
Real-World Applications of Heptagons and Angle Calculations
The heptagon, although less commonly encountered than triangles, squares, or hexagons, has its place in various real-world applications:
-
Architecture and Design: Heptagons can be seen in some building designs, creating unique architectural features. Accurate calculations of interior angles are crucial for precise construction.
-
Tessellations: While regular heptagons cannot tessellate (completely cover a surface without gaps or overlaps), irregular heptagons, combined with other polygons, can be used to create interesting and complex tessellations in art and design.
-
Engineering: Heptagonal shapes might be incorporated in certain engineering designs, requiring precise calculations of angles for structural integrity.
-
Nature: Although not as prevalent as other shapes, heptagonal structures can sometimes be observed in natural formations, though often imperfectly.
Exterior Angles of a Heptagon
The exterior angles of a polygon offer another perspective. The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon, regardless of the number of sides, always equals 360°. This is because if you extend each side of the polygon, you will form a complete rotation around the polygon's center. Therefore, for a heptagon:
Sum of exterior angles = 360°
This fact complements the interior angle sum, providing another useful property for analyzing heptagons.
Exploring Related Polygons and Their Angle Sums
Understanding the heptagon's interior angle sum allows for a comparative analysis of other polygons. By applying the general formula (n-2) × 180°, we can easily calculate the interior angle sums of other polygons:
- Octagon (n=8): (8-2) × 180° = 1080°
- Nonagon (n=9): (9-2) × 180° = 1260°
- Decagon (n=10): (10-2) × 180° = 1440°
This demonstrates the consistent relationship between the number of sides and the sum of interior angles in any polygon.
Conclusion: The Significance of the Heptagon's Angle Sum
The sum of interior angles in a heptagon, consistently 900°, is a fundamental property that transcends the specific shape of the heptagon. Understanding this property, through both the formulaic and triangulation approaches, provides a strong foundation for tackling more complex geometric problems. Its applications extend beyond theoretical mathematics, playing a role in design, engineering, and even appreciating the subtle geometrical patterns found in the natural world. The heptagon, with its seven sides and its distinct angle sum, reinforces the beauty and power of mathematical relationships in understanding and shaping our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does Nitrogen Follow The Octet Rule
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is 37 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 26, 2025
-
21 Out Of 30 Is What Percent
Mar 26, 2025
-
Cos 4x Sin 4x Cos 2x
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 4 And 2
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sum Of Interior Angles In A Heptagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
