Sugar Is A Compound Or Mixture
listenit
Mar 26, 2025 · 5 min read
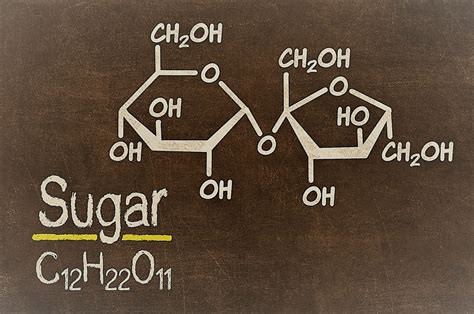
Table of Contents
Sugar: A Compound, Not a Mixture
Sugar, a ubiquitous ingredient in our daily lives, is often perceived as a simple substance. However, understanding its true nature requires delving into the fascinating world of chemistry. This article will comprehensively explore the question: Is sugar a compound or a mixture? We'll unravel the scientific definition of compounds and mixtures, examine the chemical structure of sugar, and differentiate it from common mixtures. Furthermore, we'll explore the different types of sugar, their properties, and their roles in various applications.
Understanding Compounds and Mixtures
Before we can classify sugar, we need to understand the fundamental differences between compounds and mixtures.
Compounds: A Chemical Bond
A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more different elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio. This chemical combination involves the formation of chemical bonds, which are strong forces of attraction between atoms. The properties of a compound are distinctly different from the properties of its constituent elements. For instance, water (H₂O) is a compound formed from the elements hydrogen and oxygen. The properties of water are vastly different from those of hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. Compounds have a fixed chemical formula, representing the precise ratio of atoms involved. They can only be separated into their constituent elements through chemical means, such as electrolysis or chemical reactions.
Mixtures: No Chemical Bonds
A mixture, on the other hand, is a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. The substances in a mixture retain their individual properties and can be separated by physical means, such as filtration, distillation, or evaporation. Mixtures do not have a fixed composition; the ratio of components can vary. Examples of mixtures include saltwater (salt and water), air (various gases), and sand (various minerals).
The Chemical Composition of Sugar
Sugar, in its most common form, is sucrose, a disaccharide. Let's dissect its chemical structure. Sucrose is formed from two simpler sugars: glucose and fructose. These two monosaccharides are bonded together through a glycosidic linkage, a covalent bond formed between the carbon atoms of the two sugar molecules. This chemical bond is a defining characteristic of compounds.
The chemical formula of sucrose is C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁. This fixed ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms highlights its nature as a compound. The properties of sucrose – its sweetness, solubility in water, and crystalline structure – are distinctly different from the properties of its constituent elements (carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen). You cannot simply mix carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen together and expect to get sucrose. A complex chemical reaction is required to form this compound.
Different Types of Sugar: Still Compounds
While sucrose is the most common type of sugar, other sugars exist, each a distinct compound. These include:
-
Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆): A monosaccharide, often called dextrose or grape sugar. It's a primary source of energy for living organisms.
-
Fructose (C₆H₁₂O₆): Another monosaccharide, found naturally in fruits and honey. It is the sweetest of all naturally occurring sugars.
-
Lactose (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁): A disaccharide found in milk, composed of glucose and galactose.
-
Maltose (C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁): A disaccharide composed of two glucose molecules, often found in germinating grains.
Each of these sugars has its unique chemical formula and properties, all confirming their classification as compounds. They are all formed through specific chemical reactions, and their constituent elements are chemically bonded.
Distinguishing Sugar from Mixtures
To further solidify the understanding of sugar as a compound, let's compare it to common mixtures:
-
Sugar dissolved in water: This is a mixture. The sugar molecules are dispersed within the water, but they are not chemically bonded to the water molecules. The sugar can be easily separated from the water through evaporation.
-
Sand and sugar: This is another mixture. The sugar and sand are physically mixed, but they are not chemically combined. They can be separated by methods like sieving or dissolving the sugar in water.
-
Honey: While honey contains various sugars like fructose and glucose, it's still technically a mixture. Apart from the sugars, it also contains water, enzymes, and other substances. These components aren't chemically bonded to the sugars, although the sugars themselves are compounds.
The key difference is the presence or absence of chemical bonds. In pure sugar, the constituent elements are chemically bonded, forming a distinct compound with its own unique properties. In mixtures containing sugar, the sugar molecules exist alongside other substances without forming chemical bonds.
The Importance of Understanding Sugar's Chemical Nature
Understanding that sugar is a compound, and not just a simple substance, has important implications across various fields:
-
Food Science and Technology: Understanding the chemical structure of different sugars allows food scientists to manipulate their properties, for example, to control sweetness, texture, and browning reactions during food processing.
-
Medicine and Biochemistry: The role of sugars in biological processes is critical. Glucose is the primary energy source for cells, and other sugars play essential roles in cellular structure and signaling pathways. Understanding their chemical structure is fundamental to understanding these biological processes.
-
Chemistry and Material Science: Sugar's chemical properties can be harnessed to create novel materials and applications. For example, sugar can be used as a starting material in the synthesis of other chemicals and as a component in some bioplastics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sugar is definitively a compound. Its constituent elements are chemically bonded in a fixed ratio, resulting in unique properties that differ from those of its individual components. While sugar can be part of mixtures, pure sugar itself is a compound, specifically a carbohydrate with a defined chemical structure and formula. Understanding this fundamental distinction is crucial for various scientific disciplines and everyday applications. The various types of sugars, all compounds themselves, highlight the complexity and multifaceted nature of this seemingly simple ingredient.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
X 2 6x 9 0 Graph
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 15 And 6
Mar 29, 2025
-
How Many Feet Are In A Hundred Yards
Mar 29, 2025
-
What Is The Mass In Grams Of 5 90 Mol C8h18
Mar 29, 2025
-
Whats The Atomic Number For Potassium
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sugar Is A Compound Or Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
