One Degree Celsius Is Equal To How Many Degrees Fahrenheit
listenit
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
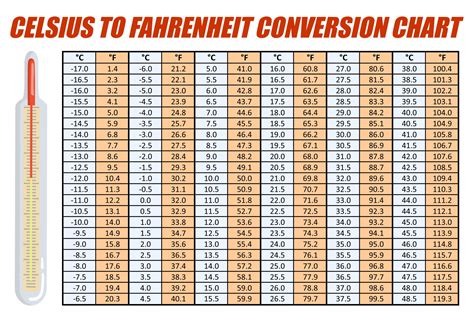
Table of Contents
One Degree Celsius is Equal to How Many Degrees Fahrenheit? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit is crucial for anyone working with temperature measurements, whether in scientific research, cooking, or simply checking the daily weather forecast. While seemingly straightforward, the conversion can be tricky if you don't grasp the underlying principles. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question "One degree Celsius is equal to how many degrees Fahrenheit?" but also delve into the history, formulas, and practical applications of this essential conversion.
The Fundamental Difference: Scales and Zero Points
The core difference between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) lies in their defining points: the freezing and boiling points of water. The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is based on the freezing point of water at 0°C and its boiling point at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. This creates a 100-degree interval between these two crucial points.
Conversely, the Fahrenheit scale sets the freezing point of water at 32°F and its boiling point at 212°F. This results in a 180-degree interval between these points. This difference in scale is the key to understanding the conversion. The non-linear relationship between the two scales means that a one-degree change in Celsius doesn't equate to a one-degree change in Fahrenheit.
The Conversion Formula: Unveiling the Magic
The most common and reliable method for converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit involves using a simple formula. To convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit, use this equation:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Let's break it down:
- °C: Represents the temperature in degrees Celsius.
- 9/5: This fraction accounts for the difference in the scale intervals between Celsius and Fahrenheit (180°F / 100°C = 9/5).
- + 32: This adds the offset required to account for the difference in the zero points between the two scales.
To illustrate, let's convert 1°C to Fahrenheit:
°F = (1°C × 9/5) + 32 = 33.8°F
Therefore, one degree Celsius is equal to 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit. This is crucial to remember for any accurate conversion.
Converting Fahrenheit to Celsius: The Reverse Operation
The reverse conversion, from Fahrenheit to Celsius, is equally important. The formula for this conversion is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
This formula reverses the process:
- °F - 32: First, we subtract 32 to align the zero points.
- × 5/9: Then, we multiply by 5/9 to adjust for the different scale intervals.
Let's try converting 33.8°F to Celsius:
°C = (33.8°F - 32) × 5/9 = 0.99°C (approximately 1°C)
This demonstrates the accuracy of the conversion formulas.
Practical Applications: Real-World Scenarios
Understanding the Celsius to Fahrenheit conversion is vital in various aspects of daily life and professional fields:
Weather Forecasting and Meteorology:
Many countries use either Celsius or Fahrenheit for weather reporting. Understanding the conversion ensures you can easily interpret weather forecasts from different sources or locations.
Cooking and Baking:
Recipes often specify temperatures in either Celsius or Fahrenheit. Knowing how to convert accurately is essential for baking and cooking success, especially when dealing with precise temperature requirements.
Medicine and Healthcare:
Temperature measurement is crucial in healthcare. Converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit ensures accurate communication and record-keeping between healthcare professionals and patients.
Science and Engineering:
Accurate temperature conversions are critical in scientific experiments, engineering design, and industrial processes where precise temperature control is necessary.
International Travel:
Familiarizing yourself with both scales is essential when traveling internationally, as different regions use different temperature scales.
Beyond the Formulas: Understanding the History
The development of both the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales is rich in history and reflects the evolution of scientific measurement.
Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, proposed a scale in 1742 where 0° represented the boiling point of water and 100° represented the freezing point. Later, this scale was reversed to its current form, with 0° representing the freezing point and 100° the boiling point.
Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German-Dutch physicist, introduced his scale around 1724. His scale's zero point was initially defined by a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride, while his 32° and 212° points corresponded to the freezing and boiling points of water, respectively.
The differences in their origins and defining points explain why the conversion between the two scales isn't as simple as a direct proportionality.
Advanced Concepts: Kelvin and Absolute Zero
While Celsius and Fahrenheit are commonly used, the Kelvin (K) scale is crucial in scientific contexts. The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale, meaning its zero point (0 K) represents absolute zero – the theoretical point at which all molecular motion ceases. This makes it particularly useful in thermodynamics and other scientific fields.
The relationship between Celsius and Kelvin is straightforward:
K = °C + 273.15
This simple addition allows for effortless conversion between the Celsius and Kelvin scales. Understanding the Kelvin scale provides a more complete picture of temperature measurement and its implications in various scientific domains.
Tips for Accurate Conversions and Avoiding Errors
While the formulas are straightforward, common mistakes can occur during conversions:
- Order of Operations: Ensure you follow the correct order of operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS) when calculating. Incorrect order can lead to significant errors.
- Fraction Calculation: Double-check your calculations involving the fractions 9/5 and 5/9.
- Unit Labeling: Always label your units (°C or °F) to avoid confusion and ensure clarity in your calculations.
- Calculator Use: If using a calculator, carefully enter the values and operations to minimize the risk of errors.
- Verification: When possible, verify your conversion using an online calculator or a different method to confirm accuracy.
Conclusion: Mastering the Conversion
Understanding the relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a fundamental skill with wide-ranging applications. By mastering the conversion formulas and appreciating the historical context, you'll not only be able to accurately convert between these two scales but also gain a deeper understanding of temperature measurement and its importance across various fields. Remember, the key to accurate conversion lies in the careful application of the formulas and attention to detail in your calculations. From weather forecasting to culinary arts, scientific research to everyday life, the ability to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit will enhance your understanding and efficiency in numerous situations. So, next time you encounter a temperature reading in a different scale, you'll be ready to tackle the conversion with confidence and accuracy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Does A Higher Specific Heat Mean
Apr 04, 2025
-
Question Plane Draw The Skeletal Structures
Apr 04, 2025
-
100 Yards On A Football Field
Apr 04, 2025
-
A Consumer That Eats Only Plants
Apr 04, 2025
-
The Amount Of Energy Required To Raise The Temperature
Apr 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about One Degree Celsius Is Equal To How Many Degrees Fahrenheit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
