Name The 2 Functional Groups In Amino Acids
listenit
Apr 02, 2025 · 7 min read
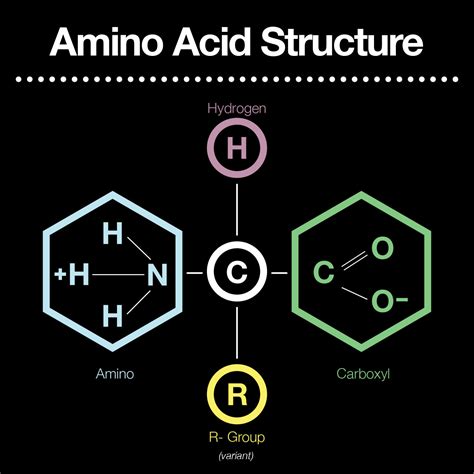
Table of Contents
Name the 2 Functional Groups in Amino Acids: A Deep Dive into the Building Blocks of Life
Amino acids, the fundamental building blocks of proteins, are organic compounds characterized by the presence of two crucial functional groups: the amino group (-NH2) and the carboxyl group (-COOH). Understanding the properties and roles of these functional groups is key to comprehending the diverse functions of amino acids and proteins in biological systems. This article delves deep into the characteristics of these functional groups, exploring their impact on amino acid properties and their crucial role in protein structure and function.
The Amino Group (-NH2): A Basic Building Block
The amino group, also known as the amine group, is a nitrogen-containing functional group that plays a pivotal role in the chemical behavior of amino acids. Its presence is responsible for the basic properties of amino acids.
Understanding the Chemistry of the Amino Group
The amino group consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms (-NH2). This structure allows the nitrogen atom to accept a proton (H+), thereby acting as a base. This basic nature is a defining characteristic of amino acids and significantly influences their behavior in solution.
The Role of the Amino Group in Peptide Bond Formation
The amino group's crucial role in protein synthesis lies in its participation in peptide bond formation. During protein synthesis, the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid. This reaction, a dehydration reaction (loss of a water molecule), forms a peptide bond, linking the two amino acids together. This process continues, resulting in the formation of long chains of amino acids, known as polypeptides, which ultimately fold into functional proteins.
The Amino Group's Influence on Amino Acid Properties
The presence of the amino group directly impacts several key properties of amino acids:
-
Solubility: The amino group contributes to the solubility of amino acids in water, due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules. This solubility is critical for their transport and interaction within the aqueous environment of cells.
-
pKa Value: The amino group has a characteristic pKa value, which represents the pH at which half of the amino groups are protonated and half are deprotonated. This pKa value is essential in determining the overall charge of an amino acid at a given pH.
-
Reactivity: The amino group's reactive nature allows it to participate in various chemical reactions, including acylation, alkylation, and other modifications. These modifications can alter the properties of amino acids and play a crucial role in post-translational modifications of proteins.
The Carboxyl Group (-COOH): An Acidic Contributor
The carboxyl group, also known as the carboxylic acid group, is another critical functional group found in all amino acids. Its presence is responsible for the acidic properties of amino acids.
Understanding the Chemistry of the Carboxyl Group
The carboxyl group consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom and single-bonded to a hydroxyl group (-OH). This structure allows the carboxyl group to readily donate a proton (H+), acting as an acid. This acidic property is just as critical as the basic property of the amino group in determining the overall behavior of amino acids.
The Role of the Carboxyl Group in Peptide Bond Formation
As previously mentioned, the carboxyl group plays a central role in peptide bond formation. The carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of the next amino acid, leading to the formation of the peptide bond and the release of a water molecule. This fundamental reaction is responsible for the synthesis of all proteins in living organisms.
The Carboxyl Group's Influence on Amino Acid Properties
Similar to the amino group, the carboxyl group significantly impacts various properties of amino acids:
-
Solubility: Like the amino group, the carboxyl group contributes to the solubility of amino acids in water. Its ability to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules is critical for amino acid transport and interaction within cells.
-
pKa Value: The carboxyl group has a characteristic pKa value, typically around 2. This pKa value is crucial in determining the net charge of the amino acid at a specific pH.
-
Reactivity: The carboxyl group's reactive nature allows it to participate in several chemical reactions, including esterification, amidation, and decarboxylation. These reactions play important roles in various metabolic pathways and protein modifications.
The Zwitterionic Nature of Amino Acids
The presence of both an amino group and a carboxyl group gives amino acids a unique characteristic: they are zwitterions. A zwitterion is a molecule that carries both positive and negative charges, but has an overall neutral charge.
At physiological pH (around 7.4), the amino group is protonated (positively charged, -NH3+), while the carboxyl group is deprotonated (negatively charged, -COO-). This results in a net neutral charge, even though the molecule possesses both positive and negative charges. This zwitterionic nature significantly influences the solubility and other physicochemical properties of amino acids.
The Importance of Side Chains (R-Groups)
While the amino and carboxyl groups are common to all amino acids, the side chain (R-group) is what differentiates one amino acid from another. The side chain's chemical properties dictate the unique characteristics of each amino acid, influencing its interactions within proteins and its overall contribution to protein structure and function.
The diversity of side chains leads to a wide range of amino acid properties, including:
-
Hydrophobic vs. Hydrophilic: Some side chains are hydrophobic (water-repelling), while others are hydrophilic (water-attracting). This property plays a crucial role in protein folding and interactions.
-
Charged vs. Uncharged: Some side chains carry a net charge (positive or negative) at physiological pH, while others are uncharged. These charges influence protein interactions and protein stability.
-
Aromatic vs. Aliphatic: Some side chains contain aromatic rings, while others are aliphatic (non-aromatic). These structural differences impact the interactions between amino acids and their contribution to protein structure.
The Impact of Functional Groups on Protein Structure and Function
The properties of the amino and carboxyl groups, combined with the diverse nature of side chains, dictate the overall properties of proteins. These properties are crucial for protein folding, stability, and function.
-
Protein Folding: The interactions between amino acid side chains, driven by hydrophobic and hydrophilic effects, guide the protein's folding process. The arrangement of amino acids and their functional groups determines the protein's three-dimensional structure.
-
Protein Stability: The interactions between amino acids, including hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, and disulfide bonds (involving cysteine side chains), contribute to the overall stability of the protein structure.
-
Protein Function: The specific arrangement of amino acids and their functional groups dictates the protein's function. Enzymes, for instance, have specific active sites containing amino acids with functional groups capable of catalyzing reactions. Other proteins have functional groups that enable them to bind to specific ligands, or carry out structural roles.
Conclusion: The Foundation of Life
In conclusion, the amino and carboxyl groups are indispensable functional groups within amino acids, forming the very foundation of protein structure and function. Their distinct chemical properties—the basic amino group and the acidic carboxyl group—play a crucial role in peptide bond formation, influence amino acid solubility and reactivity, and contribute significantly to the diverse properties observed in proteins. Understanding the chemical behavior of these functional groups is essential for comprehending the complexities of biological systems and the intricate machinery of life itself. Further investigation into the interplay of these functional groups, along with the diverse side chains, unravels the mechanisms underlying protein folding, stability, and the remarkable array of functions proteins perform in all living organisms. This foundational knowledge is crucial for advancing fields such as medicine, biotechnology, and materials science, where manipulating and understanding protein structure and function are key areas of research and development.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does The Period Come Before Or After The Quote
Apr 03, 2025
-
How Are Elements Arranged In The Modern Periodic Table
Apr 03, 2025
-
How To Integrate On A Ti 84
Apr 03, 2025
-
Two Lines Intersecting At A Right Angle
Apr 03, 2025
-
What Is 7 Out Of 15 As A Percentage
Apr 03, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Name The 2 Functional Groups In Amino Acids . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
