Molecular Mass Of Ca No3 2
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
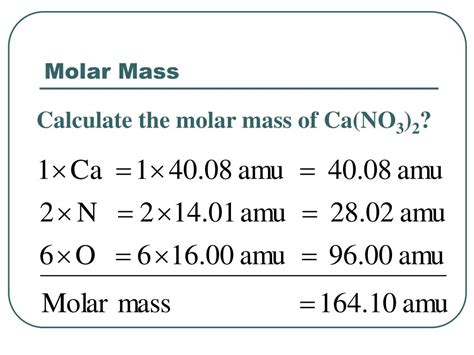
Table of Contents
Determining the Molecular Mass of Ca(NO₃)₂: A Comprehensive Guide
Calcium nitrate, with its chemical formula Ca(NO₃)₂, is a vital compound in various applications, ranging from fertilizers to pyrotechnics. Understanding its molecular mass is crucial for numerous chemical calculations and processes. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of determining the molecular mass of Ca(NO₃)₂, offering a step-by-step approach and exploring the underlying principles.
Understanding Molecular Mass
Before we delve into the calculation, let's establish a clear understanding of what molecular mass represents. The molecular mass (also known as molecular weight) is the mass of a molecule, expressed in atomic mass units (amu). It's essentially the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms constituting the molecule. This value is crucial for various stoichiometric calculations, including determining the number of moles, reacting ratios, and solution concentrations.
Atomic Mass vs. Atomic Number
It's vital to differentiate between atomic mass and atomic number. The atomic number represents the number of protons in an atom's nucleus, defining the element's identity. In contrast, the atomic mass (or atomic weight) reflects the average mass of an atom of an element, considering the different isotopes and their relative abundances. These atomic masses are readily available in the periodic table.
Calculating the Molecular Mass of Ca(NO₃)₂: A Step-by-Step Approach
To determine the molecular mass of Ca(NO₃)₂, we need to consider the atomic masses of each element present: Calcium (Ca), Nitrogen (N), and Oxygen (O). These values can be found on a periodic table. For our calculations, we will use the following approximate atomic masses:
- Ca (Calcium): 40.08 amu
- N (Nitrogen): 14.01 amu
- O (Oxygen): 16.00 amu
Now, let's break down the calculation step-by-step:
-
Identify the number of atoms of each element: In one molecule of Ca(NO₃)₂, we have:
- 1 Calcium atom (Ca)
- 2 Nitrogen atoms (2N)
- 6 Oxygen atoms (3O x 2 = 6O)
-
Multiply the atomic mass of each element by the number of atoms:
- Calcium: 1 Ca atom × 40.08 amu/Ca atom = 40.08 amu
- Nitrogen: 2 N atoms × 14.01 amu/N atom = 28.02 amu
- Oxygen: 6 O atoms × 16.00 amu/O atom = 96.00 amu
-
Sum the individual masses: Add the masses calculated in step 2 to obtain the total molecular mass:
40.08 amu + 28.02 amu + 96.00 amu = 164.10 amu
Therefore, the molecular mass of Ca(NO₃)₂ is approximately 164.10 amu.
Importance of Accurate Molecular Mass Determination
The accuracy of the molecular mass determination is paramount in various chemical applications. Inaccurate values can lead to significant errors in:
-
Stoichiometric Calculations: Incorrect molecular mass values will directly impact calculations involving moles, molarity, and reaction yields. This is crucial in quantitative analysis and synthesis.
-
Titrations: In acid-base titrations, precise molecular mass values are necessary for accurate concentration determination.
-
Spectroscopy: Molecular mass plays a role in interpreting spectroscopic data, particularly in mass spectrometry.
-
Crystallography: Accurate molecular mass is essential for determining crystal structures and unit cell parameters.
-
Formulation and Manufacturing: In industries like pharmaceuticals and fertilizers, accurate molecular mass is critical for precise formulation and quality control.
Beyond the Basic Calculation: Isotopes and Isotopic Abundance
The calculation above uses the average atomic masses from the periodic table. However, elements exist as a mixture of isotopes – atoms with the same number of protons but differing numbers of neutrons. This variation in neutron number slightly alters the atomic mass. To calculate a more precise molecular mass, one must consider the isotopic composition of each element.
For example, Calcium has several isotopes, including ⁴⁰Ca, ⁴²Ca, ⁴³Ca, ⁴⁴Ca, ⁴⁶Ca, and ⁴⁸Ca. Each isotope has a specific atomic mass and natural abundance. To calculate the molecular mass considering isotopes, you would need to:
-
Determine the isotopic composition: Find the percentage abundance of each isotope for all elements in the compound (Ca, N, and O). This information is available in isotopic abundance tables.
-
Calculate the weighted average atomic mass for each element: For each element, multiply the atomic mass of each isotope by its percentage abundance and sum these values. This will give you a more precise atomic mass to use in the molecular mass calculation.
-
Proceed with the standard molecular mass calculation: Use the weighted average atomic masses calculated in step 2 to perform the molecular mass calculation as described earlier. This calculation will yield a more accurate molecular mass than the one obtained using average atomic masses.
This more sophisticated approach provides a more precise molecular mass, particularly critical in high-precision analytical work.
Applications of Calcium Nitrate and the Relevance of its Molecular Mass
The precise molecular mass of Ca(NO₃)₂ is crucial in understanding and utilizing this important chemical compound. Ca(NO₃)₂ finds extensive application in various fields:
1. Agriculture:
- Fertilizer: Calcium nitrate is a valuable nitrogen and calcium source for plants. Knowing its molecular mass enables precise fertilizer formulation to provide optimal nutrient levels for different crops and soil conditions. Calculating the amount of nitrogen delivered per unit mass of fertilizer relies heavily on the accurate molecular mass.
2. Industrial Applications:
-
Concrete admixtures: It's used to accelerate setting time and improve the strength of concrete. Precise molecular mass calculations are vital for optimizing its concentration in these mixtures.
-
Pyrotechnics: Ca(NO₃)₂ is an oxidizer in fireworks, contributing to their vibrant colors. The correct stoichiometric ratios, dependent on its molecular mass, ensure controlled combustion and desired effects.
3. Laboratory and Research Applications:
-
Reagent: It serves as a reagent in various chemical reactions, requiring precise molar calculations for accurate results.
-
Standard Solutions: Its molecular mass is essential for preparing solutions of known concentrations.
Conclusion
Determining the molecular mass of Ca(NO₃)₂ is a fundamental exercise in chemistry with significant practical implications. While the basic calculation offers a good approximation, considering isotopic abundances provides a more precise value critical for accurate stoichiometric calculations and various applications across diverse fields. Understanding the principles involved ensures accurate results in experimental work and industrial processes, highlighting the importance of this seemingly simple calculation. The precise molecular mass is crucial for many chemical applications, highlighting its significance in various industries and scientific research. The detailed step-by-step approach outlined in this guide provides a clear and comprehensive understanding of how to calculate the molecular mass, ensuring accuracy and precision in related applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Pauli Exclusion Principle Aufbau Principle And Hunds Rule
Mar 18, 2025
-
1 3 Divided By 1 6
Mar 18, 2025
-
Integral Of X 3 Sqrt 1 X 2
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Percent Is 21 Of 30
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Are The Common Factors Of 36 And 24
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Molecular Mass Of Ca No3 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
