Is Speed A Vector Or A Scalar
listenit
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
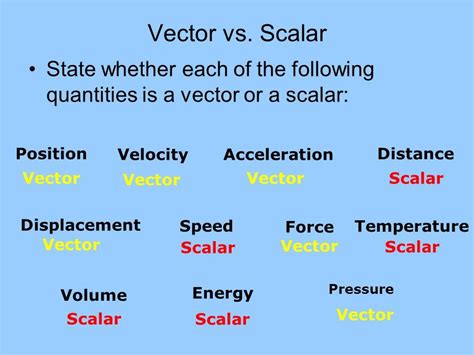
Table of Contents
Is Speed a Vector or a Scalar? Understanding the Difference
The question of whether speed is a vector or a scalar is a fundamental concept in physics that often causes confusion. While seemingly simple, understanding the distinction is crucial for grasping more complex physics concepts. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the definitions of scalars and vectors, explore the nature of speed and velocity, and clarify why speed is definitively a scalar quantity.
Scalars vs. Vectors: A Fundamental Distinction
Before tackling the speed question directly, let's establish a clear understanding of scalars and vectors. These are two fundamental classifications of physical quantities:
Scalars: Magnitude Only
A scalar quantity is defined solely by its magnitude. It's a single number, often accompanied by a unit. Think of things like temperature (25°C), mass (70 kg), or energy (100 Joules). These quantities don't have a direction associated with them. You simply state their value, and that's all there is to it.
Vectors: Magnitude and Direction
A vector quantity, on the other hand, possesses both magnitude and direction. This means it requires more information to fully describe it. Examples include displacement (5 meters east), velocity (20 m/s north), and force (10 Newtons upward). The direction is an integral part of the vector's definition. Changing the direction changes the vector itself, even if the magnitude remains the same.
Key Differences Summarized:
| Feature | Scalar | Vector |
|---|---|---|
| Magnitude | Only magnitude | Magnitude and direction |
| Representation | Single number with unit | Arrow (length = magnitude, direction = arrow pointing) |
| Examples | Mass, temperature, energy | Displacement, velocity, force |
Speed and Velocity: A Closer Look
Now, let's focus on speed and velocity. These two quantities are often confused, but understanding their differences is essential to understanding why speed is a scalar.
Speed: The Scalar Measure of Rate of Motion
Speed is the scalar measure of how quickly an object is moving. It only tells us the rate at which the distance covered changes over time. The formula for speed is:
Speed = Distance / Time
For instance, if a car travels 100 kilometers in 2 hours, its speed is 50 km/h. Notice that we don't specify a direction. The speed is simply 50 km/h. This is a magnitude only, making it a scalar.
Velocity: The Vector Measure of Rate of Motion
Velocity, in contrast, is the vector quantity that describes both the rate of motion and its direction. It's the rate of change of displacement (which is also a vector) over time. The formula is:
Velocity = Displacement / Time
The crucial difference lies in the use of displacement instead of distance. Displacement is a vector that represents the change in position from the starting point to the ending point, regardless of the path taken. Distance, on the other hand, is the total length of the path traveled.
Consider a runner completing a 400-meter lap on a track. Their distance is 400 meters. However, their displacement is zero because they end up back where they started. Therefore, their average speed over that lap is non-zero while their average velocity is zero. This clearly illustrates that speed and velocity are different quantities.
Why Speed is a Scalar: A Concrete Example
Let's illustrate this with an example. Imagine a car driving around a circular track at a constant speed of 60 km/h. At any given moment, the car's speed remains 60 km/h. However, its velocity is constantly changing because the direction of motion is constantly changing. The magnitude of the velocity might be 60 km/h, but the direction is always tangential to the circular path.
This example perfectly highlights the difference. The speed remains constant, a single numerical value (scalar), while the velocity is constantly changing because the direction of movement is changing (vector).
Advanced Concepts: Instantaneous Speed and Velocity
The concepts of instantaneous speed and velocity further clarify the distinction. Instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at a particular instant in time. It's the magnitude of the instantaneous velocity. Instantaneous velocity is the velocity at a specific instant, including both magnitude and direction.
Imagine a rollercoaster. At the peak of a hill, the instantaneous speed might be close to zero, but its instantaneous velocity is also close to zero. However, as it starts down the hill, the instantaneous speed increases, and the instantaneous velocity vector points downwards.
Applications in Physics and Engineering
Understanding the difference between speed and velocity is crucial for various applications:
- Navigation: GPS systems utilize velocity to determine the position and direction of movement.
- Projectile motion: Calculating the trajectory of a projectile requires considering both velocity and acceleration, which are vector quantities.
- Fluid dynamics: Analyzing fluid flow involves understanding velocity fields, which are vector fields describing the velocity at each point in the fluid.
- Engineering design: Designing structures and machines necessitates considering the forces acting upon them, which are vector quantities.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
A common misconception is that speed is simply the magnitude of velocity. While this is true in many cases, it's not always strictly accurate. For example, consider a situation with non-uniform motion where an object accelerates, decelerates, or changes directions frequently.
The total distance divided by total time will give you the average speed. However, due to the changes in direction and magnitude, the average velocity might be smaller (or even zero, in the case of a round trip). Therefore, the average speed isn't simply the magnitude of the average velocity in these scenarios.
Conclusion: Speed's Scalar Identity
In conclusion, speed is unequivocally a scalar quantity. It's a measure of how fast something is moving, regardless of the direction. Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that incorporates both speed and direction. Understanding this fundamental distinction is vital for mastering physics and its many applications in various fields. By grasping the concept of scalars and vectors, you'll gain a much clearer understanding of the physical world around us. While they may seem like minor details, these distinctions are the foundation upon which a deep understanding of physics is built.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Millimeters In 6 Centimeters
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is 1 4 Of A Pound
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Half Life Of Cobalt 60 Is 5 26 Years
Mar 18, 2025
-
Why Are Covalent Compounds Not Conductive
Mar 18, 2025
-
28 5g Of Iron Shot Is Added To A
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Speed A Vector Or A Scalar . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
