Is Melting Ice A Chemical Reaction
listenit
Mar 31, 2025 · 4 min read
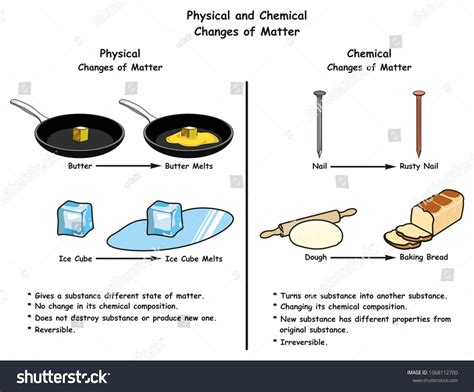
Table of Contents
Is Melting Ice a Chemical Reaction? Understanding Physical vs. Chemical Changes
The question, "Is melting ice a chemical reaction?" is a deceptively simple one that touches upon fundamental concepts in chemistry and physics. The short answer is no, melting ice is not a chemical reaction. It's a physical change. However, understanding why it's a physical change requires a deeper dive into the nature of matter, phases of matter, and the differences between physical and chemical transformations. This article will explore these concepts thoroughly, addressing common misconceptions and providing a comprehensive understanding of the melting process.
Understanding the Nature of Matter and Phases
Matter exists in various states or phases, the most common being solid, liquid, and gas. These phases are defined by the arrangement and movement of the constituent particles (atoms or molecules).
-
Solids: In solids, particles are tightly packed together in a fixed arrangement, exhibiting strong intermolecular forces. This results in a definite shape and volume.
-
Liquids: Liquids have particles that are close together but not in a fixed arrangement. Intermolecular forces are weaker than in solids, allowing particles to move and slide past each other. Liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container.
-
Gases: Gases have particles that are far apart and move randomly with high kinetic energy. Intermolecular forces are very weak, resulting in indefinite shape and volume. Gases expand to fill their container.
The Process of Melting Ice: A Physical Change
Melting ice is a transition from the solid (ice) phase to the liquid (water) phase. During melting, the intermolecular forces between water molecules weaken, but the chemical composition remains unchanged. Each water molecule (H₂O) retains its two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. No new molecules are formed, and no existing molecules are broken down.
What Happens at a Molecular Level?
As heat is applied to ice, the kinetic energy of the water molecules increases. This increased kinetic energy overcomes the intermolecular forces (hydrogen bonds) holding the molecules in a rigid crystalline structure. The molecules gain more freedom of movement, transitioning from the ordered arrangement of a solid to the more disordered arrangement of a liquid. This process is reversible. By lowering the temperature, the kinetic energy decreases, and the water molecules return to their ordered solid state, forming ice again.
Key Differences Between Physical and Chemical Changes
The distinction between a physical change and a chemical change is crucial:
-
Physical Change: A physical change alters the form or appearance of a substance but does not change its chemical composition. Examples include melting, freezing, boiling, condensation, dissolving (in many cases), and changes in shape or size. Physical changes are often reversible.
-
Chemical Change (Chemical Reaction): A chemical change involves a rearrangement of atoms and molecules, resulting in the formation of new substances with different chemical properties. Examples include burning, rusting, digestion, and cooking. Chemical changes are often irreversible.
In the case of melting ice, only the physical state changes; the chemical identity remains the same. This is a hallmark of a physical change.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Several misconceptions surround the melting of ice:
-
Misconception 1: Melting involves a chemical reaction because heat is involved. Heat is required for many physical changes, not just chemical reactions. Heat simply provides the energy needed to overcome the intermolecular forces.
-
Misconception 2: The change in state is a chemical change because the properties of ice and water differ. While the properties differ (ice is solid, water is liquid), the chemical composition remains the same (H₂O). The change in properties is a consequence of the change in state, not a chemical transformation.
-
Misconception 3: Because water can be electrolyzed to produce hydrogen and oxygen, melting ice is a chemical change. Electrolysis is a completely different process involving the application of an electric current to break water molecules into their constituent elements. This is a chemical reaction, entirely distinct from the simple physical process of melting.
Further Exploring Phase Transitions
The melting of ice is just one example of a phase transition. Other phase transitions include:
- Freezing: Liquid to solid
- Boiling/Vaporization: Liquid to gas
- Condensation: Gas to liquid
- Sublimation: Solid to gas (e.g., dry ice)
- Deposition: Gas to solid (e.g., frost formation)
All these transitions are physical changes, involving alterations in the arrangement and movement of particles but not changes in chemical composition.
The Importance of Understanding Physical Changes
Understanding the difference between physical and chemical changes is essential in various fields:
- Chemistry: For comprehending the behavior of matter and predicting reactions.
- Materials Science: For designing and synthesizing materials with specific properties.
- Engineering: For selecting appropriate materials for various applications.
- Environmental Science: For understanding environmental processes, such as melting glaciers and sea ice.
Conclusion: Melting Ice – A Physical Phenomenon
To reiterate, melting ice is definitively a physical change, not a chemical reaction. The process involves a transition in the state of matter from solid to liquid due to an increase in kinetic energy overcoming intermolecular forces. The chemical identity of the substance—water (H₂O)—remains unchanged throughout the entire process. Understanding this fundamental difference is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of the physical world. By clearly distinguishing between physical and chemical transformations, we can better appreciate the intricacies of matter and its various forms. This knowledge is fundamental to various scientific disciplines and has significant implications in many areas of life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm For 6 And 10
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Organelles Supply Energy To The Cell
Apr 02, 2025
-
Why Is Density A Physical Property
Apr 02, 2025
-
Is Koh A Base Or Acid
Apr 02, 2025
-
Why Did Small States Object To The Virginia Plan
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Melting Ice A Chemical Reaction . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
