Integral Of Sqrt 9 X 2
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 4 min read
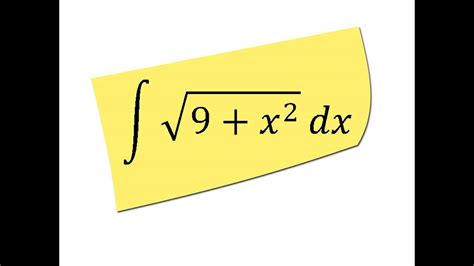
Table of Contents
Decoding the Definite Integral of √(9x²): A Comprehensive Guide
The definite integral of √(9x²) presents a seemingly straightforward challenge, yet its solution unfolds a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of solving this integral, exploring various methods, highlighting potential pitfalls, and illustrating the process with detailed examples. We will not only solve the integral but also understand the underlying principles, empowering you to tackle similar problems with confidence.
Understanding the Problem:
The expression √(9x²) represents the square root of a quadratic function. Before jumping into integration, let's simplify it:
√(9x²) = √(9) * √(x²) = 3|x|
Notice the absolute value sign around 'x'. This is crucial. The square root of a squared number is always non-negative. Therefore, we must account for the sign of 'x'. This seemingly small detail significantly impacts the solution, especially when dealing with definite integrals over intervals that include both positive and negative values of 'x'.
Method 1: Direct Integration using Absolute Value
The most straightforward approach involves directly integrating the simplified expression:
∫ 3|x| dx
This integral requires careful consideration of the absolute value function. We must split the integral based on the sign of 'x':
-
For x ≥ 0: |x| = x, so the integral becomes ∫ 3x dx = (3/2)x² + C
-
For x < 0: |x| = -x, so the integral becomes ∫ -3x dx = -(3/2)x² + C
Therefore, the indefinite integral is a piecewise function:
∫ 3|x| dx = (3/2)x² if x ≥ 0 -(3/2)x² if x < 0
Method 2: Definite Integral Evaluation
Let's consider a definite integral, for example:
∫<sub>-2</sub><sup>2</sup> 3|x| dx
To evaluate this, we must split the integral into two parts, based on the absolute value:
∫<sub>-2</sub><sup>2</sup> 3|x| dx = ∫<sub>-2</sub><sup>0</sup> -3x dx + ∫<sub>0</sub><sup>2</sup> 3x dx
Now we can integrate each part:
∫<sub>-2</sub><sup>0</sup> -3x dx = [- (3/2)x²]<sub>-2</sub><sup>0</sup> = 0 - [-(3/2)(-2)²] = 6
∫<sub>0</sub><sup>2</sup> 3x dx = [(3/2)x²]<sub>0</sub><sup>2</sup> = (3/2)(2)² - 0 = 6
Therefore, the definite integral is:
∫<sub>-2</sub><sup>2</sup> 3|x| dx = 6 + 6 = 12
Method 3: Graphical Interpretation
Visualizing the problem graphically can provide valuable insight. The function y = 3|x| represents two lines: y = 3x for x ≥ 0 and y = -3x for x < 0. The definite integral represents the area under the curve. For the integral ∫<sub>-2</sub><sup>2</sup> 3|x| dx, this area consists of two triangles, each with base 2 and height 6. The total area, and hence the integral, is 2 * (1/2) * 2 * 6 = 12. This confirms our previous result.
Addressing Common Mistakes and Challenges:
Several common errors can arise when dealing with the integral of √(9x²):
-
Ignoring the Absolute Value: Forgetting the absolute value of x leads to an incorrect result, especially for definite integrals over intervals that include both positive and negative values.
-
Incorrect Simplification: Incorrectly simplifying the square root can lead to significant errors in the integration process. Remember the rules for simplifying square roots and always account for the domain of the function.
-
Improper Application of Integration Techniques: Using inappropriate integration techniques, like ignoring the piecewise nature of the absolute value function when evaluating definite integrals, can yield inaccurate results.
Extending the Concepts:
The techniques discussed above extend to more complex integrals involving the square root of quadratic functions. For example, consider:
∫ √(ax² + bx + c) dx
Solving this generally involves completing the square, trigonometric substitution, or other advanced integration techniques, depending on the values of a, b, and c.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios:
Integrals involving square roots of quadratic functions appear frequently in various applications:
-
Physics: Calculating the arc length of a curve, work done by a variable force, or the area under a parabolic trajectory.
-
Engineering: Determining the volume of solids of revolution or the centroid of a plane region.
-
Economics: Modeling economic phenomena where quadratic relationships are involved.
Conclusion:
The integral of √(9x²) = 3|x| requires careful attention to detail, particularly regarding the absolute value function. Understanding the piecewise nature of this function is paramount for accurately evaluating both indefinite and definite integrals. By employing the methods outlined in this guide, and understanding the potential pitfalls, you can confidently tackle similar integrals and expand your knowledge of calculus. Remember, visualization through graphical interpretation can provide a powerful intuitive understanding of the problem and its solution. Mastering this concept forms a strong foundation for tackling more intricate integration problems encountered in higher-level mathematics and real-world applications. The key is to break down complex problems into manageable steps, applying the appropriate techniques systematically, and always verifying your results using different methods where possible. This thorough approach ensures accuracy and develops a deep understanding of the underlying mathematical principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Is Bigger 2 3 Or 3 4
Mar 19, 2025
-
Why Do Chemical Equations Need To Be Balanced
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Does The Cell Membrane Help Maintain Homeostasis
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are Columns Of The Periodic Table Called
Mar 19, 2025
-
X 4 X 2 3x 2
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Integral Of Sqrt 9 X 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
