How To Find Vertex In Factored Form
listenit
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
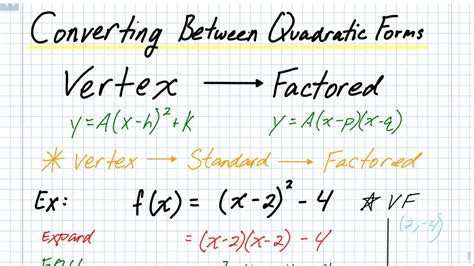
Table of Contents
How to Find the Vertex of a Quadratic Function in Factored Form
Finding the vertex of a quadratic function is a crucial step in graphing the parabola and understanding its key features. The vertex represents the minimum or maximum point of the parabola, depending on whether the parabola opens upwards (positive leading coefficient) or downwards (negative leading coefficient). While the vertex form of a quadratic equation readily reveals the vertex, many quadratic equations are presented in factored form. This article will thoroughly guide you through several methods to efficiently find the vertex of a quadratic function expressed in factored form, complete with examples and explanations.
Understanding Quadratic Functions and Their Forms
A quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree two, generally represented as:
f(x) = ax² + bx + c
where 'a', 'b', and 'c' are constants, and 'a' is not equal to zero. This is the standard form. Another common form is the vertex form:
f(x) = a(x - h)² + k
where (h, k) represents the coordinates of the vertex. Finally, we have the factored form:
f(x) = a(x - r₁)(x - r₂)
where r₁ and r₂ are the x-intercepts (roots) of the quadratic function. It's from this factored form that we'll learn to extract the vertex information.
Method 1: Converting to Standard Form and Using the Vertex Formula
The most straightforward approach to find the vertex from the factored form involves converting the equation back into standard form and then employing the vertex formula.
Steps:
-
Expand the Factored Form: Multiply out the factors to obtain the standard form ax² + bx + c.
-
Apply the Vertex Formula: The x-coordinate of the vertex is given by:
x = -b / 2a
-
Substitute: Substitute the x-coordinate back into the original factored form (or the standard form) to find the y-coordinate of the vertex.
Example:
Let's consider the quadratic function f(x) = 2(x - 1)(x - 5).
-
Expand: f(x) = 2(x² - 6x + 5) = 2x² - 12x + 10. Now we have the standard form with a = 2, b = -12, and c = 10.
-
Vertex Formula: x = -(-12) / (2 * 2) = 12 / 4 = 3
-
Substitute: f(3) = 2(3 - 1)(3 - 5) = 2(2)(-2) = -8
Therefore, the vertex is (3, -8).
Method 2: Using the Axis of Symmetry and the Midpoint of the x-intercepts
The factored form directly provides the x-intercepts (roots). The x-coordinate of the vertex lies exactly midway between these intercepts.
Steps:
-
Identify the x-intercepts: From the factored form a(x - r₁)(x - r₂), the x-intercepts are r₁ and r₂.
-
Find the midpoint: The x-coordinate of the vertex is the average of the x-intercepts:
x = (r₁ + r₂) / 2
-
Substitute: Substitute this x-coordinate into the factored form to find the y-coordinate of the vertex.
Example:
Using the same function f(x) = 2(x - 1)(x - 5), we have:
-
x-intercepts: r₁ = 1 and r₂ = 5
-
Midpoint: x = (1 + 5) / 2 = 3
-
Substitute: f(3) = 2(3 - 1)(3 - 5) = -8
Again, the vertex is (3, -8). This method is significantly faster and more intuitive than converting to standard form.
Method 3: Completing the Square (for more complex factored forms)
While less direct than the previous methods, completing the square can be helpful for more complex factored forms or when dealing with fractions or decimals in the intercepts.
Steps:
-
Expand the factored form: Begin by expanding the factored form into standard form, ax² + bx + c.
-
Complete the square: Manipulate the equation to achieve the vertex form a(x - h)² + k. This involves factoring out 'a' from the x² and x terms, then adding and subtracting the appropriate constant to create a perfect square trinomial.
-
Identify the vertex: Once in vertex form, the vertex is directly identifiable as (h, k).
Example:
Let's consider a more complex example: f(x) = 3(x + 1/2)(x - 3/4).
-
Expand: f(x) = 3(x² - 3/4x + 1/2x - 3/8) = 3(x² - 1/4x - 3/8) = 3x² - 3/4x - 9/8
-
Complete the square: f(x) = 3(x² - 1/4x) - 9/8 f(x) = 3(x² - 1/4x + 1/64 - 1/64) - 9/8 f(x) = 3((x - 1/8)² - 1/64) - 9/8 f(x) = 3(x - 1/8)² - 3/64 - 9/8 f(x) = 3(x - 1/8)² - 75/64
-
Identify the vertex: The vertex is (1/8, -75/64).
Choosing the Best Method
The most efficient method depends on the specific quadratic function.
- For simple factored forms with integer intercepts: Method 2 (using the midpoint of x-intercepts) is the quickest and most straightforward.
- For complex factored forms or when dealing with fractions/decimals: Method 1 (converting to standard form and using the vertex formula) or Method 3 (completing the square) might be more suitable, depending on your comfort level with algebraic manipulations.
Practical Applications and Further Exploration
Understanding how to find the vertex of a quadratic function in factored form is crucial in various applications, including:
- Graphing parabolas: The vertex is the turning point of the parabola, essential for accurately sketching its graph.
- Optimization problems: In many real-world scenarios, quadratic functions model optimization problems (e.g., maximizing profit or minimizing cost). The vertex represents the optimal point.
- Projectile motion: The trajectory of a projectile often follows a parabolic path, and the vertex represents the maximum height reached.
- Quadratic regression analysis: In statistics, quadratic regression involves fitting a quadratic model to data. Finding the vertex helps interpret the model's predictions.
Further exploration could include:
- Investigating the relationship between the discriminant and the nature of the vertex: The discriminant (b² - 4ac) determines whether the parabola intersects the x-axis at two distinct points, one point (vertex on the x-axis), or no points (vertex above or below the x-axis).
- Exploring the impact of the leading coefficient 'a' on the vertex and the parabola's orientation: A positive 'a' indicates a parabola opening upwards (minimum point), while a negative 'a' indicates a parabola opening downwards (maximum point). The magnitude of 'a' affects the parabola's width.
- Applying these techniques to solve word problems involving quadratic equations: This helps solidify your understanding of the concepts and their practical applications.
By mastering these methods, you'll gain a deeper understanding of quadratic functions and their behavior, enabling you to solve various mathematical and real-world problems effectively. Remember to choose the method that best suits the complexity of the given factored form. Practice is key to mastering these techniques.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Orbitals Are In The S Sublevel
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Much Is In A Half Gallon
Mar 19, 2025
-
40 Is What Percent Of 200
Mar 19, 2025
-
3 Inches Is How Many Centimeters
Mar 19, 2025
-
9 Ounces Equals How Many Cups
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find Vertex In Factored Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
