How Many Valence Electrons Sodium Have
listenit
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
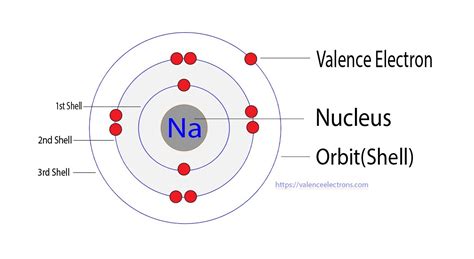
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Does Sodium Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Understanding the number of valence electrons an atom possesses is crucial for comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. This article will delve deep into the fascinating world of atomic structure, focusing specifically on sodium (Na) and its valence electrons. We'll explore the concepts of electron shells, electron configurations, and the significance of valence electrons in chemical bonding. By the end, you'll not only know how many valence electrons sodium has but also grasp the underlying principles that govern its reactivity.
Understanding Valence Electrons: The Key to Chemical Bonding
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons in an atom. They are the electrons most involved in chemical reactions and bonding. These electrons occupy the highest energy level, often referred to as the valence shell. The number of valence electrons an atom possesses directly dictates its bonding capacity and determines the type of chemical bonds it can form (ionic, covalent, or metallic).
Atoms strive for stability, usually achieved by having a full valence shell. This is often referred to as the "octet rule," where atoms aim to have eight electrons in their outermost shell (exceptions exist, particularly for elements in the first and second rows of the periodic table). This drive for stability is the fundamental reason behind chemical reactions and the formation of compounds.
Sodium's Position on the Periodic Table: A Clue to its Valence Electrons
Sodium (Na), with an atomic number of 11, is located in Group 1 (also known as Alkali Metals) of the periodic table. The periodic table is organized in a way that reveals important information about an element's electron configuration and chemical properties. The group number for main group elements directly indicates the number of valence electrons.
Therefore, sodium, being in Group 1, has one valence electron.
Electron Configuration: Unveiling Sodium's Electron Arrangement
To understand why sodium has one valence electron, let's explore its electron configuration. The electron configuration describes how electrons are distributed among the different energy levels and sublevels within an atom. Sodium's electron configuration is: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s¹.
Let's break this down:
- 1s²: Two electrons occupy the 1s orbital (lowest energy level).
- 2s²: Two electrons occupy the 2s orbital.
- 2p⁶: Six electrons occupy the three 2p orbitals.
- 3s¹: One electron occupies the 3s orbital.
The 3s¹ electron is the outermost electron, residing in the highest energy level (n=3). This solitary electron in the 3s orbital is sodium's valence electron.
The Significance of Sodium's Single Valence Electron
The presence of only one valence electron has profound consequences for sodium's chemical behavior:
-
High Reactivity: Sodium readily loses its single valence electron to achieve a stable octet configuration, resembling the noble gas neon (Ne). This electron loss forms a positively charged sodium ion (Na⁺).
-
Ionic Bonding: Sodium's tendency to lose an electron makes it highly reactive and prone to forming ionic bonds with nonmetals, particularly halogens (Group 17 elements) like chlorine (Cl). The ionic bond results from the electrostatic attraction between the positively charged sodium ion (Na⁺) and the negatively charged chloride ion (Cl⁻), forming sodium chloride (NaCl), or common table salt.
-
Metallic Bonding: Sodium also exhibits metallic bonding in its pure elemental form. Metallic bonding arises from the delocalized valence electrons that are shared among a lattice of positively charged sodium ions. This allows for the characteristic properties of metals, such as electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, and ductility.
Visualizing Sodium's Atomic Structure: Electron Shells and Orbitals
To further solidify the understanding of sodium's valence electron, let's visualize its atomic structure. We can represent the atom using a simplified model showing electron shells:
- Shell 1: Contains two electrons (1s²)
- Shell 2: Contains eight electrons (2s²2p⁶)
- Shell 3: Contains one electron (3s¹) – this is the valence shell.
The single electron in the outermost shell (Shell 3) is easily lost, explaining sodium's reactivity and the formation of Na⁺ ions.
Sodium's Role in Biological Systems: Importance of Valence Electrons
The reactivity of sodium, stemming from its single valence electron, plays a vital role in biological systems. Sodium ions (Na⁺) are crucial for various physiological processes:
-
Nerve Impulse Transmission: The movement of sodium ions across cell membranes is essential for generating and transmitting nerve impulses.
-
Muscle Contraction: Sodium ions are involved in muscle contraction and relaxation.
-
Fluid Balance: Sodium ions contribute to maintaining the balance of fluids within and outside cells.
These crucial biological functions highlight the importance of understanding sodium's atomic structure and its single valence electron.
Beyond Sodium: Understanding Valence Electrons Across the Periodic Table
The principles discussed for sodium apply to other elements as well. The number of valence electrons determines the reactivity and bonding characteristics of all elements. Understanding periodic trends in valence electrons helps predict the properties of elements and the types of compounds they can form.
Conclusion: Sodium's Single Valence Electron – A Powerful Determinant of its Properties
In conclusion, sodium (Na) possesses one valence electron. This seemingly simple fact dictates its high reactivity, its tendency to form ionic bonds, its participation in metallic bonding, and its crucial roles in biological systems. The study of valence electrons is fundamental to understanding the chemical behavior and properties of all elements, forming the cornerstone of chemistry. This single electron holds the key to understanding much of sodium's fascinating and essential chemistry. Further exploration into atomic structure and electron configuration will deepen your understanding of the periodic table and the remarkable diversity of chemical behavior exhibited by the elements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 36 And 12
Apr 02, 2025
-
Greatest Common Factor Of 24 And 42
Apr 02, 2025
-
What 3 Particles Make Up An Atom
Apr 02, 2025
-
Blood Is What Type Of Mixture
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is The Empirical Formula Of Ibuprofen
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Sodium Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
