How Many Valence Electrons Are In Zinc
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
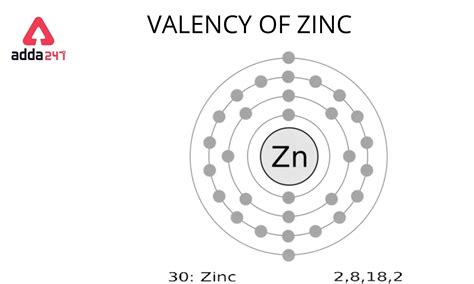
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Are in Zinc? A Deep Dive into Zinc's Electronic Structure
Zinc, a ubiquitous element crucial in numerous biological processes and industrial applications, holds a unique position in the periodic table. Understanding its electronic structure, particularly the number of valence electrons, is fundamental to comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. This in-depth article will explore the question: How many valence electrons are in zinc? We'll delve into the intricacies of its electron configuration, its role in chemical bonding, and its significance in various fields.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Before we pinpoint the number of valence electrons in zinc, let's establish a clear understanding of what valence electrons are. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are the primary players in chemical bonding, determining an element's reactivity and the types of bonds it can form. They are responsible for the element's chemical properties and how it interacts with other atoms.
The number of valence electrons is crucial in predicting an element's behavior. Elements with similar valence electron numbers often exhibit similar chemical properties, a principle neatly organized in the periodic table. This is why elements within the same group (vertical column) of the periodic table share similar chemical characteristics.
Zinc's Electronic Configuration: Unraveling the Mystery
Zinc (Zn) has an atomic number of 30, meaning a neutral zinc atom contains 30 protons and 30 electrons. To determine the number of valence electrons, we need to examine its electron configuration. The electron configuration describes how electrons are distributed among the different energy levels (shells) and sub-shells within an atom.
The electron configuration of zinc is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d¹⁰. This seemingly complex notation represents the distribution of electrons across various orbitals.
-
1s², 2s², 2p⁶, 3s², 3p⁶: These represent the inner electron shells, completely filled with electrons. These electrons are tightly bound to the nucleus and generally do not participate in chemical bonding.
-
4s²3d¹⁰: These are the outermost electrons. While the 3d subshell is filled, it's crucial to understand that for many purposes, particularly concerning chemical bonding, the 4s electrons are considered the valence electrons.
Why 4s Electrons Are Considered Valence Electrons in Zinc
The conventional wisdom, and the simplest explanation, is that the 4s electrons are higher in energy than the 3d electrons and therefore more readily available for participation in chemical reactions. Thus, even though the 3d subshell is also fully filled, the 4s electrons are the ones that dictate zinc's chemical behavior.
However, a slightly more nuanced understanding is needed. The energy levels are not always strictly separated. In transition metals, like zinc, the energy difference between the 4s and 3d orbitals is relatively small. The 3d electrons can, under certain circumstances, participate in bonding. This is often observed in coordination compounds. Nevertheless, for a basic understanding of zinc's valence electrons, considering only the 4s electrons as valence electrons is a perfectly reasonable approximation.
The Definitive Answer: Two Valence Electrons
Based on the above analysis, the answer to the question "How many valence electrons are in zinc?" is two. The two electrons in the 4s orbital are the valence electrons responsible for zinc's chemical reactivity and bonding characteristics.
Zinc's Chemical Behavior: A Consequence of Two Valence Electrons
Zinc's two valence electrons explain its characteristic chemical behavior:
-
Relatively low reactivity: Unlike alkali metals with one valence electron, zinc's filled d-subshell contributes to its relatively low reactivity. The filled subshells provide stability.
-
Formation of Zn²⁺ ions: Zinc readily loses its two valence electrons to achieve a stable, filled electron configuration, forming a Zn²⁺ ion. This is a highly common oxidation state for zinc.
-
Coordination complexes: The Zn²⁺ ion is a Lewis acid, readily accepting electron pairs from ligands to form coordination complexes. This property is extensively used in various chemical and biological systems.
-
Metallic bonding: In metallic zinc, the valence electrons are delocalized, creating a "sea" of electrons that contribute to the metal's unique properties like electrical conductivity and malleability.
Zinc's Importance: Applications Across Diverse Fields
Zinc's unique properties, stemming from its electron configuration and two valence electrons, make it an indispensable element in a wide range of applications:
-
Biological Roles: Zinc is an essential trace element in numerous biological processes. It's a crucial component of many enzymes, playing a vital role in DNA synthesis, cell growth, and immune function.
-
Galvanization: Zinc's protective properties are exploited in galvanization, a process of coating iron or steel with zinc to prevent rust. This is a critical method in construction and manufacturing.
-
Brass and Other Alloys: Zinc is a primary component of brass, an alloy with copper, possessing improved strength and workability. It's also used in numerous other alloys.
-
Die-casting: Zinc's low melting point and ability to flow well make it ideal for die-casting, a process for producing intricate metal parts.
-
Batteries: Zinc is utilized in various battery technologies, including dry-cell batteries, due to its ability to readily lose electrons and participate in redox reactions.
Conclusion: A Deeper Understanding of Zinc
Understanding the number of valence electrons in zinc is paramount to grasping its chemical behavior and diverse applications. Its two valence electrons dictate its relatively low reactivity, its tendency to form Zn²⁺ ions, and its participation in various chemical and biological processes. From its role in protecting infrastructure through galvanization to its essential contributions to biological systems, zinc's significance is undeniable, a testament to the profound impact of a seemingly simple aspect of its atomic structure – its two valence electrons. This detailed exploration highlights the interconnectedness of atomic structure, chemical properties, and real-world applications, underscoring the importance of understanding fundamental concepts in chemistry. The seemingly simple question of how many valence electrons are in zinc opens a fascinating doorway into the complex world of materials science and biochemistry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Centimeters In 4 Meters
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 10
Mar 20, 2025
-
3 Equivalent Fractions For 3 8
Mar 20, 2025
-
1 Meter Is How Many Nanometers
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Are Reactants And Products Of Photosynthesis
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Are In Zinc . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
