1 Meter Is How Many Nanometers
listenit
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
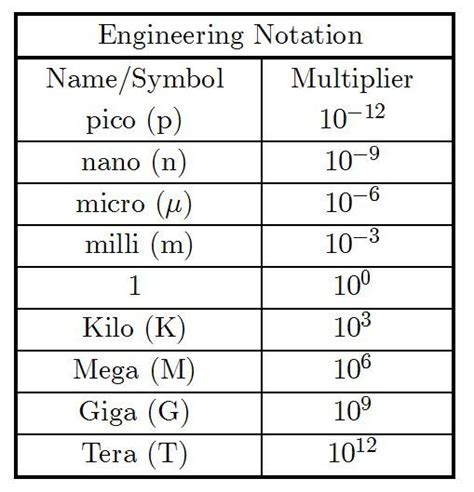
Table of Contents
- 1 Meter Is How Many Nanometers
- Table of Contents
- 1 Meter is How Many Nanometers? A Deep Dive into Metric Conversions
- Understanding the Metric System: A Foundation for Conversions
- Key Metric Prefixes:
- The Answer: 1 Meter to Nanometers
- Practical Applications of Meter-Nanometer Conversions
- 1. Nanoscience and Nanotechnology:
- 2. Semiconductor Industry:
- 3. Materials Science:
- 4. Microscopy:
- 5. Biology and Medicine:
- Beyond the Basics: Advanced Conversion Techniques
- Conclusion: Mastering Metric Conversions for Success
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
1 Meter is How Many Nanometers? A Deep Dive into Metric Conversions
Understanding the relationship between meters and nanometers is crucial in various scientific, engineering, and technological fields. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question "1 meter is how many nanometers?" but also delve into the broader context of the metric system, providing you with a robust understanding of unit conversions and their applications. We'll explore the practical implications of this conversion, covering topics from nanoscience to everyday applications.
Understanding the Metric System: A Foundation for Conversions
The metric system, also known as the International System of Units (SI), is a decimal system based on powers of 10. This makes conversions between units remarkably straightforward. The fundamental unit of length in the SI system is the meter (m). All other units of length, including the nanometer, are derived from the meter using prefixes that represent powers of 10.
Key Metric Prefixes:
Understanding the prefixes is essential for navigating the metric system. Here are some crucial prefixes relevant to our discussion:
- Kilo (k): Represents 10<sup>3</sup> or 1000. (1 kilometer = 1000 meters)
- Centi (c): Represents 10<sup>-2</sup> or 0.01. (1 centimeter = 0.01 meters)
- Milli (m): Represents 10<sup>-3</sup> or 0.001. (1 millimeter = 0.001 meters)
- Micro (µ): Represents 10<sup>-6</sup> or 0.000001. (1 micrometer = 0.000001 meters)
- Nano (n): Represents 10<sup>-9</sup> or 0.000000001. (1 nanometer = 0.000000001 meters)
This systematic use of prefixes allows for easy conversion between units. For instance, if you know that 1 kilometer is 1000 meters, you can quickly convert any number of kilometers to meters by multiplying by 1000. The same principle applies to all other prefixes.
The Answer: 1 Meter to Nanometers
Now, let's address the central question: 1 meter is equal to 1,000,000,000 nanometers (1 x 10<sup>9</sup> nm).
This stems directly from the definition of the nano prefix: 1 nanometer is one billionth of a meter. Therefore, to convert meters to nanometers, you simply multiply the number of meters by 1,000,000,000.
Practical Applications of Meter-Nanometer Conversions
The conversion between meters and nanometers is essential in numerous fields, particularly those dealing with incredibly small scales:
1. Nanoscience and Nanotechnology:
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter at the atomic and molecular scale, typically involving structures with dimensions ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers. Converting measurements from macroscopic units (meters) to nanoscale units (nanometers) is crucial for designing, characterizing, and understanding nanoscale materials and devices. Researchers need to accurately convert dimensions of nanomaterials, calculate surface area to volume ratios, and determine the properties of nanoscale structures.
2. Semiconductor Industry:
The semiconductor industry relies heavily on precision at the nanoscale. Transistors and other components in modern electronics are measured in nanometers. The ability to accurately convert measurements is critical for designing and manufacturing these incredibly small components, ensuring optimal performance and reliability. Features like gate lengths and channel widths are specified in nanometers, and any discrepancy in these measurements can significantly impact the device's functionality.
3. Materials Science:
Materials scientists often work with materials at various scales, including the nanoscale. Understanding the relationships between meter and nanometer scales is crucial for studying the properties of materials at the nanoscale, such as their mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and optical properties. For example, the size of nanoparticles significantly impacts their properties, and precise measurements are essential for understanding these relationships.
4. Microscopy:
Advanced microscopy techniques, such as atomic force microscopy (AFM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), are capable of resolving structures at the nanometer scale. The images and data generated by these techniques often need to be interpreted in terms of macroscopic units, requiring accurate conversion between nanometers and meters.
5. Biology and Medicine:
Biological structures, including proteins, DNA, and viruses, are often at the nanoscale. Converting measurements from meters to nanometers is critical for understanding their structure and function. In medicine, nanotechnology is finding applications in drug delivery and diagnostics. Understanding the size and dimensions of nanoparticles used in drug delivery is crucial for optimizing their performance and minimizing side effects.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Conversion Techniques
While the basic conversion from meters to nanometers is straightforward (multiply by 10<sup>9</sup>), there are instances where more complex conversions might be necessary. For instance:
-
Converting between different units within the metric system: You might need to convert centimeters to nanometers, millimeters to nanometers, or even micrometers to nanometers. This typically involves a multi-step process, using intermediate conversions. For example, to convert centimeters to nanometers, you would first convert centimeters to meters and then meters to nanometers.
-
Working with scientific notation: Working with extremely large or small numbers is common in nanoscience. Scientific notation offers a concise way to represent these numbers, simplifying calculations and conversions.
-
Using conversion calculators and software: Many online tools and software packages are available to assist with unit conversions, providing a convenient way to perform complex calculations accurately.
Conclusion: Mastering Metric Conversions for Success
Understanding the conversion between meters and nanometers is not just a matter of knowing the numerical factor (10<sup>9</sup>); it's about grasping the fundamental principles of the metric system and its applications in various scientific and technological fields. The ability to accurately and confidently perform these conversions is a valuable skill for anyone working with nanoscale materials, devices, or phenomena. From nanoscience to everyday applications, the precision afforded by mastering these conversions is paramount to success. The meticulous understanding and application of these principles are critical for advancing research and development in countless areas. By mastering this fundamental conversion, you open the door to a deeper comprehension of the world at the nanoscale and its remarkable implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
350 F Is What In C
Mar 22, 2025
-
4 4 W 3 2w 2
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which State Of Matter Has A Definite Shape And Volume
Mar 22, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple 3 4 5
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is 1 Divided By 3 4
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 Meter Is How Many Nanometers . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
