How Many Sigma Bonds Are Present In Acetylsalicylic Acid
listenit
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
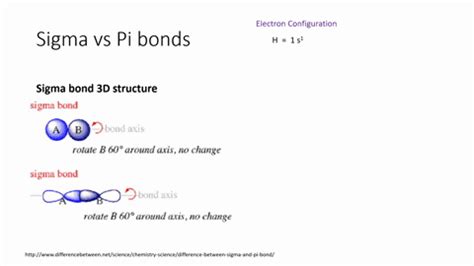
Table of Contents
How Many Sigma Bonds are Present in Acetylsalicylic Acid? A Detailed Analysis
Acetylsalicylic acid, commonly known as aspirin, is a ubiquitous analgesic and antipyretic drug. Understanding its molecular structure is crucial to grasping its properties and pharmacological actions. A key aspect of this understanding lies in determining the number of sigma (σ) bonds present within its molecule. This article will delve deep into the structure of acetylsalicylic acid, systematically counting its sigma bonds, and clarifying common misconceptions.
Understanding Sigma Bonds
Before we embark on counting sigma bonds in acetylsalicylic acid, let's establish a clear understanding of what a sigma bond is. A sigma bond (σ bond) is the strongest type of covalent bond formed by the head-on overlap of atomic orbitals. This direct overlap results in a high electron density concentrated between the two bonded nuclei, leading to strong attraction and stability. Single bonds are always sigma bonds. Double and triple bonds contain one sigma bond and one or two pi (π) bonds, respectively. Pi bonds are formed by the side-on overlap of p-orbitals and are generally weaker than sigma bonds.
The Structure of Acetylsalicylic Acid
Acetylsalicylic acid has the chemical formula C₉H₈O₄. Its molecule consists of a benzene ring (a six-carbon aromatic ring) modified with both an acetyl group (-COCH₃) and a carboxyl group (-COOH). Understanding this structure is paramount to accurately counting the sigma bonds.
Here's a breakdown of the key structural components:
-
Benzene Ring: The benzene ring is a planar structure with alternating single and double bonds. However, due to resonance, all carbon-carbon bonds are essentially equivalent and have a bond order of 1.5. This means each carbon-carbon bond in the benzene ring has one sigma bond and a partial pi bond character.
-
Acetyl Group (-COCH₃): This group consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) connected to a methyl group (-CH₃).
-
Carboxyl Group (-COOH): This group contains a carbonyl group (C=O) connected to a hydroxyl group (-OH).
Counting the Sigma Bonds: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's systematically count the sigma bonds in acetylsalicylic acid:
1. Benzene Ring: The benzene ring contains six carbon atoms. Each carbon atom forms three sigma bonds: two with neighboring carbon atoms and one with a hydrogen atom (except for the carbon atoms bonded to the acetyl and carboxyl groups, which are bonded to one carbon and one oxygen atom). Therefore, the benzene ring contributes 6 C-C sigma bonds and 3 C-H sigma bonds. (Note: we consider the resonance structure, and all the carbon-carbon bonds have one sigma bond.) Total: 9 sigma bonds
2. Acetyl Group: The acetyl group has several sigma bonds:
- C=O: One sigma bond (C-O)
- C-C: One sigma bond
- Three C-H bonds: Three sigma bonds within the methyl group (-CH₃) Total: 5 sigma bonds
3. Carboxyl Group: The carboxyl group also contributes several sigma bonds:
- C=O: One sigma bond (C-O)
- C-O: One sigma bond (C-O in -OH)
- O-H: One sigma bond Total: 3 sigma bonds
4. Connections between Functional Groups and the Benzene Ring: The acetyl and carboxyl groups are attached to the benzene ring, creating additional sigma bonds:
- One C-C sigma bond connecting the acetyl group to the benzene ring.
- One C-C sigma bond connecting the carboxyl group to the benzene ring. Total: 2 sigma bonds
Total Sigma Bonds in Acetylsalicylic Acid
Adding up all the sigma bonds from each component, we obtain the total number:
9 (benzene ring) + 5 (acetyl group) + 3 (carboxyl group) + 2 (connections) = 19 sigma bonds
Therefore, there are a total of 19 sigma bonds in a molecule of acetylsalicylic acid.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
It's essential to address some common misconceptions that can lead to inaccurate sigma bond counts:
- Double bonds: Remember that double bonds consist of one sigma bond and one pi bond. Don't count the double bonds twice.
- Resonance: While the benzene ring exhibits resonance, this does not alter the number of sigma bonds. Resonance affects the distribution of electron density but not the number of sigma bonds.
- Bond Order: Focusing solely on bond order without considering the individual bond types (sigma and pi) can lead to errors.
Applications and Importance of Understanding Sigma Bonds in Acetylsalicylic Acid
Understanding the number and type of bonds in acetylsalicylic acid has significant implications in several areas:
- Pharmacology: The specific arrangement of sigma and pi bonds influences the molecule's reactivity, stability, and interactions with biological targets, determining its pharmacological effects.
- Drug Design: This knowledge is crucial in designing new drugs with improved efficacy and reduced side effects. By modifying the structure, scientists can alter the number and types of bonds, influencing the properties of the drug.
- Spectroscopy: Techniques such as infrared (IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy are sensitive to bond vibrations and nuclear environments, respectively. The number and type of bonds influence the spectral characteristics of the molecule, aiding in structural identification and analysis.
- Chemical Reactivity: The presence and strength of sigma bonds dictate how the molecule reacts with other chemical species. For example, the carboxyl group's reactivity (including the sigma bonds involved) is key to aspirin's ability to act as a drug.
Conclusion
This detailed analysis demonstrates that acetylsalicylic acid possesses a total of 19 sigma bonds. This count is derived from a systematic examination of the molecule's structure, considering the individual sigma bonds within the benzene ring, acetyl group, carboxyl group, and the connecting bonds. Understanding the number and types of bonds in aspirin is fundamental to comprehending its chemical behavior, pharmacological properties, and potential for modification in drug design. By accurately accounting for sigma bonds, and understanding their impact, we gain a more comprehensive understanding of this important medicinal compound. This knowledge extends beyond aspirin; the principles outlined here are applicable to analyzing the molecular structures of numerous other organic compounds. The careful, methodical approach presented here provides a clear pathway for anyone seeking to determine the sigma bond count in various molecules.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Unit Is Work Measured In
Mar 27, 2025
-
Is Boron A Gas Liquid Or Solid
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Is 20 Percent Of 12
Mar 27, 2025
-
What Percent Is 1 Of 7
Mar 27, 2025
-
When Gas Exerts Pressure On Its Container The Pressure Is
Mar 27, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Sigma Bonds Are Present In Acetylsalicylic Acid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
