How Many Sides Does This Polygon Have
listenit
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
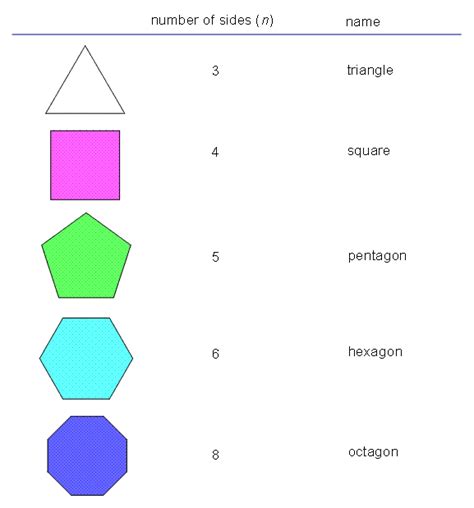
Table of Contents
How Many Sides Does This Polygon Have? A Comprehensive Guide to Polygon Classification
Determining the number of sides a polygon has might seem like a simple task, but understanding the nuances of polygon classification opens up a fascinating world of geometry and mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of identifying polygons based on their side counts, exploring various types, properties, and applications. We'll move beyond simply counting sides to understanding the deeper mathematical relationships involved.
Understanding Polygons: A Foundation
Before we delve into counting sides, let's establish a firm understanding of what constitutes a polygon. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting a finite number of straight line segments. These segments are called sides, and the points where the sides meet are called vertices or corners. Crucially, a polygon does not intersect itself – a figure that crosses over its own lines is not a polygon.
Key Polygon Characteristics:
- Sides: The straight line segments forming the polygon.
- Vertices: The points where the sides intersect. The number of vertices always equals the number of sides.
- Angles: The interior angles formed by the intersection of two adjacent sides. The sum of the interior angles of a polygon depends on the number of sides.
- Regular vs. Irregular: A regular polygon has all sides and angles equal in measure. An irregular polygon has sides and/or angles of varying lengths and measures.
Classifying Polygons by the Number of Sides
Polygons are primarily classified by the number of sides they possess. Each category has a specific name, and understanding these names is crucial for effective communication in geometry and related fields. Here's a breakdown of common polygon classifications:
3 Sides: Triangle
The simplest polygon, a triangle, boasts three sides and three angles. Triangles are further categorized into various types based on side lengths (equilateral, isosceles, scalene) and angles (acute, obtuse, right). Understanding triangle properties is fundamental to many geometric proofs and calculations.
4 Sides: Quadrilateral
Quadrilaterals possess four sides and four angles. This category encompasses a wide range of shapes, including:
- Square: All sides equal, all angles equal (90 degrees).
- Rectangle: Opposite sides equal, all angles equal (90 degrees).
- Rhombus: All sides equal, opposite angles equal.
- Parallelogram: Opposite sides parallel and equal, opposite angles equal.
- Trapezoid (or Trapezium): At least one pair of parallel sides.
- Kite: Two pairs of adjacent sides equal.
5 Sides: Pentagon
A pentagon features five sides and five angles. Regular pentagons, with all sides and angles equal, are visually striking and appear in various applications, from architecture to logos.
6 Sides: Hexagon
Hexagons, with six sides and six angles, are commonly found in nature, particularly in honeycombs. Regular hexagons, like regular pentagons, possess a unique symmetry and geometric elegance.
7 Sides: Heptagon (or Septagon)
A heptagon (or septagon) has seven sides and seven angles. While less common than triangles, quadrilaterals, and pentagons, heptagons still find applications in certain designs and constructions.
8 Sides: Octagon
Octagons, with eight sides and eight angles, are easily recognizable. Stop signs, a common example, are octagonal, utilizing their distinct shape for high visibility.
9 Sides: Nonagon (or Enneagon)
Nonagons (also called enneagons) possess nine sides and nine angles. These nine-sided polygons are less frequently encountered in everyday life but hold significance in advanced geometric studies.
10 Sides: Decagon
Decagons, with ten sides and ten angles, represent a step further in polygon complexity. Their properties and calculations require a more in-depth understanding of geometric principles.
Beyond 10 Sides: Higher-Order Polygons
As the number of sides increases, polygon names become less commonly used and often require utilizing prefixes to denote the number of sides. These prefixes are usually derived from Greek or Latin origins:
- Hendecagon (or Undecagon): 11 sides
- Dodecagon: 12 sides
- Tridecagon: 13 sides
- Tetradecagon: 14 sides
- Pentadecagon: 15 sides
- Hexadecagon: 16 sides
- Heptadecagon: 17 sides
- Octadecagon: 18 sides
- Enneadecagon: 19 sides
- Icosagon: 20 sides
And so on... the naming convention continues to increase in complexity as the number of sides grows. For polygons with a very high number of sides, it's more common to simply refer to them as an "n-gon," where 'n' represents the number of sides.
Calculating Interior Angles
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is directly related to the number of sides. The formula for calculating this sum is:
(n - 2) * 180°
Where 'n' is the number of sides.
For example:
- A triangle (n=3): (3-2) * 180° = 180°
- A quadrilateral (n=4): (4-2) * 180° = 360°
- A pentagon (n=5): (5-2) * 180° = 540°
This formula is a fundamental tool for solving various geometric problems involving polygons.
Applications of Polygon Knowledge
Understanding polygon properties is crucial in various fields:
- Architecture and Engineering: Polygons form the basis of building designs, structural frameworks, and spatial planning.
- Computer Graphics and Game Design: Polygons are the building blocks of 3D models and computer-generated imagery.
- Cartography: Polygons are used to represent geographical areas on maps.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers utilize polygon shapes to create visually appealing and functional designs.
- Tessellations: Understanding polygon angles is crucial for creating tessellations, repeating patterns that cover a plane without gaps or overlaps.
Identifying Polygons in Real-World Examples
Developing the ability to quickly identify the number of sides a polygon has is a practical skill. Practice observing your surroundings. Look for:
- Traffic Signs: Many traffic signs utilize specific polygons, such as octagons (stop signs) and triangles (yield signs).
- Buildings: Examine the shapes of buildings and their architectural features.
- Nature: Observe shapes in nature, such as honeycombs (hexagons), crystals, and the formations of some plants and flowers.
- Logos and Designs: Look for polygons used in logos, branding, and artistic representations.
By consciously observing polygons in your daily life, you will improve your ability to instantly recognise and classify them.
Conclusion: More Than Just Sides
Determining "how many sides does this polygon have?" is the starting point for a deeper exploration of geometrical concepts. Understanding polygon classification, calculating interior angles, and appreciating their real-world applications provides a solid foundation for further study in mathematics, engineering, and design. The seemingly simple act of counting sides unlocks a universe of geometric possibilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Chain Rule Quotient Rule And Product Rule
Mar 24, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration Of Arsenic
Mar 24, 2025
-
Y Mx B Solve For Y
Mar 24, 2025
-
How To Find Vertices Of Ellipse
Mar 24, 2025
-
Nouns That Start With An X
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Sides Does This Polygon Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
