How Many Protons Electrons And Neutrons Does Sulfur Have
listenit
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
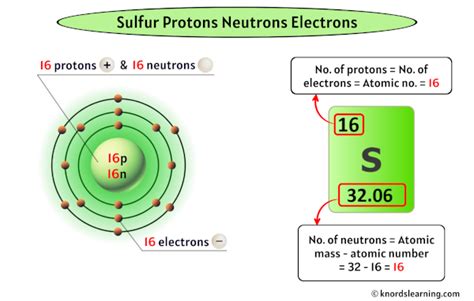
Table of Contents
How Many Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons Does Sulfur Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Sulfur, a vibrant yellow nonmetal, plays a crucial role in various biological and industrial processes. Understanding its atomic structure, specifically the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons it possesses, is fundamental to comprehending its chemical behavior and properties. This comprehensive guide delves into the atomic composition of sulfur, exploring its isotopes and explaining how to determine the subatomic particle count. We'll also touch upon its applications and significance.
Understanding Atomic Structure: The Basics
Before we delve into the specifics of sulfur, let's briefly review the fundamental concepts of atomic structure. An atom, the basic building block of matter, consists of three primary subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles located in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; it's the atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also residing in the nucleus. Along with protons, they determine the atom's mass number.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. In a neutral atom, the number of electrons equals the number of protons.
The arrangement of these subatomic particles dictates an element's chemical properties and how it interacts with other elements.
Sulfur's Atomic Number and Protons
Sulfur's atomic number is 16. This means every sulfur atom contains 16 protons in its nucleus. This fundamental number distinguishes sulfur from all other elements on the periodic table. The number of protons is unchanging and defines the very essence of sulfur's identity as an element.
Determining the Number of Electrons in Sulfur
In a neutral sulfur atom, the number of electrons is equal to the number of protons. Therefore, a neutral sulfur atom possesses 16 electrons. These electrons are distributed across different energy levels or shells around the nucleus, influencing sulfur's reactivity and bonding capabilities. The electron configuration is crucial for understanding its chemical behavior and how it forms compounds.
Neutrons in Sulfur: Isotopes and Mass Number
Unlike the fixed number of protons and electrons in a neutral atom, the number of neutrons can vary. Atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. The mass number of an atom is the sum of its protons and neutrons.
Sulfur has several naturally occurring isotopes, the most common being:
- Sulfur-32 (³²S): This isotope accounts for the vast majority of naturally occurring sulfur. It has 16 protons and 16 neutrons (32 - 16 = 16).
- Sulfur-33 (³³S): A less abundant isotope with 16 protons and 17 neutrons.
- Sulfur-34 (³⁴S): Another naturally occurring isotope with 16 protons and 18 neutrons.
- Sulfur-36 (³⁶S): A rarer isotope with 16 protons and 20 neutrons.
The average atomic mass of sulfur, as listed on the periodic table, reflects the weighted average of the masses of these isotopes and their relative abundances.
Sulfur's Electron Configuration and Chemical Behavior
The arrangement of electrons in sulfur's electron shells significantly impacts its chemical properties. Sulfur's electron configuration is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁴. This configuration indicates that sulfur has six valence electrons – electrons in the outermost shell. Atoms tend to achieve a stable electron configuration, often resembling that of a noble gas, by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons. Sulfur's six valence electrons often lead to the formation of covalent bonds, where it shares electrons with other atoms to complete its outermost shell. This explains sulfur's tendency to form compounds with various elements.
Understanding Valence Electrons and Chemical Bonding
Valence electrons are the key players in chemical reactions. They determine the element's reactivity and the types of bonds it can form. For sulfur, with its six valence electrons, it's more energetically favorable to gain two electrons to achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in its outermost shell) rather than lose six. This explains why sulfur often forms covalent bonds, sharing electrons with other atoms to achieve this stable configuration.
Sulfur's Applications and Significance
Sulfur's unique properties have led to its widespread use in various industries and applications:
-
Manufacturing of sulfuric acid: Sulfuric acid, a highly corrosive acid, is a crucial industrial chemical used in the production of fertilizers, detergents, and other chemicals. The vast majority of sulfur produced globally is used in sulfuric acid manufacturing.
-
Vulcanization of rubber: Sulfur is an essential component in the vulcanization process of rubber, which enhances its strength, elasticity, and durability. This process is critical in producing durable tires and other rubber products.
-
Production of fertilizers: Sulfur is a vital plant nutrient and is incorporated into various fertilizers to boost crop yields. Sulfur deficiency in soil can negatively impact plant growth and agricultural productivity.
-
Medicinal uses: Sulfur compounds have found applications in various medicinal preparations, including antifungal and antibacterial agents. Historically, sulfur has been used to treat skin conditions.
-
Matches and fireworks: The easily combustible nature of sulfur makes it a key ingredient in matches and fireworks. Its role is to readily react with other substances, generating the heat and light needed for ignition.
Determining the Number of Protons, Electrons, and Neutrons in Other Elements
The principles discussed for sulfur apply to all other elements. To determine the number of protons, electrons, and neutrons for any element:
-
Identify the atomic number: This number, found on the periodic table, represents the number of protons and, in a neutral atom, the number of electrons.
-
Find the mass number: This number is usually given in the element's isotopic notation (e.g., ¹²C, where 12 is the mass number). It represents the total number of protons and neutrons.
-
Calculate the number of neutrons: Subtract the atomic number (number of protons) from the mass number to find the number of neutrons.
This systematic approach allows one to determine the subatomic particle count for any element and its various isotopes.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Sulfur's Atomic Structure
Understanding the precise number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in sulfur is crucial for comprehending its chemical behavior, reactivity, and applications. This knowledge extends to the broader field of chemistry, enabling us to understand the properties of other elements and the formation of compounds. By grasping the fundamental principles of atomic structure, we can better appreciate the role of sulfur in various industrial processes and its importance in sustaining life. The detailed examination of sulfur's isotopes further underscores the complexity and diversity within even a single element, highlighting the intricate nature of the atomic world. Furthermore, this knowledge is essential for advancements in various fields ranging from materials science to medicine, showcasing the practical significance of fundamental scientific principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
100 Cm Is Equal To How Many Meters
Apr 05, 2025
-
Where Are The Most Asteroids Located
Apr 05, 2025
-
Graph Of Y 4x X 2
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many 1 3 In 1 2
Apr 05, 2025
-
What Is 8 Percent Of 4000
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Protons Electrons And Neutrons Does Sulfur Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
